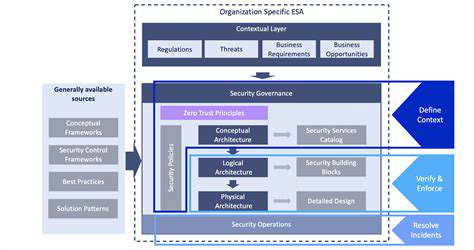
Understanding the Scope of Third-Party Risks
Modern software ecosystems depend significantly on third-party components and services. From cloud storage to payment gateways, these external integrations are indispensable for functionality, yet they simultaneously introduce a substantial attack surface. Vulnerabilities in these third-party systems can create pathways for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or manipulate critical business operations. Organizations must transcend a simplistic trust model and actively evaluate the security posture of every third-party application or service they integrate. Recognizing the diverse ways these integrations can be compromised is the initial step in mitigating potential threats.
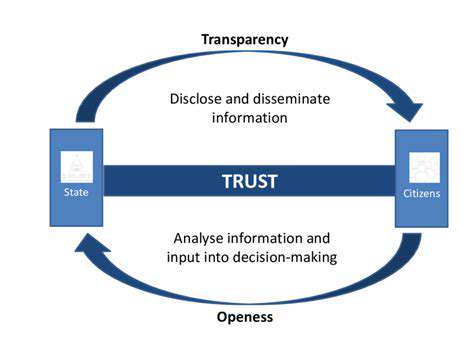
The expanding attack surface extends beyond immediate access granted by a vulnerability. Consider the ripple effect: if a third-party service is compromised, it can expose internal systems to malware, data breaches, or even malicious manipulation of sensitive information. This indirect exposure often remains undetected until it's too late, underscoring the necessity of proactive security measures and stringent third-party risk management protocols. A holistic approach must incorporate regular security assessments, continuous monitoring, and clear communication channels with vendors to ensure alignment on security best practices.
Mitigating Third-Party Risks Through Proactive Measures
Proactive security measures are indispensable for reducing exploitation risks by malicious actors. This involves more than merely signing contracts with vendors that include security clauses; it requires an ongoing process of assessing and managing the security posture of every third-party component. Organizations should implement exhaustive due diligence during the selection process to identify potential vulnerabilities and confirm that vendors adhere to robust security practices. This proactive strategy includes conducting regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability scanning to detect and rectify weaknesses before exploitation occurs.
Beyond the initial assessment, continuous monitoring and response are equally critical. Persistent monitoring of third-party systems helps detect anomalies and potential breaches in real time. Establishing transparent communication channels with vendors is also vital, facilitating swift information exchange about security incidents and enabling timely remediation. Implementing stringent security policies and standards for third-party vendors, encompassing access controls, data encryption, and incident response plans, is essential for maintaining a resilient security posture across the entire ecosystem. This proactive approach is pivotal for managing the expanding attack surface and safeguarding sensitive information.
Regular security awareness training for employees is a cornerstone of mitigating third-party risks. Employees should be cognizant of the potential risks tied to third-party applications and services and know how to identify and report suspicious activities. This education empowers employees to serve as a first line of defense against potential threats. Moreover, implementing robust incident response plans that include explicit procedures for addressing third-party security incidents is crucial for minimizing breach impacts and preventing further damage.
Identifying and Classifying Third-Party Access Needs
Identifying Third-Party Risks
Grasping the multifaceted nature of third-party risks is imperative for organizations striving to maintain operational stability and protect sensitive data. These risks arise from reliance on external vendors, suppliers, and partners, who may introduce vulnerabilities into an organization's systems and processes. Comprehensive identification entails a thorough evaluation of potential threats, ranging from data breaches to reputational harm. Identifying these risks is not a one-off task but an ongoing process demanding perpetual vigilance.
A pivotal aspect of identifying third-party risks is assessing the vendor's security posture. This involves scrutinizing their security policies, procedures, and technological safeguards. Evaluating their compliance with industry standards and regulations is also essential. Additionally, the organization must consider the sensitivity of the data shared with the third party and the potential consequences of a breach.
Classifying Third-Party Risks Based on Impact
Third-party risks can be categorized by their potential impact on an organization. One significant category centers on the financial repercussions of a security incident involving a third party, such as direct financial losses or reputational damage affecting revenue streams. Another critical consideration is the potential for operational disruption, which could span from service interruptions to complete system failures, including project delays and impacts on business continuity.
Furthermore, analyzing the potential for reputational damage resulting from a third-party breach is essential. A negative incident involving a partner or vendor can severely tarnish the organization's reputation, affecting its brand image and customer trust. The severity of reputational damage often hinges on the incident's nature and public perception of the affected parties.
Classifying Third-Party Risks Based on Likelihood
Assessing the likelihood of a third-party risk materializing is equally important. This involves evaluating the probability of a security incident occurring within the third-party organization. The analysis should account for various factors, including the third-party's security controls, their history of security incidents, and the complexity of the systems and processes they handle. A thorough risk assessment should also examine the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities in the third-party's infrastructure or processes.
Mitigating Third-Party Risk Through Due Diligence
Implementing rigorous due diligence procedures is vital for mitigating third-party risks. This involves conducting exhaustive background checks on potential partners and vendors, examining their security policies and procedures, and verifying their compliance with industry standards. Regular audits of the third-party's security practices are also necessary to ensure sustained compliance. This vigilance helps ensure that the third-party remains aligned with the organization's security standards and policies.
