The Evolving Threat Landscape and the Need for Zero Trust
The Rise of Sophisticated Cyberattacks
Cyber threats continue to advance at an alarming pace, with malicious actors refining their methods to bypass traditional security measures. This rapid evolution demands that businesses adopt dynamic cybersecurity strategies, regularly refreshing their protective systems and employee education initiatives. Gone are the days when simple email scams posed the greatest danger; modern attacks frequently combine customized malware with psychological manipulation techniques.
These complex operations increasingly focus on essential services, banking systems, and public sector organizations, potentially disrupting operations and eroding public confidence. Recognizing attacker behavior patterns and preferred methods becomes vital for creating robust defenses against these digital incursions.
The Growing Importance of Data Security
As digital information becomes the lifeblood of modern enterprises, safeguarding this data has risen to the forefront of organizational priorities. Security incidents involving sensitive information can trigger severe financial repercussions and brand deterioration, potentially alienating clients and disrupting business continuity. Comprehensive protection strategies must incorporate multiple layers including data encryption, strict permission systems, and periodic vulnerability assessments.
The Expanding Role of AI and Machine Learning
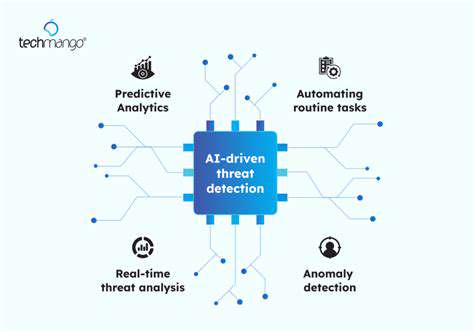
Modern cybersecurity increasingly relies on artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. These intelligent systems can process enormous datasets to spot unusual patterns that may indicate security breaches, allowing for quicker identification and resolution of potential threats. Integration of these technologies into security operations centers has become essential for maintaining rapid response capabilities in today's digital environment.
However, AI implementation isn't without its complications, including potential algorithmic prejudices and the requirement for specialized staff to properly utilize these tools. Businesses must weigh these considerations carefully when adopting AI-based security solutions.
The Impact of Remote Work Environments
The widespread adoption of distributed work arrangements has created new vulnerabilities for cyber criminals to exploit. Home-based employees often operate on less protected networks, increasing their susceptibility to credential theft and malicious software. Companies must deploy comprehensive security protocols to shield their remote teams and maintain the integrity of confidential information.
Educating staff on secure remote practices, implementing virtual private networks, and requiring multiple verification methods represent critical steps in addressing these emerging risks.
The Need for Enhanced Security Awareness Training
Comprehensive cybersecurity education remains vital for all team members, irrespective of their technical background. Human factors represent the most common security vulnerability, making targeted awareness programs one of the most effective defenses against digital threats. Effective training should address various risks including fraudulent communications, psychological manipulation techniques, and proper credential management.
Ongoing security education and periodic refreshers help maintain organizational vigilance against constantly changing digital risks.
The Emergence of Zero Trust Security Models
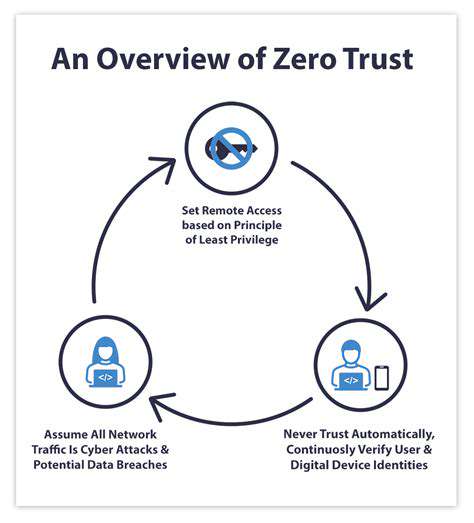
Zero trust architectures are gaining prominence as traditional perimeter-based security shows its limitations. This model operates on continuous verification principles, requiring authentication for every access request regardless of origin. Such an approach dramatically contains potential breaches by restricting unauthorized movement within digital environments.
Transitioning to zero trust requires substantial infrastructure changes, but the resulting security improvements and risk reduction justify the investment for most enterprises.
Benefits of Zero Trust Network Segmentation
Improved Security Posture
Network segmentation based on zero trust principles fundamentally strengthens organizational defenses through precise access management. Rather than assuming internal safety, every access request undergoes verification regardless of source. This methodology shrinks potential attack vectors by compartmentalizing network access. Dividing infrastructure into isolated sections contains security incidents, preventing widespread system contamination. Such architectural improvements significantly boost resistance against advanced persistent threats, representing a necessary evolution in digital protection strategies.
The core philosophy of continuous verification underpins zero trust implementations. This standard demands ongoing authentication for all network interactions, creating additional barriers against unauthorized access attempts. In today's threat environment, zero trust transitions from optional enhancement to critical requirement for safeguarding sensitive operations and information assets.
Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
Beyond security improvements, zero trust architectures offer notable operational benefits. By creating logical network divisions based on actual requirements, organizations can streamline data flows. This optimized approach reduces unnecessary network congestion while improving application responsiveness. The granular control enabled by segmentation simplifies infrastructure management and maintenance tasks. Precise resource allocation becomes possible, driving organizational efficiency across multiple departments.
Customized access permissions allow specialized teams to operate without impacting unrelated systems. Research departments, for instance, can maintain exclusive access to sensitive datasets while other business units function independently. This targeted resource management leads to optimized operational workflows and improved data handling practices.
Granular permission systems, when combined with comprehensive monitoring solutions, create adaptable network environments capable of meeting evolving business requirements while maintaining protection against emerging threats. The dual benefits of strengthened security and operational efficiency make zero trust implementations particularly compelling for contemporary enterprises.
Properly configured access controls working in tandem with monitoring systems ensure optimal network resource utilization. The resulting infrastructure demonstrates improved stability and reliability while accommodating growing operational demands.
In conclusion, zero trust network segmentation delivers comprehensive advantages that address both security concerns and operational efficiency, establishing itself as an essential component for modern organizations navigating complex digital landscapes.