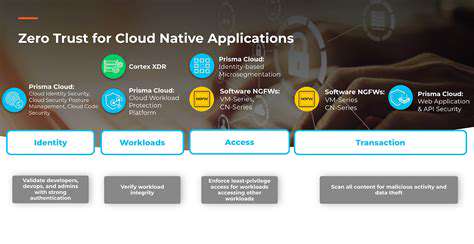
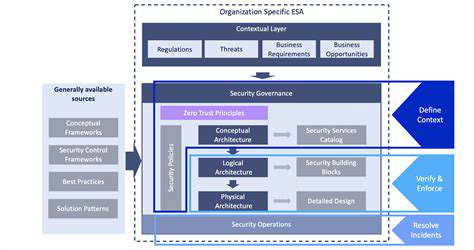
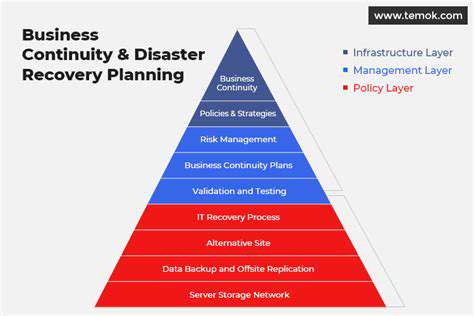
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Modern smart city infrastructure, with its interconnected systems and vast datasets, presents a unique and evolving threat landscape. Cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure components, data breaches compromising sensitive information, and physical security vulnerabilities in public spaces all pose significant risks. Understanding the diverse nature of these threats, from sophisticated hacking attempts to opportunistic vandalism, is crucial for developing effective security strategies.
Identifying potential weaknesses and vulnerabilities in various systems, including communication networks, energy grids, and transportation systems, is a critical first step in mitigating risks. Proactive threat intelligence gathering and analysis are essential to anticipate emerging threats and adapt security measures accordingly.
Implementing Network Segmentation and Isolation
To limit the impact of a security breach, dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments is vital. This strategy isolates sensitive systems and data from less critical components, effectively containing the damage if a breach occurs. Implementing robust firewalls and intrusion detection systems at strategic points within these segments is essential to monitor and control network traffic.
Utilizing virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure remote access and encrypting data transmitted over public networks are additional layers of protection to secure sensitive data and communication channels. This segmentation strategy helps prevent widespread compromise by containing any potential security breaches within specific network segments.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Protecting sensitive data is paramount in a smart city environment. Implementing robust encryption protocols for both in-transit and at-rest data is essential. This ensures that even if unauthorized access is gained, the data remains unreadable without proper decryption keys.
Implementing granular access controls is crucial for managing user permissions and restricting access to specific data and systems based on roles and responsibilities. This principle of least privilege, granting only the necessary access for a user to perform their tasks, significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized data modification or disclosure.
Physical Security Measures and Surveillance
Physical security is equally important, especially for critical infrastructure components such as power grids, water treatment plants, and transportation hubs. Implementing robust physical security measures, including surveillance systems, access control systems, and security personnel, is crucial. These measures deter potential intruders and enhance response times in case of security incidents.
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is essential for managing and mitigating security incidents effectively. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, responding to, and recovering from cyberattacks and security breaches. Regular drills and simulations are crucial for testing the effectiveness of the plan and ensuring that personnel are prepared to handle real-world scenarios.
Establishing clear communication channels and protocols for reporting and escalating incidents are paramount for swift and coordinated responses. Having a robust backup and recovery strategy is essential for minimizing downtime and data loss in the event of a major security incident. This includes having redundant systems and data backups stored in secure offsite locations.
Continuous Monitoring and Vulnerability Management
Maintaining a proactive approach to security is critical in a dynamic environment. Continuous monitoring of system logs, network traffic, and security alerts is essential to detect anomalies and potential threats early on. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are essential for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in the smart city infrastructure.
Implementing automated patching and update processes for software and hardware components is crucial for minimizing the impact of known vulnerabilities. Regular security awareness training for all personnel is also vital to promote a strong security culture and prevent human error from becoming a security weakness.
Building Resilience Through Data Protection and Incident Response
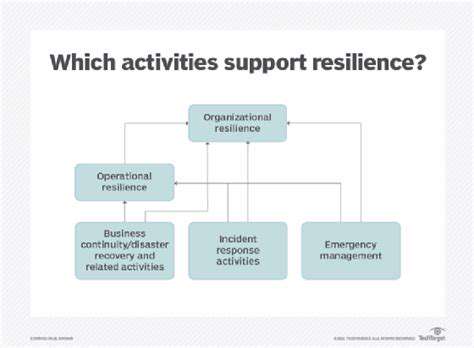
Understanding the Foundation of Data-Driven Resilience
Data-driven resilience strategies are built upon a strong foundation of understanding the specific vulnerabilities and risks facing an organization or system. This involves a thorough analysis of historical data, identifying patterns, and pinpointing potential weaknesses. By understanding these underlying factors, proactive measures can be developed to mitigate future risks and enhance overall resilience. This initial phase is crucial for establishing a framework for future data collection and analysis.
Furthermore, it is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of various factors contributing to resilience. For example, understanding how economic fluctuations, environmental changes, or social trends can affect the system's overall stability is key to developing comprehensive and effective strategies.
