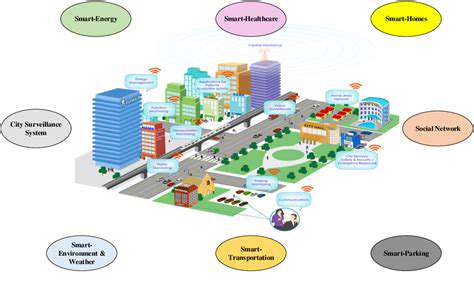
The Expanding Threat Landscape in Smart Cities
Smart City Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
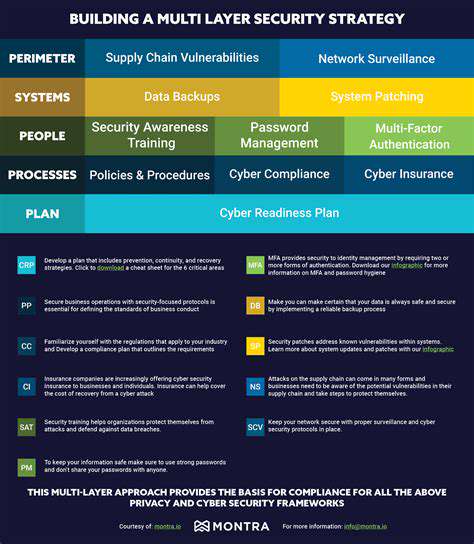
Modern smart cities rely heavily on interconnected systems, from traffic management and energy grids to public safety and waste management. This interconnectedness, while offering significant efficiency gains, also creates a complex web of potential vulnerabilities. Legacy systems often lack the robust security protocols of newer technologies, creating a patchwork of defenses that can be exploited by sophisticated attackers. This inherent complexity makes it crucial to implement comprehensive security measures across all interconnected systems within a smart city's infrastructure.
The reliance on IoT devices for data collection and control also introduces unique security challenges. These devices, often manufactured with limited security features, can become entry points for malicious actors seeking access to critical city infrastructure. Poorly configured or outdated software on these devices further exacerbates the risk. Addressing these vulnerabilities requires proactive security measures, rigorous testing, and ongoing monitoring to adapt to evolving threats.
Cybersecurity Threats Targeting Critical Infrastructure
Smart city systems often control critical infrastructure like water treatment plants, power grids, and transportation networks. A successful cyberattack on these systems can have devastating consequences, disrupting essential services and potentially endangering public safety. Attackers may target these systems to cause widespread damage, extort money, or steal sensitive data. Protecting these vital components requires a layered security approach, including robust authentication mechanisms, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks necessitates ongoing training and development of cybersecurity personnel. Smart city authorities need to invest in skilled professionals who can identify and respond to emerging threats. This includes not only technical expertise but also an understanding of the potential impact of cyberattacks on societal well-being.
The Role of IoT Device Security in Smart City Protection
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in smart cities significantly increases the attack surface. From smart streetlights and traffic signals to smart meters and security cameras, each device represents a potential vulnerability if not properly secured. Manufacturers must prioritize security in the design and development of these devices, implementing strong encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular software updates. This proactive approach ensures that security is baked into the core functionality of each device.
Furthermore, smart city administrators must enforce strict security policies for IoT devices, including mandatory updates, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments. Regular audits and penetration testing of these devices are crucial in identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns
Smart city systems collect and process vast amounts of data, including personal information from citizens. A data breach could expose sensitive data, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. Protecting this data requires implementing robust data encryption, access controls, and secure data storage solutions. Implementing strict data governance policies and educating citizens about data security practices are also vital aspects of this strategy.
Maintaining public trust in smart city initiatives is crucial. Transparency about data collection practices, clear privacy policies, and readily available channels for reporting security incidents are essential. Citizens must feel confident that their data is being handled responsibly and securely.
The Importance of Collaboration and International Standards
Addressing the expanding threat landscape in smart cities requires a collaborative approach. Sharing best practices, threat intelligence, and security solutions between cities and organizations is crucial. Establishing international standards for IoT security and data protection will help ensure a more secure and interoperable environment. This cooperation is essential to prevent the spread of cyberattacks and to foster a culture of security across the globe.
