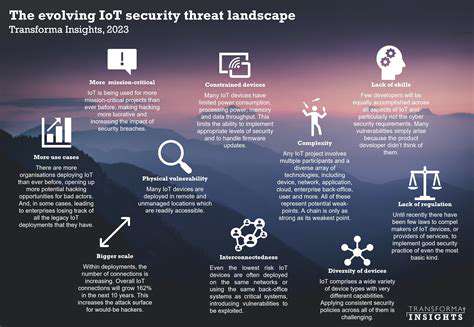
Traditional VPNs: A Legacy Approach
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have long been the cornerstone of remote access, providing a secure tunnel for users to connect to a company's network. However, their reliance on a central point of access and the inherent trust placed in users connecting through the VPN creates inherent security vulnerabilities in today's dynamic threat landscape. They often struggle to adapt to the ever-growing complexity of modern networks and the diverse range of devices and locations employees use for work. The broad access granted by VPNs to the entire network poses a significant risk, as a single compromised user account can potentially expose the entire organization's infrastructure to malicious activity.
Furthermore, managing VPN connections can be complex and resource-intensive, leading to performance bottlenecks and increased administrative overhead. The inherent trust model embedded within VPNs also makes it challenging to enforce granular access controls and policies, which are crucial in today's increasingly sophisticated security environments. This lack of granular control makes it difficult to precisely determine who has access to what resources and when.
Zero Trust Network Access: A Modern Solution
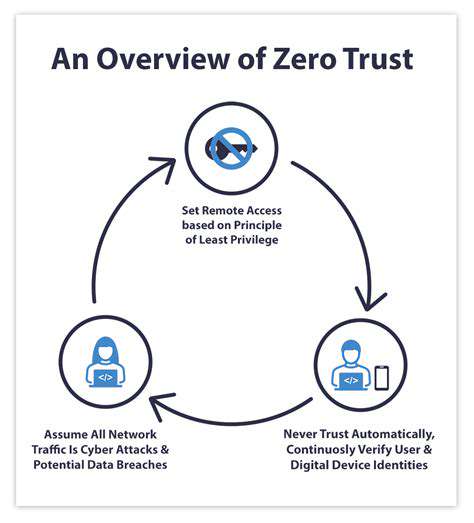
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a paradigm shift in remote access security. Instead of assuming trust, ZTNA adopts a never trust, always verify approach, meticulously scrutinizing every access request, regardless of the user's location or device. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface by limiting the access granted to only the necessary resources and applications, mitigating the risk associated with compromised accounts or devices.
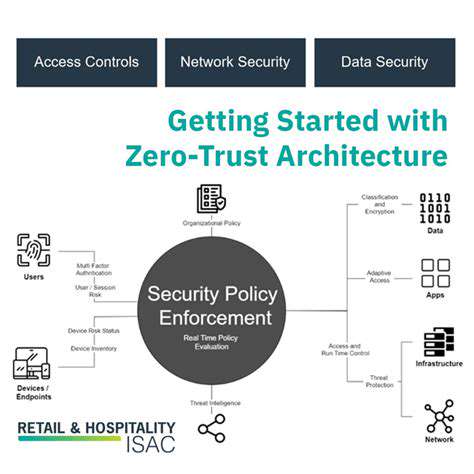
ZTNA solutions employ micro-segmentation techniques to isolate network resources, creating granular access controls. This allows organizations to grant access to specific applications and data only when necessary, reducing the potential damage from a security breach. By enforcing context-aware access policies, ZTNA ensures that users only have access to the resources they require, based on their identity, device, location, and even the specific task they're performing. This granular control is significantly more secure than the broad access afforded by traditional VPNs.
ZTNA also offers enhanced visibility and control over network traffic, enabling organizations to monitor and analyze access patterns in real-time. This real-time visibility allows for quick identification and response to suspicious activity, significantly improving the overall security posture of the organization. The ability to dynamically adjust access based on changing circumstances, such as location changes or device posture, makes ZTNA highly adaptable to the evolving needs of the modern enterprise.
Quantum computers hold the potential to revolutionize climate modeling, offering unprecedented accuracy and speed in simulating complex systems. This capability could lead to significantly more accurate predictions of future climate scenarios, allowing for more effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. The ability to model intricate interactions within the climate system, including feedback loops and chaotic dynamics, could provide far more detailed and reliable projections.

The Future of Remote Access Security: A ZTNA-Centric Approach
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Redefining Perimeter Security
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is rapidly emerging as the cornerstone of modern remote access security. ZTNA fundamentally shifts the paradigm from a traditional, perimeter-based approach to a more dynamic and granular security model. This shift is crucial in today's increasingly distributed and mobile work environment, where employees access company resources from a multitude of locations and devices.
Instead of relying on a broad, often porous, network perimeter, ZTNA establishes a zero-trust security posture. This means that every access request, regardless of the user or device, is meticulously authenticated and authorized before granting access. This granular control is a significant departure from the traditional trust until proven otherwise approach.
The Critical Role of Identity and Access Management (IAM) in ZTNA
Effective ZTNA implementation hinges significantly on robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. IAM solutions are essential for verifying user identities and ensuring only authorized individuals have access to specific resources. This verification process goes beyond simple usernames and passwords, often incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other advanced security mechanisms.
Strong IAM capabilities are vital for establishing and maintaining a zero-trust security posture. By meticulously verifying identities and authorizing access, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, a paramount concern in today's digital landscape.
Implementing ZTNA: Strategies for Success
Successful ZTNA implementation requires a strategic approach that considers various factors, including the organization's specific needs, existing infrastructure, and security policies. Careful planning and phased implementation can mitigate potential disruptions and ensure a smooth transition to a zero-trust security model.
Organizations should also prioritize ongoing monitoring and continuous improvement of their ZTNA deployments. This includes regularly assessing security posture, identifying vulnerabilities, and adapting security protocols to evolving threats. Proactive measures are crucial to maintaining a robust defense against potential security breaches.
Addressing the Challenges of ZTNA Adoption
Transitioning to a ZTNA-centric approach presents certain challenges, including the need for significant infrastructure changes and potential integration issues with existing systems. Careful planning and thorough testing are essential to mitigate these challenges and ensure a smooth transition.
Organizations must also address potential resistance from users who may be unfamiliar with the new security protocols. Effective communication and training programs can help to alleviate these concerns and facilitate a seamless adoption process.
Enhancing Security Through Microsegmentation and Network Segmentation
ZTNA goes hand-in-hand with microsegmentation and network segmentation. These techniques allow for the granular control of network access, isolating resources to only those users and devices that absolutely require access. This significantly reduces the blast radius of a potential security breach.
The Future of ZTNA: Emerging Trends and Innovations
The future of ZTNA looks bright, with ongoing developments in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) poised to enhance security posture. AI and ML can be leveraged to detect anomalies, predict potential threats, and automate responses to security events, thereby bolstering the effectiveness of ZTNA solutions.
Emerging trends also include the integration of ZTNA with cloud-based security services. This integration provides a more holistic approach to security, enhancing the overall protection of company resources in today's complex digital ecosystem.