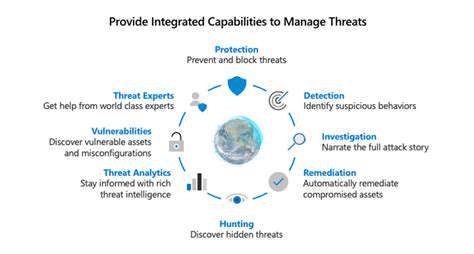
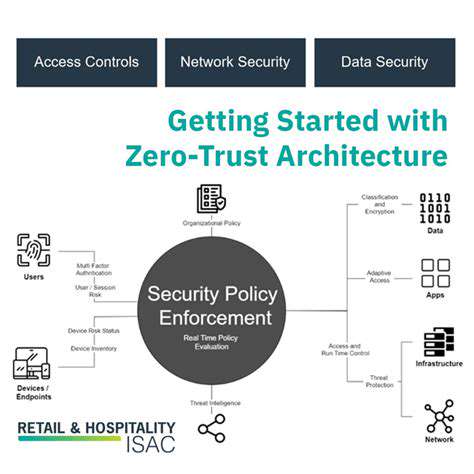
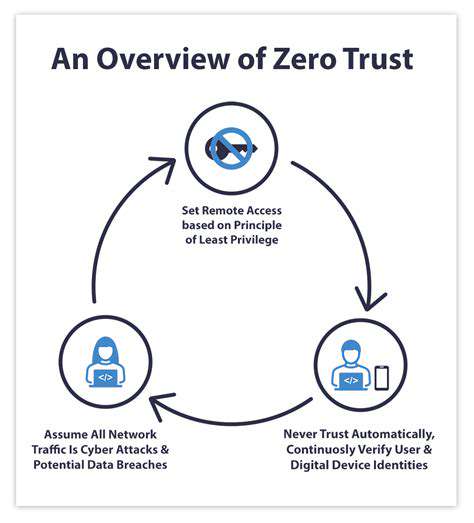
Zero Trust demands microscopic visibility into network behaviors. Through granular segmentation, organizations gain X-ray vision into traffic patterns, enabling policy crafting that reflects actual operational needs. This precision becomes increasingly vital as cyber threats evolve into sophisticated, targeted attacks that exploit traditional security blind spots.
Implementing Micro-segmentation Effectively
Deploying micro-segmentation resembles conducting a symphony—it requires meticulous preparation and perfect timing. Organizations must map their digital ecosystems comprehensively, analyzing application dependencies, user workflows, and data highways. Specialized security instruments become essential for managing the complex rhythms of segmented traffic. Successful implementation demands continuous refinement, adapting to emerging threats like a living security organism.
The Benefits of a Micro-segmented Network
Beyond security hardening, micro-segmentation offers operational superpowers. Network visibility transforms from foggy to crystal clear, enabling security teams to spot and neutralize threats with sniper-like precision. Troubleshooting becomes surgical rather than guesswork, while incident response teams gain the ability to quarantine threats instantly. In today's cyber battlegrounds, this rapid containment often makes the difference between inconvenience and catastrophe.
Challenges and Considerations in Micro-segmentation
The complexity of micro-segmented networks presents formidable challenges. Organizations must invest in specialized expertise and advanced monitoring tools to navigate this new security landscape. Compliance becomes a moving target, requiring agile policy frameworks that evolve with regulatory changes. A phased rollout strategy proves essential, allowing security teams to refine their approach through controlled implementation.
Future Trends and Evolution of Micro-segmentation
The next frontier involves intelligent automation and predictive security. Machine learning algorithms will analyze network patterns like digital bloodhounds, sniffing out anomalies before they manifest as threats. Self-healing networks will automatically adjust segment defenses, creating adaptive security ecosystems that outmaneuver attackers. This evolution will prove critical as networks grow more complex and dynamic.