Data Collection and Integration Strategies
Robust data collection is paramount for building resilience. This involves establishing clear criteria for data collection, ensuring data quality, and implementing systems for efficient data storage and management. Thorough documentation of the data collection process is also critical for reproducibility and future analysis.
Integrating disparate data sources is another crucial step. This might involve consolidating data from various departments, external partners, or public sources. Effective integration allows for a holistic view of the system, revealing hidden correlations and dependencies that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Developing Predictive Models for Risk Assessment
Predictive modeling plays a pivotal role in anticipating potential risks and vulnerabilities. By analyzing historical data, these models can identify patterns and trends that indicate potential future challenges. This allows for proactive measures to be implemented before a crisis occurs, minimizing potential damage. This ability to foresee potential issues is a cornerstone of data-driven resilience strategies.
Different types of models, like machine learning algorithms, can be applied depending on the specific needs and characteristics of the data. Choosing the right model is critical for accurate predictions and informed decision-making.
Implementing Data-Driven Decision-Making Processes
Data-driven decision-making is essential for translating insights gained from analysis into actionable steps. This involves establishing clear processes for interpreting data, identifying actionable insights, and communicating findings effectively to stakeholders. This ensures that decisions are grounded in evidence and not subjective opinions, leading to more effective and efficient responses to challenges.
Effective communication is crucial. Presenting data in a clear, concise, and accessible manner to decision-makers is essential for fostering understanding and buy-in. This will ultimately contribute to the successful implementation of resilience strategies.
Monitoring and Evaluating System Performance
Continuous monitoring of system performance is vital to ensure that the resilience strategies are effective. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and identifying any deviations from expected trends. Regular evaluations of the effectiveness of resilience strategies are crucial for adjusting and refining them over time.
Regular feedback loops, incorporating input from various stakeholders, will help ensure the strategies remain relevant and adaptable to changing circumstances. This iterative approach is key to maintaining and improving the system's resilience.
Building a Culture of Data Literacy and Collaboration
Data literacy is essential for fostering a culture of resilience. This requires equipping personnel with the necessary skills and knowledge to understand, interpret, and utilize data effectively. Organizations need a culture that embraces data analysis and collaboration to fully leverage its potential.
Cultivating a collaborative environment where different departments and teams share data and insights will facilitate a more comprehensive understanding of the system's vulnerabilities and strengths. This collaborative approach is critical for developing truly effective resilience strategies.
Collaboration and International Standards: Fortifying Security through Knowledge Sharing

International Collaboration in Research
International collaboration is crucial for advancing scientific knowledge and tackling global challenges. Researchers from different countries bring diverse perspectives, expertise, and resources to collaborative projects, leading to more comprehensive and innovative solutions. This cross-cultural exchange fosters a deeper understanding of various approaches to problem-solving. The sharing of data and methodologies also accelerates progress in specific fields.
By collaborating on research projects, scientists can pool their knowledge and resources, leading to greater efficiency and effectiveness in the research process. This can result in breakthroughs that might not have been possible through individual efforts alone. International collaboration also facilitates the dissemination of research findings, allowing for broader impact and potential application in multiple contexts.
Global Challenges and Collaborative Solutions
Many global challenges, such as climate change, pandemics, and resource scarcity, require international collaboration to effectively address them. These complex issues demand a coordinated response and the pooling of resources and expertise from various nations. International research teams can develop innovative strategies and solutions that address the multifaceted nature of these challenges.
Sharing best practices and knowledge across borders is essential for developing effective solutions. By learning from each other's experiences and successes, nations can improve their capacity to address these issues. Collaborative research allows for the development of standardized approaches and protocols, leading to more reliable and consistent outcomes.
Cultural Exchange and Knowledge Sharing
International collaboration fosters cultural exchange and the sharing of knowledge, which is valuable for understanding different perspectives and approaches to research. This process can promote mutual respect and understanding among scientists from diverse backgrounds. International research projects can introduce researchers to new methodologies and approaches to problem-solving, broadening their horizons and inspiring new avenues of inquiry.
Funding and Resources for International Collaborations
Securing funding for international research collaborations often requires navigating complex bureaucratic procedures and international agreements. International organizations and governments often play a critical role in facilitating these collaborations, providing financial and logistical support. This support can include grants, fellowships, and infrastructure development, enabling researchers to work effectively across borders.
Research funding agencies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the value of international collaborations. They understand that shared resources and expertise can lead to more significant breakthroughs and advancements in various fields of study. This understanding is crucial for supporting researchers who are committed to engaging in international collaborations.
Ethical Considerations in International Collaborations
International research collaborations raise important ethical considerations regarding data sharing, intellectual property rights, and the equitable distribution of benefits. These considerations must be carefully addressed to ensure that all partners are treated fairly and that the research is conducted in a responsible and ethical manner. Understanding and addressing these issues is essential for building trust and maintaining strong collaborative relationships.
Clear agreements and protocols need to be established to ensure that all parties involved understand their responsibilities and rights concerning intellectual property and data ownership. Open communication and transparency are vital to address potential conflicts and ensure that all participants feel respected and valued. This approach also promotes mutual trust and understanding.