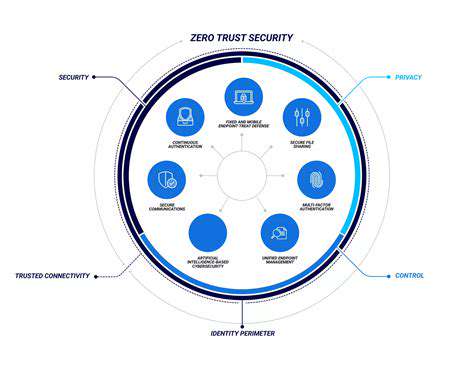
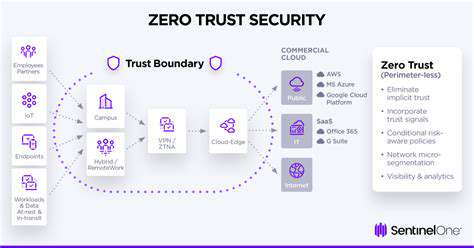
Zero Trust and the Need for Verification
Zero Trust security models fundamentally shift the paradigm from a perimeter-based approach to a more granular, continuous verification process. Instead of assuming trust within a network boundary, Zero Trust mandates that every access request, regardless of its source, be meticulously vetted. This proactive approach acknowledges the ever-present threat of insider and outsider attacks, as well as the increasing prevalence of sophisticated phishing and malware campaigns. This verification process is crucial in preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive data.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Zero Trust
A robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) system is paramount in a Zero Trust environment. It necessitates a detailed understanding of user roles, privileges, and access rights. This involves not only verifying the identity of users but also ensuring that their access permissions are aligned with their job responsibilities and the principle of least privilege. Effective IAM helps organizations limit the potential damage caused by compromised accounts, as only necessary access is granted to authorized users.
Thorough user provisioning and de-provisioning procedures are also essential elements. These procedures ensure that access rights are immediately revoked when an employee leaves or their role changes, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access after the employee has departed.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
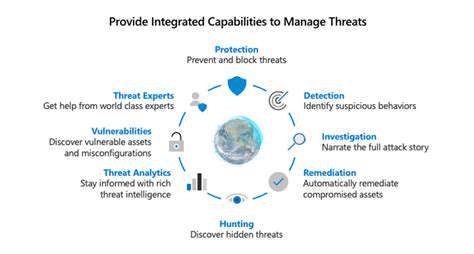
Zero Trust security isn't a one-time implementation; it requires continuous monitoring and a proactive approach to threat detection. This involves regularly evaluating user behavior, system activity, and network traffic to identify anomalies and potential security breaches. Real-time threat intelligence feeds and advanced analytics tools are vital to quickly detect and respond to suspicious activities, preventing data breaches before they occur.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Integration
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions are critical components of a Zero Trust architecture. They provide granular controls to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization's authorized channels or systems. By integrating DLP tools with Zero Trust principles, organizations can enforce policies that restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles, locations, and devices. This helps limit the potential for unauthorized data exfiltration and ensures that data is only accessible to those who need it.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Strong Passwords
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is another critical aspect of Zero Trust. Requiring more than one form of verification, such as a password and a one-time code, significantly strengthens security measures. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access even if they have compromised one form of authentication. Strong passwords, combined with MFA, form an important line of defense against various types of cyber threats, further bolstering the overall security posture.
Enforcing Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege is fundamental to Zero Trust security. It dictates that users should only have the minimum necessary access rights to perform their job functions. By restricting access to specific resources and data, organizations drastically reduce the potential damage from a security breach. This stringent access control approach is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity, minimizing the impact of potential security incidents.
Implementing Zero Trust DLP: Key Considerations

Zero Trust DLP: Foundation
Implementing a Zero Trust Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategy requires a fundamental shift in mindset and security architecture. Instead of relying on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust DLP assumes no implicit trust, verifying every user and device attempting access to sensitive data. This proactive approach dramatically reduces attack surface and strengthens overall security posture. Zero Trust DLP is crucial for protecting sensitive information in today's increasingly complex and distributed environments.