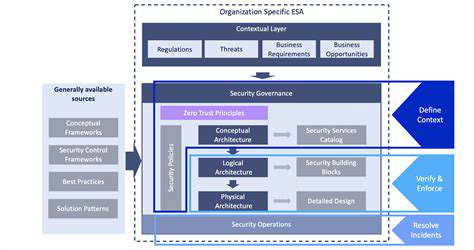
Zero Trust: A Foundation for Secure Segmentation
Understanding Zero Trust
Zero Trust shatters conventional security dogma by eliminating implicit trust completely. Continuous authentication becomes the new normal, with every access request scrutinized regardless of origin. This paradigm shift transforms security from perimeter-based to interaction-focused, creating an environment where nothing moves without verification. In our era of hybrid work and cloud proliferation, this approach provides the only viable defense against modern threats.
The model's core principle—verify first, trust never—turns traditional network security on its head. Gone are the days of assumed safety behind corporate firewalls. Advanced authentication mechanisms now guard every digital doorway, proving particularly effective for distributed workforces and cloud environments where perimeter defenses fail.
The Role of Micro-segmentation in Zero Trust
Micro-segmentation acts as Zero Trust's enforcement mechanism, creating digital quarantine zones throughout networks. When breaches occur, these microscopic containment fields prevent cyber infections from spreading. This granular approach transforms networks into collections of impenetrable vaults, where compromising one doesn't endanger others. The technique proves invaluable in complex infrastructures, minimizing attack surfaces through precise access controls.
By implementing microscopic security zones, organizations operationalize Zero Trust principles practically. Least privilege access becomes enforceable reality rather than security theory, with continuous verification built into network architecture. This approach proves particularly effective against lateral movement tactics favored by advanced attackers.
Implementing Zero Trust Security Practices
Transitioning to Zero Trust requires fundamental security metamorphosis. Organizations must replace traditional segmentation with dynamic verification systems incorporating multi-factor authentication and advanced IAM solutions. Identity management transforms into the security cornerstone, ensuring only verified entities access specific resources, regardless of location or access history.
Successful implementation demands comprehensive planning and stakeholder alignment. Robust identity systems, granular access controls, and persistent monitoring form the triad of Zero Trust deployment. Integration with existing workflows proves critical, ensuring security enhancements don't disrupt operational efficiency.
Benefits of Combining Micro-segmentation and Zero Trust
The synergy between these approaches creates security superpowers. Attack surfaces shrink dramatically, while breach impacts become contained events rather than network catastrophes. This combined strategy provides dynamic defense mechanisms that adapt to evolving threats in real-time, creating resilient security postures.
The result is security infrastructure that's both robust and agile. Granular visibility and control enable rapid threat response, while verified access minimizes breach potential. Organizations gain the adaptability needed to counter today's sophisticated cyber threats effectively.
Implementing Micro-segmentation for Zero Trust Networks
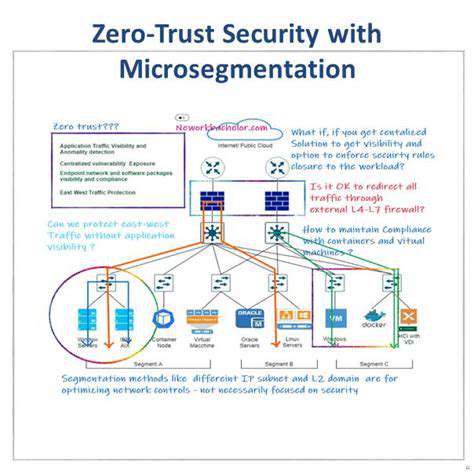
Understanding the Need for Micro-segmentation
Micro-segmentation has emerged as a game-changing security approach in contemporary IT environments. Rather than relying on outdated broad network divisions, it creates precise security zones tailored to application and user requirements. This surgical approach to network division creates digital containment fields, dramatically reducing vulnerabilities and limiting breach fallout. In our interconnected digital ecosystems, this precision proves indispensable against advanced threats.
The advantages extend well beyond security. Network visibility improves exponentially, compliance verification simplifies, and performance often enhances. Security teams gain rapid response capabilities, protecting critical systems and sensitive data with unprecedented efficiency.
Defining the Components of Micro-segmentation
Effective micro-segmentation begins with comprehensive asset identification. Security teams must catalogue applications, data repositories, and user groups meticulously. This inventory forms the blueprint for security zone creation, guiding the development of access rules governing inter-segment communication.