Government agencies, industry partners, and academic institutions must work together to develop and implement comprehensive security strategies. This includes fostering research and development in advanced cybersecurity technologies, providing training programs, and establishing secure communication channels for incident response.
Data Security and Privacy in Smart City Applications
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
A fundamental principle of data security and privacy in smart systems is data minimization. This principle dictates that systems should only collect and process the minimum amount of data necessary to achieve their intended purpose. Collecting excessive data increases the attack surface and the potential for misuse. This requires careful design and implementation of data collection processes. Data should be explicitly linked to specific purposes, and any data not needed for the stated purpose should not be collected.
Furthermore, data should be used only for the explicitly stated purpose. This concept is known as purpose limitation. This prevents unintended use of data and reduces the risk of privacy violations. Clear policies and procedures are crucial to ensure adherence to these principles, and these policies must be consistently enforced.
Data Encryption and Secure Storage
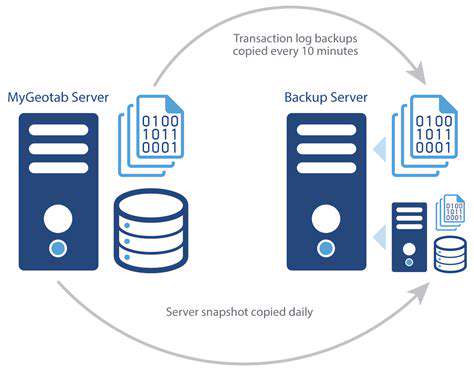
Robust encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data at rest and in transit. This involves using strong encryption algorithms to transform data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access or use the data. Implementing strong encryption throughout the entire data lifecycle is critical.
Data should be stored in secure environments, limiting physical and logical access to authorized personnel. Multi-factor authentication and access controls should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access to data storage systems. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Access Control and Authorization
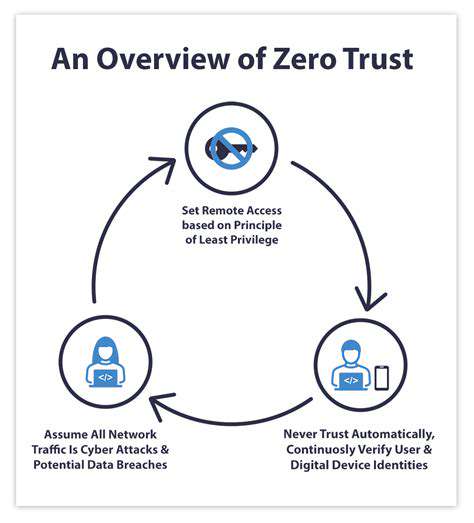
Implementing strict access control mechanisms is paramount for ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. This includes defining clear roles and responsibilities for different users within the system, and granting access based on these roles and responsibilities. This prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining access and compromising the system.
Implementing strong authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication, can significantly improve the security posture of the system. This ensures that only legitimate users can access the resources they need. Regular reviews and updates to access control lists are essential to ensure continued security.
Secure Development Practices
Security should be integrated into every stage of the smart system development lifecycle. This includes designing systems with security considerations in mind from the initial planning stage, through implementation and deployment. Adopting secure coding practices helps prevent common vulnerabilities.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing should be conducted throughout the development process. This helps identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Thorough testing will also help ensure the system functions as intended without compromising security.
Data Integrity and Validation
Ensuring data integrity throughout the system is vital for maintaining accuracy and reliability. This involves implementing mechanisms to verify the authenticity and consistency of data. Data validation helps to prevent malicious or erroneous data from entering the system. This includes checking data types, formats, and ranges to ensure data quality.
Compliance and Governance
Adherence to relevant data security and privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, is critical for maintaining trust and avoiding legal repercussions. Organizations must establish clear policies and procedures to ensure compliance with these regulations. Continuous monitoring and auditing of data handling practices are crucial to ensure compliance.
Having a robust governance framework for data security and privacy is essential. This framework should outline roles, responsibilities, and procedures for handling data breaches and other security incidents. This ensures that appropriate action is taken to mitigate any potential risks and restore the system to a secure state.