It's essential to understand that the core principle of Zero Trust DLP is to verify every access request, regardless of location or user role. This granular control is vital for preventing unauthorized data breaches and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. This granular approach allows for a highly targeted and adaptable security strategy.
Identifying and Classifying Sensitive Data
A critical first step in implementing Zero Trust DLP is identifying and classifying sensitive data within your organization. This involves meticulously reviewing all data types, locations, and usage patterns to pinpoint what needs protection. This process often necessitates collaboration between security teams, data owners, and business units to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Once identified, sensitive data should be categorized based on its value and potential impact in case of a breach. This classification process helps prioritize security controls and resources, ensuring the most critical data receives the highest level of protection. Understanding the value of data is crucial to successful DLP implementation.
Implementing Access Controls and Policies
Zero Trust DLP relies heavily on granular access controls. Each user, device, and application must be meticulously assessed and granted only the necessary access rights to sensitive data. This stringent approach minimizes the potential damage from a compromised account or device.
These access controls must be dynamic and adaptable, changing based on context, user activity, and device characteristics. This adaptive approach ensures that access permissions align with current needs and reduces the risk of unauthorized data access.
Enforcing Data Loss Prevention Policies
After establishing access controls, DLP tools and policies need to be implemented to actively monitor and enforce data usage rules. This includes setting limits on data transfer, blocking unauthorized file types, and scrutinizing data leaving the organization's network. This proactive enforcement is crucial for preventing data exfiltration.
Monitoring and Auditing DLP Systems
Implementing a robust monitoring system is essential to ensure the effective operation of your Zero Trust DLP strategy. Regular monitoring and auditing of DLP systems help detect anomalies, identify potential vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with established policies. This continuous monitoring is vital to maintaining a proactive security posture.
Auditing logs and reports provide crucial insights into data access patterns and potential security incidents. This allows for rapid response to security threats and ensures the ongoing effectiveness of your DLP solution. Thorough auditing helps identify weaknesses in the system and improve overall security.
When you roast food, something magical happens at the molecular level. The Maillard reaction, named after French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard, transforms ordinary ingredients into culinary masterpieces. This isn't just browning - it's a symphony of chemical changes that creates hundreds of new flavor compounds. Chefs have harnessed this process for centuries, though now we understand the science behind why roasted foods develop such complex flavors.
Beyond Traditional DLP: Data Loss Prevention in the Cloud and Modern Work Environments

Understanding the Evolving Threat Landscape
Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions have traditionally focused on preventing sensitive data from leaving a company's network. However, the modern threat landscape is far more complex and sophisticated, with attackers employing increasingly sophisticated tactics to gain access to and exfiltrate valuable data. This requires a shift in thinking, moving beyond reactive measures to proactive strategies that anticipate and mitigate emerging threats. This evolving threat landscape includes insider threats, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and the rise of cloud-based data storage, all of which demand a more comprehensive approach to data security.
Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and use is crucial in today's digital world. Organizations must recognize that data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Addressing this necessitates a broader understanding of the risks associated with data loss, extending beyond the traditional perimeter of the network. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of remote work and BYOD policies further complicates the security landscape, necessitating robust strategies to safeguard sensitive data regardless of location.
Proactive Data Loss Prevention Strategies
A proactive approach to data loss prevention involves more than just implementing technical controls. It requires a comprehensive security strategy encompassing employee training, data classification, and access management. Strong security awareness programs are crucial in educating employees about the importance of data security and the risks associated with negligent behavior.
Implementing robust data classification policies is essential to identify and categorize sensitive data, enabling the organization to apply appropriate security controls based on the data's sensitivity. This approach ensures that the right level of protection is applied to the right data. Data loss prevention should be integrated into the organization's overall security posture, not treated in isolation.
