Defining and Implementing Robust Access Control Policies
Understanding the Need for Robust Access Control
Robust access control policies are crucial for protecting sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access. In today's interconnected world, where third-party systems and individuals interact with internal systems, maintaining a strong security posture is paramount. This necessitates meticulous planning and implementation to ensure that only authorized users and applications can access specific data and functionalities.
A well-defined access control strategy prevents data breaches, protects intellectual property, and maintains compliance with industry regulations. Failing to implement robust policies can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Thorough analysis of potential vulnerabilities and risks is essential to build a comprehensive approach to access control.
Defining Access Control Policies
Defining access control policies involves a clear articulation of who has access to what data and resources, and under what circumstances. This includes specifying user roles, permissions, and the conditions under which access can be granted or revoked. Precisely defining these parameters ensures that access is restricted to only those individuals or systems who have a legitimate need to access the specified information or functionalities.
Furthermore, these policies should be documented thoroughly, providing a clear reference for all stakeholders. This documentation should be easily accessible and regularly reviewed to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness.
Implementing Access Control Mechanisms
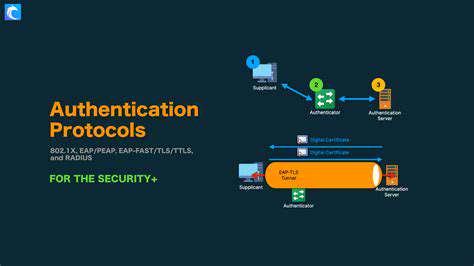
Implementing robust access control mechanisms requires the selection and integration of appropriate technologies. This includes using strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, to verify user identities. These methods significantly enhance security by making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
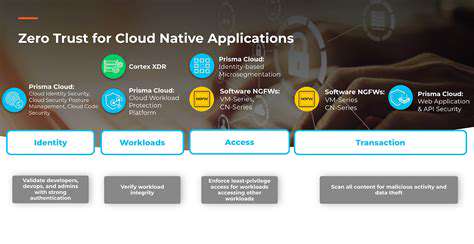
Employing authorization mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), is essential to limit the actions that users can perform within the system. RBAC assigns specific permissions based on predefined roles, ensuring that users only have access to the data and functionalities required for their job responsibilities.
Granular Access Control for Third-Party Systems
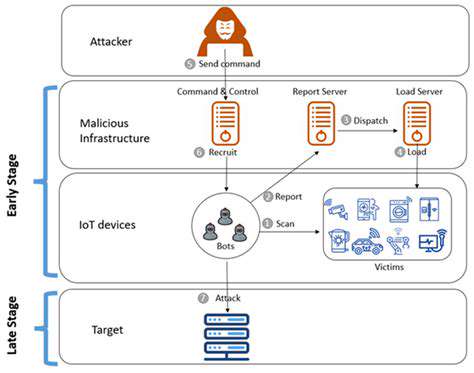
When dealing with third-party access, granular control is absolutely critical. Instead of blanket permissions, fine-grained access control allows administrators to precisely define what data or functions a third-party application or user can access. This is vital to mitigate the risk associated with allowing external entities into sensitive internal systems.
This level of control ensures that third-party access is limited to only the necessary data and functionalities, minimizing potential damage from unauthorized access or malicious intent. This granular control is a cornerstone of a secure access control environment.
Regular Policy Review and Updates
Security threats are constantly evolving, demanding that access control policies be reviewed and updated regularly. This continuous review process ensures that the policies remain aligned with the current security landscape and address any newly identified vulnerabilities. Regular assessments of the effectiveness of existing policies are crucial to identify weaknesses or areas for improvement.
Monitoring and Auditing Access Activities
Implementing robust monitoring and auditing mechanisms is essential to track access activities and detect any suspicious or unauthorized behavior. This allows for proactive identification of security breaches or potential threats in real-time. These mechanisms provide valuable insights into access patterns, helping to identify anomalies and potential vulnerabilities.
Detailed audit logs should be maintained, providing a comprehensive record of all access attempts and activities. This historical record is critical for incident response, investigation, and regulatory compliance.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Access control policies must adhere to relevant industry regulations and legal requirements. Compliance with data privacy laws, such as GDPR or CCPA, is essential to protect user data and maintain a strong security posture. Understanding and implementing these legal requirements is paramount for minimizing risks and ensuring legal adherence.
Thorough legal review and compliance checks are crucial to ensure that the policies meet the standards of applicable laws and regulations. This helps organizations avoid potential legal issues and maintain a positive reputation.