Zero Trust: A Foundation for Secure Access
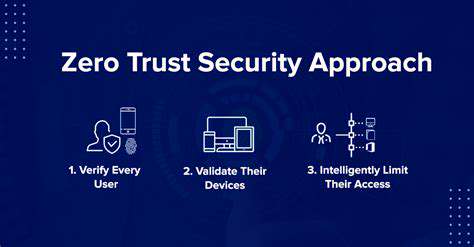
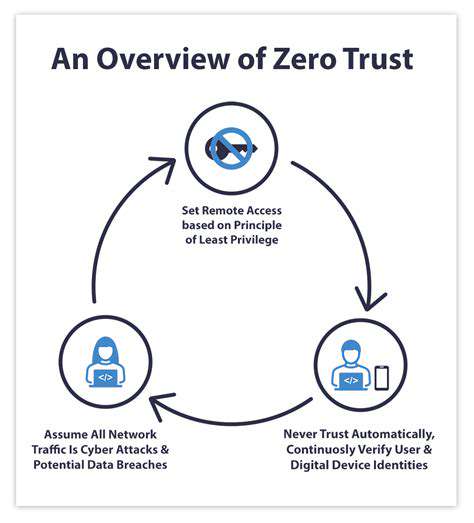
Zero Trust security represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, abandoning outdated perimeter-based models. Rather than assuming trust, it mandates verification for every user, device, and application attempting to access resources—regardless of location or network status. This relentless verification process dramatically shrinks potential attack vectors by treating every access attempt as potentially malicious until proven otherwise.
The implementation of Zero Trust fundamentally rewrites security playbooks. Traditional fortress-like defenses give way to granular, identity-centric controls powered by sophisticated IAM systems. This proactive stance effectively contains breaches by preventing compromised credentials from becoming network-wide disasters.
Core Tenets of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust operates on several non-negotiable principles: stringent access controls, perpetual monitoring, and preemptive threat identification. The principle of least privilege stands paramount, ensuring users receive only the bare minimum access required for their duties. This containment strategy severely limits both the impact of credential theft and attackers' ability to pivot through networks.
Operationalizing Zero Trust Principles
Successful Zero Trust adoption demands tailored strategies aligned with organizational requirements. The transition necessitates meticulous planning, typically involving IAM deployment, network micro-segmentation, and robust authentication protocols. Organizations must balance security enhancements with operational continuity during this transformation.
The Power of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation forms the backbone of Zero Trust implementations. Dividing networks into isolated compartments contains potential breaches, preventing threat actors from freely traversing systems. Micro-segmentation elevates this concept further, creating microscopic security zones that shrink potential blast radii to minimal footprints.
Vigilance Through Continuous Monitoring
Zero Trust isn't a set-and-forget solution. Maintaining security requires round-the-clock surveillance and threat analysis. Automated detection systems and live threat feeds become critical watchdogs, identifying and neutralizing risks before they escalate into full-blown incidents.
IAM: The Gatekeeper of Zero Trust
Identity and Access Management systems serve as the sentinels of Zero Trust environments. Through multifactor authentication and role-based controls, IAM enforces the never trust mandate. Proper identity governance significantly lowers unauthorized access risks while supporting uninterrupted business operations.
Zero Trust's Evolving Landscape
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, Zero Trust must continuously adapt. The framework is rapidly expanding into cloud and edge computing environments, transitioning from emerging concept to security essential in our increasingly digital world.
Seasonal roasted vegetables offer a colorful celebration of summer's bounty. Vibrant bell peppers, sweet corn, tender zucchini, and crisp broccoli transform when roasted with herb-infused oils. This simple cooking method coaxes out natural sugars, creating versatile side dishes that pair beautifully with plant-based entrees. Creative seasoning—from garlic and herbs to smoked paprika—allows for endless flavor variations.
Zero Trust's Critical Role in Remote Work
Hybrid Work Demands Zero Trust Solutions
The hybrid work revolution has made Zero Trust essential infrastructure. Traditional perimeter defenses crumble when employees access resources from countless locations and devices. Zero Trust's location-agnostic verification provides the only viable security framework for today's distributed workforce.
With endpoint proliferation and network complexity at all-time highs, Zero Trust's granular access controls become the ultimate safeguard. By verifying every access attempt—regardless of network position—organizations can dramatically reduce their attack surface and breach impacts.
Implementation Hurdles and Solutions
Transitioning to Zero Trust presents significant challenges, especially for enterprises with legacy systems. The journey requires substantial investments in new technologies and security paradigm shifts. Organizations must thoroughly evaluate their infrastructure to develop appropriate migration strategies.
User experience remains a critical consideration. Poorly implemented Zero Trust controls can frustrate employees and hinder productivity. Thoughtful design and comprehensive training ensure security enhancements don't come at operational costs. Solutions must also scale to accommodate future growth and emerging threats.
Integration complexities demand cross-departmental collaboration. Effective Zero Trust adoption requires balancing ironclad security with business fluidity, ensuring protective measures don't disrupt critical operations.
Securing Remote Work with Zero Trust
Multifactor authentication forms the first line of defense for remote environments. When combined with continuous behavior monitoring and automated threat response, MFA creates formidable barriers against unauthorized access.
Network segmentation strategies isolate potential breaches, while regular security audits proactively address vulnerabilities. Most importantly, employee education transforms staff into security assets, equipping them to recognize threats and uphold Zero Trust principles in their daily work.