Identifying Potential Vulnerabilities
A crucial first step in securing third-party components is identifying potential vulnerabilities. This involves a thorough assessment of all dependencies used in your applications and systems. Thorough research into the security history of each component is essential. This includes checking for known vulnerabilities, security advisories, and any reported exploits that might affect the component.
Diligent tracking of updates and patches is also critical. Regularly checking for and implementing security updates for third-party components can significantly reduce the risk of exploitation.
Implementing Secure Coding Practices
Ensuring that third-party components are integrated securely within your application is vital. This involves using secure coding practices throughout the development lifecycle. Careful consideration of input validation and output encoding is essential to prevent common vulnerabilities like injection attacks. Developers should be aware of potential risks associated with using external libraries or frameworks and should implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are necessary to identify weaknesses in the implementation of control measures. These audits should assess the effectiveness of security protocols and identify any potential vulnerabilities in how third-party components are integrated and managed.
Security audits should be conducted on a recurring basis, ideally quarterly or annually, to maintain a strong security posture. Regular reviews will ensure that control measures remain effective and adapt to emerging threats.
Employing Vulnerability Management Tools
Leveraging vulnerability management tools is a practical approach to managing third-party risks. These tools can automate the identification and prioritization of vulnerabilities across your entire software supply chain. These tools can significantly streamline the process of detecting and addressing security issues.
They can also provide comprehensive reports on the identified vulnerabilities, allowing for informed decision-making regarding remediation strategies.
Establishing Secure Supply Chain Management
A robust supply chain management process is crucial for ensuring the security of third-party components. This involves establishing clear communication channels and protocols with vendors. Transparency and communication between all parties in the supply chain is fundamental to maintaining a secure environment.
This also includes procedures for vetting and verifying the security practices of third-party vendors. This verification process helps mitigate the risk of compromised components.
Employing Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all access points is an essential security measure. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive data or systems. This is particularly important for accounts that manage or interact with third-party components.
Monitoring and Response Mechanisms
Establishing robust monitoring and response mechanisms is vital to proactively address security incidents. These mechanisms should include continuous monitoring of systems and applications for suspicious activity related to third-party components. Rapid response protocols for addressing security incidents related to third-party components are crucial. This will reduce the window of vulnerability and limit the potential impact of a breach.
Proactive Security Measures: Implementing Advanced Threat Detection and Response
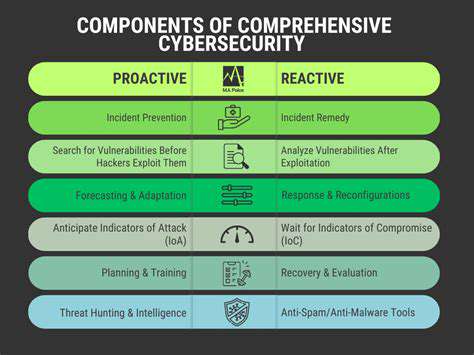
Proactive Security Measures: Implementing Robust Defenses
Proactive security measures are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and systems from potential threats. These measures go beyond simply reacting to incidents; instead, they focus on anticipating and mitigating vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Implementing a comprehensive proactive security strategy requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing various layers of protection. This proactive stance significantly reduces the likelihood of costly breaches and maintains the integrity of valuable information.
A key aspect of proactive security is the implementation of robust access controls. This involves carefully defining user permissions and privileges, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to specific data and resources. Regularly reviewing and updating these controls is essential to adapt to changing organizational needs and maintain a secure environment. Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are additional critical elements in this process.
Identifying and Mitigating Potential Threats
Proactive security strategies often involve identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems and processes. This process may include penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and threat modeling to proactively identify potential attack vectors. By understanding these vulnerabilities, organizations can develop targeted mitigation strategies to address specific weaknesses. This approach not only strengthens the overall security posture but also increases the resilience of the system to unexpected threats.
Regular security audits and updates of software and hardware are essential components of proactive security. Out-of-date systems often present easy targets for attackers. Proactive updates and patches mitigate known vulnerabilities and ensure the latest security protections are in place. This approach ensures that the system is consistently protected against emerging threats and exploits.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
A significant component of proactive security is employee training and awareness programs. These programs educate employees about potential security threats, phishing scams, and best practices for safe online behavior. Empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and avoid potential security risks is an essential part of a comprehensive security strategy. Regular training sessions and resources can help employees understand their role in maintaining a secure environment.
Beyond basic security awareness, training should also cover incident response procedures. This equips employees with the knowledge to handle suspicious emails, unusual activity, or other potentially harmful situations. Training empowers employees to react appropriately in a crisis situation, minimizing the potential impact of a security incident. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of breaches but also fosters a security-conscious culture within the organization.