Device Posture Assessment and Endpoint Security
Understanding Device Posture
Device posture assessment is a crucial component of a robust zero-trust security strategy. It involves evaluating the configuration and security posture of each device connecting to your network, regardless of its location. This assessment goes beyond simply verifying the operating system and installed applications. It delves into crucial aspects like software updates, security patches, and the presence of potentially harmful or unauthorized software. A comprehensive device posture assessment is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that adapts to the ever-evolving threat landscape, ensuring that your endpoint devices remain aligned with your security policies.
Understanding the current posture of your endpoints allows you to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This proactive approach is a cornerstone of zero-trust security, as it dramatically reduces the attack surface and enhances the overall security posture of your entire organization. By continuously monitoring and assessing device posture, you gain valuable insights into the security health of your network, enabling you to implement targeted security measures and mitigate potential risks.
Assessing Endpoint Security Controls
Beyond device posture, a comprehensive endpoint security assessment also needs to evaluate the effectiveness of security controls already implemented on each device. This involves verifying the configuration of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software, ensuring they are correctly configured and actively protecting against potential threats. Regular audits and assessments of these controls are essential to guarantee they remain aligned with evolving security standards and threat intelligence, and are not bypassed by malicious actors.
Furthermore, the assessment should evaluate the effectiveness of multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions in place on endpoints. The strength and usability of MFA are critical factors in the overall security posture of each endpoint device. The assessment must also determine if the endpoint security solutions are properly integrated with your overall security information and event management (SIEM) system, enabling effective threat detection and response.
Implementing Zero-Trust Principles for Secure Endpoints
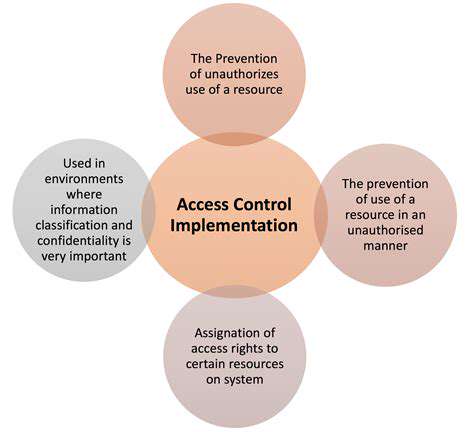
Implementing zero-trust principles for endpoint security requires a shift in mindset from traditional security models. Instead of assuming trust based on device location or network access, a zero-trust approach demands continuous verification and validation of each device and user. This means implementing strict access controls and micro-segmentation to limit the potential damage from a compromised endpoint. By segmenting networks and limiting access based on context, you significantly reduce the blast radius of a security breach.
Implementing strong authentication protocols is also paramount, requiring users to prove their identity and access authorization before being granted access to resources. This includes utilizing strong passwords and employing robust multi-factor authentication. Furthermore, regular security awareness training for employees is crucial to educate them on the risks associated with phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. This educational component is essential in building a zero-trust culture within the organization.
Continuous monitoring and analysis of endpoint activity are essential for detecting anomalies and malicious behavior. This involves leveraging advanced threat detection technologies and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. The data gathered from these systems will help you identify and respond to emerging threats, keeping your endpoints secure in a dynamic and ever-evolving threat landscape.
Regular software updates and patch management are vital for maintaining a strong endpoint security posture. Outdated software is often vulnerable to exploitation, making timely updates critical to preventing attackers from gaining unauthorized access. Automated patching processes and proactive security measures will significantly strengthen the overall security posture.
Zero-trust principles dictate that access to resources should be based on need-to-know and least privilege. Implementing these principles on endpoints ensures that only authorized users have access to necessary resources, reducing potential damage in case of a compromise.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection for Proactive Security

Continuous Monitoring for Improved Security
Continuous monitoring is a critical component of a robust security posture. It involves the constant observation of systems, networks, and applications for suspicious activity. This proactive approach allows security teams to detect and respond to threats in real-time, minimizing the impact of potential breaches. By continuously monitoring, organizations can identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
The key to effective continuous monitoring lies in establishing comprehensive baselines. These baselines represent the typical behavior of the monitored systems, providing a reference point for identifying anomalies. Deviating patterns trigger alerts, allowing security personnel to investigate and address potential threats swiftly. This proactive approach significantly enhances the overall security posture of an organization.
Threat Detection Strategies
Various threat detection strategies are employed to identify malicious activity. These strategies leverage a combination of signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis. Signature-based detection identifies known threats by matching them against a database of malicious signatures. Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns that deviate from established baselines, potentially indicating malicious activity. Behavioral analysis analyzes the behavior of users and systems to identify suspicious patterns.
Data Collection and Analysis
Effective threat detection hinges on the ability to collect and analyze data from various sources. This data encompasses logs from servers, network devices, and applications. Collecting this data involves establishing robust logging mechanisms across the entire infrastructure. Advanced analytics techniques are then applied to identify patterns and anomalies, uncovering potential threats that might otherwise remain undetected.
Real-Time Threat Response
A crucial aspect of continuous monitoring is the ability to respond to threats in real-time. This involves automated responses to alerts, enabling swift containment and remediation. Implementing automated response mechanisms is critical to minimizing the impact of a security breach. Security teams can then focus on investigating the root cause of the threat and implementing preventative measures.
Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Integrating continuous monitoring with SIEM systems is essential for comprehensive threat management. SIEM systems provide a centralized platform for collecting, analyzing, and correlating security events. This integration enables a holistic view of the security posture, allowing for more effective threat detection and response. The combination of monitoring and SIEM provides a powerful tool for improving security visibility.
Vulnerability Management
Continuous monitoring plays a significant role in vulnerability management. By constantly scanning systems for known vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively patch and mitigate risks. This proactive approach reduces the attack surface and strengthens the overall security posture. This process is crucial for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities, preventing exploitation by malicious actors.
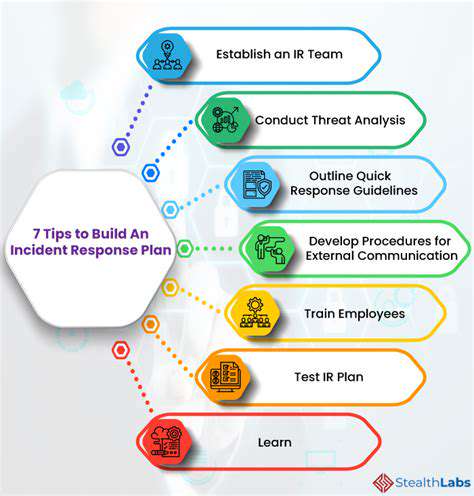
Incident Response and Remediation
Effective incident response and remediation procedures are vital components of a robust security strategy. These procedures outline the steps to be taken when a security incident is detected. Continuous monitoring provides the critical data needed to initiate these procedures. A well-defined incident response plan ensures rapid containment and remediation of security incidents, minimizing damage. This ensures that the organization can recover quickly and learn from the incident to improve future security measures.