Implementing Micro-segmentation Tools and Technologies
The market offers diverse solutions for micro-segmentation implementation, from network virtualization platforms to specialized security appliances. Tool selection requires careful evaluation of compatibility with existing infrastructure and future growth potential. Many solutions now incorporate automation features that simplify policy management and segment maintenance.
Designing Effective Micro-segmentation Policies
Crafting segmentation policies demands deep understanding of organizational needs, compliance requirements, and system interdependencies. Effective policies function like digital bouncers, strictly controlling segment interactions to prevent breach escalation. Regular policy reviews ensure defenses remain effective against emerging threats.
Managing and Maintaining Micro-segmentation
Ongoing micro-segmentation management requires robust monitoring systems. Continuous traffic analysis and segment behavior tracking enable rapid anomaly detection. Automated alert systems function as early warning networks, triggering immediate responses to potential security incidents.
Addressing Challenges and Considerations
Network complexity presents significant implementation hurdles. Integration with legacy systems demands careful planning to avoid operational disruption. The security tools themselves require hardening, as they become attractive targets for sophisticated attackers seeking to bypass segment defenses.
Global food insecurity represents one of our most complex humanitarian challenges, intertwining agricultural, economic, and social factors into a Gordian knot of hunger. The consequences reverberate through societies, stunting educational achievement, crippling workforce potential, and perpetuating cycles of poverty. Only holistic solutions addressing this multidimensional problem can create meaningful change.
Beyond Segmentation: Enhancing Visibility and Control

Beyond the Basics of Visual Segmentation
Traditional visual segmentation often fails to capture the nuanced relationships within complex imagery. While effective for basic categorization, it lacks the sophistication needed for advanced applications. True visual understanding requires deeper analysis that reveals contextual relationships and underlying structures.
For critical applications like medical diagnostics or autonomous systems, surface-level segmentation proves inadequate. Advanced interpretation techniques unlock richer data insights, enabling more accurate and reliable decision-making processes.
Advanced Techniques for Enhanced Visual Interpretation
Modern solutions employ sophisticated methods like instance and semantic segmentation, providing pixel-perfect classification. These technologies prove indispensable when precise object identification becomes paramount, offering unprecedented detail in visual analysis.
When combined with complementary vision technologies, these advanced methods create comprehensive interpretation systems capable of handling complex real-world scenarios.
Contextual Information and Relationships
Understanding visual context transforms simple object recognition into meaningful interpretation. Analyzing spatial relationships and interactions between elements provides crucial insights that basic segmentation misses entirely.
This contextual awareness becomes particularly valuable in dynamic environments where relationships between objects determine appropriate responses.
Applications and Future Directions
Enhanced visual interpretation finds applications across diverse fields, from healthcare to urban planning. Future advancements will focus on creating adaptive systems that integrate multiple data sources, paving the way for truly intelligent visual analysis platforms.
The Future of Network Security: A Unified Approach
Network Segmentation and the Evolution of Zero Trust
Modern network security requires abandoning perimeter-based models in favor of dynamic, zero trust architectures. Micro-segmentation serves as the implementation backbone, creating microscopic security zones that contain threats effectively. This approach represents a fundamental rethinking of network defense, where verification replaces assumption and containment replaces perimeter.
The outdated castle and moat security model collapses under modern threat pressures. Zero trust frameworks enable proactive threat neutralization regardless of origin point. Real-time anomaly detection and response capabilities become critical in countering increasingly sophisticated attack methodologies.
Zero Trust: A Holistic Approach to Security
Zero trust architecture eliminates trust assumptions completely, subjecting every access request to rigorous verification. This extends beyond simple authentication to encompass comprehensive access governance. Data protection becomes granular and dynamic, with permissions adapting to contextual factors in real-time.
Micro-segmentation: A Critical Component of Zero Trust
As Zero Trust's enforcement mechanism, micro-segmentation creates digital containment fields throughout networks. These microscopic security zones prevent breach escalation through strict access governance. Policy frameworks dictate segment interactions precisely, creating resilient network architectures that withstand modern cyber threats.