Moreover, contract negotiations should include provisions that explicitly define both parties' responsibilities regarding security. It is imperative to understand how the organization will monitor and enforce these responsibilities. This ensures that third-party risks are addressed proactively and effectively. Clear communication channels and protocols for incident reporting and response are essential for maintaining a robust security posture.
Implementing a Third-Party Risk Management Framework
Establishing a formal third-party risk management framework is crucial for organizations to effectively oversee and mitigate risks. This framework should delineate clear responsibilities, processes, and procedures for identifying, assessing, and mitigating third-party risks. The framework should also foster ongoing communication and collaboration between different departments within the organization to ensure a coordinated approach. Regular reporting and updates on the status of third-party risk management are indispensable for maintaining an effective framework.
This framework guarantees a consistent approach to managing third-party risk, enhancing the organization's ability to respond to potential threats and vulnerabilities. Implementing a robust framework can help an organization proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks, bolstering its overall security posture and preserving its reputation.
Implementing Strong Access Control Mechanisms
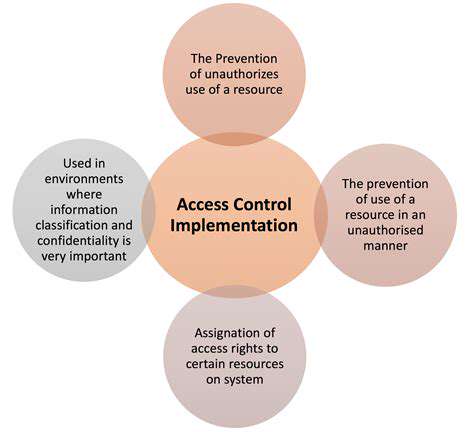
Defining Access Control Policies
Implementing robust access control policies is fundamental for protecting sensitive data and resources within any organization. These policies dictate who can access what information and under what circumstances. Clearly defining these permissions ensures that only authorized personnel can view, modify, or delete data, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches. This involves a meticulous process of identifying critical assets, evaluating potential threats, and establishing appropriate access levels based on job roles and responsibilities. A well-defined policy framework serves as the foundation for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality throughout the organization.
Comprehensive documentation is paramount to the efficacy of these policies. This documentation should include detailed descriptions of the specific data and resources subject to access control, along with a clear delineation of the permissions granted to different user groups. This documentation provides an accessible reference for both administrators and users, ensuring everyone understands their access rights and responsibilities. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation is essential for the sustained effectiveness of the access control system.
Implementing Access Control Mechanisms
Beyond policy definition, effective access control requires the implementation of robust mechanisms. These mechanisms are the practical tools that enforce the policies and ensure that only authorized individuals gain access. This encompasses a range of technologies and procedures, including authentication methods, authorization protocols, and auditing systems. These measures are indispensable for preventing unauthorized access and swiftly identifying security breaches.
Implementing strong authentication is key to securing access. This includes using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identities and prevent unauthorized access. Employing robust encryption techniques for data in transit and at rest is also a critical component of access control. These measures protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view it.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital for ensuring that the implemented access control mechanisms function effectively and are resilient to potential vulnerabilities. These activities help identify system gaps and allow for timely adjustments and improvements. A proactive approach to security audits and penetration testing is essential for maintaining a robust and secure access control system.
Regular training and awareness programs for employees are equally important for successful access control implementation. This educational effort helps employees understand the importance of access control policies and their role in maintaining data security. Clear communication and consistent reinforcement of security protocols help cultivate a security-conscious culture within the organization.
Building a Culture of Security Awareness
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Third-party access management is critical in today's interconnected world, where organizations rely heavily on external vendors and partners for various services. A significant portion of security breaches stems from vulnerabilities within these external relationships. Understanding the evolving threat landscape, including sophisticated social engineering tactics, malware distribution through compromised vendors, and the potential for insider threats within third-party organizations, is paramount. Proactive measures are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the security of sensitive data.
Establishing Clear Access Policies and Procedures
A comprehensive security policy for third-party access should be meticulously crafted and clearly communicated. This policy should define the specific roles and permissions granted to each third-party entity, outlining their access scope to organizational resources. It should also detail the procedures for access requests, approvals, and regular reviews, ensuring accountability and transparency. Furthermore, the policy should address data handling responsibilities, specifying how sensitive information should be protected and used by third-party personnel.
Implementing robust access controls and procedures is critical for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of organizational data. This includes defining clear access levels, conducting regular audits, and establishing mechanisms for revoking access when necessary. This proactive approach significantly reduces the potential for unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Strong Passwords
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all third-party access is a fundamental security measure. This adds a layer of security beyond simple usernames and passwords, making it significantly more challenging for unauthorized individuals to gain access. Strict password policies for both internal and external users are also necessary, mandating strong, unique passwords and regular password changes. This multifaceted approach substantially enhances the organization's overall security posture, mitigating the risks associated with weak passwords and single-factor authentication.
Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Regular security audits and monitoring of third-party access are crucial for identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system. These audits should assess the effectiveness of the implemented policies and procedures, ensuring compliance with industry best practices and regulations. Continuous monitoring enables proactive responses to emerging threats and potential security breaches. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of security incidents and ensures the ongoing protection of sensitive data.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Educating employees about the importance of secure practices when interacting with third-party vendors is essential. Robust training programs should cover topics like recognizing phishing attempts, maintaining confidentiality, and reporting suspicious activities. Employee awareness plays a critical role in preventing social engineering attacks and ensuring that all stakeholders understand their role in maintaining a secure environment. Regular training reinforces best practices and empowers employees to contribute to a stronger overall security posture.