The Role of Advanced Technologies
Advanced technologies such as machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) can play a critical role in enhancing data loss prevention efforts. These technologies can be deployed to identify anomalies and suspicious activities in real-time, enabling organizations to proactively respond to threats and prevent data breaches. This proactive approach is vital in today's dynamic threat landscape.
AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, allowing for early detection of potential threats and malicious activity. This can include identifying unusual data access patterns or suspicious file transfers, which may indicate a data breach attempt. This level of sophistication is essential to combating the advanced techniques used by modern attackers.
Beyond the Perimeter: Protecting Cloud-Based Data
The increasing reliance on cloud-based services necessitates a shift in data loss prevention strategies to protect data stored in the cloud. Traditional on-premises DLP solutions often fall short in the cloud environment, requiring a new generation of solutions. Organizations must implement robust security controls that extend to cloud environments, ensuring compliance with security standards and regulations relevant to cloud data storage.
Implementing strong access controls, encryption, and secure configurations within cloud platforms is critical. This includes configuring access permissions carefully and encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
The Human Factor in Data Loss Prevention
Despite the significant advancements in technology, the human element remains a critical component of effective data loss prevention. Employee training and awareness programs are essential for fostering a culture of data security. Empowering employees to recognize and report potential threats is crucial in preventing data breaches.
Security awareness training should cover topics such as phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and the importance of following security protocols. Empowering employees to recognize and report suspicious activities can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Regular updates and refresher courses are also vital to ensure that employees maintain their vigilance in the face of evolving threats.
Enhancing Security Posture with Advanced Analytics and Automation

Implementing Robust Access Controls
Implementing robust access controls is a fundamental aspect of enhancing security posture. This involves carefully defining and enforcing rules that govern who can access what resources within your systems and networks. These controls should be based on the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their job functions. This minimizes the potential damage from compromised accounts or malicious actors.
Specific controls might include multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and strict authorization policies for sensitive data. Regular reviews and updates to access controls are crucial to maintaining a strong security posture as organizational needs and threats evolve.
Utilizing Advanced Threat Detection
Staying ahead of evolving threats requires proactive security measures. Advanced threat detection systems can identify subtle anomalies and suspicious activities that traditional security tools might miss. This proactive approach allows for quicker responses to potential incidents, minimizing the potential for widespread damage. These systems often leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to learn and adapt to new threats.
Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, and threat intelligence feeds are crucial components of a comprehensive threat detection strategy. This proactive approach can significantly enhance the overall security posture.
Strengthening Network Segmentation
Network segmentation isolates different parts of a network, limiting the impact of a security breach. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, you can contain the spread of malware or unauthorized access attempts. This approach greatly reduces the potential for a single security vulnerability to compromise the entire network. Proper segmentation requires careful planning and implementation, taking into account the specific needs and dependencies within the organization.
Implementing firewalls, virtual LANs (VLANs), and other network segmentation technologies can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Regular reviews and adjustments to the segmentation strategy are essential to maintain its effectiveness.
Employing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
Protecting sensitive data is paramount in today's digital landscape. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) measures are essential for identifying and preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization's control. These measures can identify and block unauthorized transfers of confidential information, reducing the risk of data breaches and regulatory violations. Implementing DLP policies and tools can significantly improve your organization's security posture.
Enhancing Endpoint Security
Protecting endpoints, such as laptops and mobile devices, is critical for a strong security posture. Endpoint security solutions provide critical protection against threats targeting these devices. These solutions often include antivirus software, intrusion prevention systems, and other security tools tailored for the specific endpoint. Regular patching and updates of endpoint security software are essential.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that security controls are effective. These assessments provide valuable insights into the current security posture and help pinpoint areas needing improvement. Regular assessments and audits help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a strong security posture. By consistently evaluating and improving security measures, organizations can reduce the risk of breaches and maintain compliance with security standards.