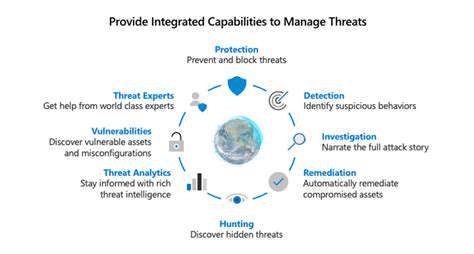
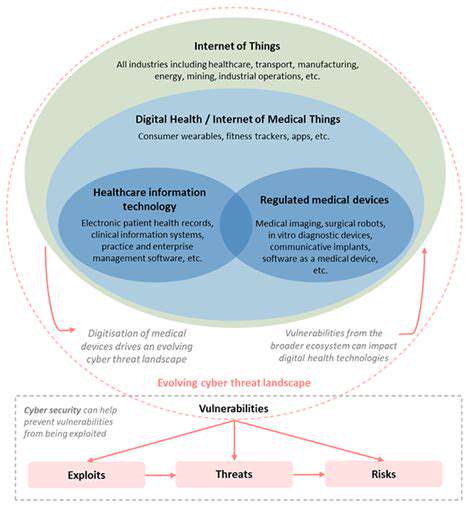
Understanding the Scope of AI-Driven Prioritization
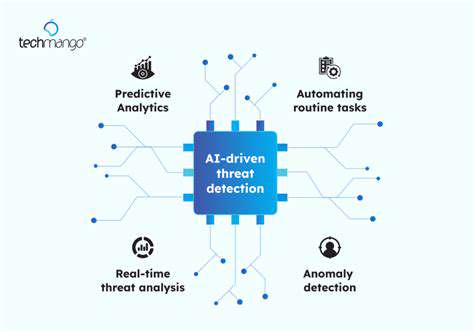
Modern vulnerability management powered by artificial intelligence transcends basic automated scanning. It examines potential threats in granular detail, evaluating both their probability of being exploited and the potential consequences for the organization. This advanced methodology doesn't just flag vulnerabilities - it assesses their severity within the broader security framework, helping teams address the most urgent risks first.
This approach dramatically enhances operational efficiency by optimizing the vulnerability management cycle. Security personnel can bypass overwhelming lists of minor issues to concentrate on genuine threats, enabling more precise and impactful mitigation strategies.
Identifying Critical Vulnerabilities with Machine Learning
Machine learning plays a pivotal role in spotting high-risk vulnerabilities. These algorithms process enormous volumes of historical security data, threat reports, and vulnerability databases to recognize patterns and forecast emerging threats. This predictive power proves indispensable for preemptive defense, allowing organizations to implement protective measures before attacks materialize.
Prioritizing Based on Exploitability and Impact
The essence of intelligent prioritization lies in assessing both exploit potential and potential damage. Key considerations include attack complexity, possible operational disruption, and the vulnerability's attractiveness to attackers. This sophisticated evaluation enables security teams to allocate resources where they're needed most.
AI systems synthesize these factors to generate risk scores for each vulnerability, creating a clear hierarchy for remediation efforts.
Integrating Threat Intelligence into the Process
Real-time threat intelligence integration forms the backbone of effective prioritization. Current data on attack methods, new threats, and adversary behaviors helps refine the assessment process, keeping security measures aligned with the evolving threat environment.
Threat-aware AI models continuously adjust to new information, providing organizations with up-to-the-minute evaluations of their most pressing vulnerabilities.
Optimizing Remediation Efforts with AI
Artificial intelligence further enhances remediation by recommending tailored solutions for specific vulnerabilities. These might include specialized patches, configuration adjustments, or other targeted security measures. This intelligent automation dramatically reduces remediation time and resource expenditure.
Automating the Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
AI-powered systems can automate substantial portions of vulnerability management, from initial detection through to resolution and documentation. This automation liberates security experts from routine tasks, allowing them to concentrate on strategic initiatives like threat analysis and incident management.
The automated approach improves both precision and consistency across the entire security management process.
Ensuring Accuracy and Transparency in Prioritization
Maintaining transparent and accurate prioritization remains essential. Security teams must comprehend the AI's decision-making process to verify that prioritization aligns with organizational risk profiles. Detailed audit logs and clear explanations of model decisions foster trust in system outputs.
This transparency enables security professionals to evaluate AI recommendations, ensuring alignment with the company's specific security requirements and objectives.
Automated Patching and Remediation: Streamlining the Process

Automated Patching: A Foundation for Security
Automated security updates form the cornerstone of modern cyber defense strategies. Automating the application of patches and system updates dramatically shrinks vulnerability windows and reduces exploitation risks. This proactive methodology minimizes operational disruptions while ensuring systems operate on the most secure available versions. It simultaneously reallocates IT resources toward strategic initiatives.
The automated update process typically involves system assessment, patch acquisition, and controlled implementation. Incorporating verification steps to check patch integrity and compatibility further strengthens this process. Such meticulous execution proves vital for maintaining robust security.
Remediation Strategies for Vulnerabilities
Comprehensive vulnerability management extends beyond patching alone. Effective remediation requires an integrated approach encompassing thorough scanning, detailed analysis, and intelligent prioritization. This ensures organizations address critical vulnerabilities first, substantially reducing potential attack surfaces.
Additional mitigation measures might include access control modifications, firewall adjustments, or security parameter changes. These supplementary precautions significantly lessen potential damage from successful exploits. Such comprehensive vulnerability handling remains crucial for sustained security.
Benefits of Implementing Automation
Automated patching and remediation deliver substantial advantages. Minimized operational disruption stands as a key benefit, as automated processes can execute during low-activity periods. Automation also drastically reduces implementation timeframes, consequently shrinking exposure to potential exploits.
Automated systems generate comprehensive reports on update and remediation activities. These analytics prove invaluable for performance tracking, pattern identification, and overall security process improvement.
Challenges and Considerations
While automation offers significant benefits, implementation requires careful planning. Securing the patching process itself is paramount, demanding robust protections against unauthorized access or malicious interference.
Potential system impacts require thorough evaluation. Comprehensive testing remains essential to confirm patches and remediation measures don't introduce new vulnerabilities or compatibility problems.
Contemporary packaging predominantly utilizes materials like cardboard, various plastics, and paper products, all carrying significant environmental consequences. Producing these materials initiates with resource extraction, often causing deforestation, ecological damage, and water pollution. The manufacturing, transportation, and disposal processes for these items generate enormous greenhouse gas emissions contributing to climate change. Many such materials persist in landfills for extended periods, disrupting natural decomposition and releasing harmful substances into ecosystems.