Identifying and Assessing Component Risks
Identifying Component Failures
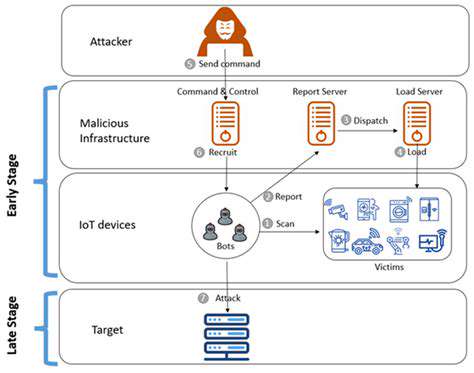
Component failures are a significant concern in various industries, from manufacturing to aerospace. Identifying these failures early and accurately is crucial for preventing further damage, downtime, and costly repairs. A thorough understanding of the potential failure points within a component is vital. This involves detailed analysis of the component's design, materials, and operating conditions. Understanding the potential for fatigue, corrosion, or other degradation mechanisms is critical for proactive maintenance strategies.
Effective failure identification often relies on a combination of visual inspections, non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, and data analysis. Visual inspections can reveal surface defects, while NDT methods like ultrasonic testing can detect internal flaws. Data analysis of operating parameters, such as temperature and stress levels, can also provide valuable insights into potential failure scenarios. Careful documentation of all findings is essential for future reference and analysis.
Assessing Component Severity
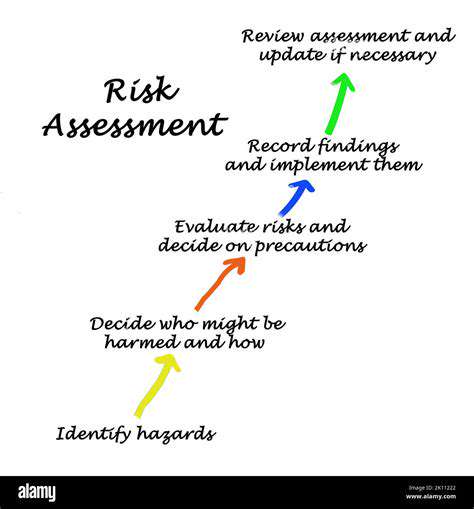
Once a component failure is identified, assessing its severity is paramount. This involves evaluating the extent of the damage, its potential impact on the overall system, and the likelihood of further failures. Factors such as the component's criticality to the system's function, the potential for cascading failures, and the environmental conditions must be considered. A thorough risk assessment helps prioritize maintenance and repair activities.
Several factors contribute to the severity assessment. These factors include the type and extent of the damage, the component's function within the system, and the potential for secondary failures. Accurate assessment allows for informed decision-making regarding repair strategies and potential replacements. This proactive approach to severity assessment minimizes downtime and maintains operational efficiency.
Considering the potential impact on safety, operational efficiency, and cost is essential in the severity assessment process. A comprehensive approach that considers all these factors is crucial for a robust and effective assessment.
Implementing Corrective Actions
After identifying and assessing the severity of a component failure, implementing corrective actions is crucial. This process involves developing and implementing strategies to prevent future failures. This may include design modifications, material improvements, or enhanced maintenance procedures. A crucial aspect of implementing corrective actions is the careful consideration of the root cause of the failure. This analysis often helps prevent similar failures in the future.
Implementing corrective actions may involve a variety of approaches, from simple adjustments to significant overhauls or replacements. The specific corrective action will depend heavily on the severity and nature of the failure. Regular inspections, improved maintenance schedules, and the use of advanced technologies are vital in preventing future incidents.
Documentation of the corrective actions taken is essential for future reference and for learning from past experiences. This helps in developing more robust and reliable systems in the long run. Thorough documentation of the corrective actions, the root cause analysis, and the implementation process is extremely important.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response

Continuous Monitoring Strategies
Continuous monitoring is a critical aspect of maintaining a stable and reliable system. It involves constantly observing system performance metrics, resource utilization, and application behavior to proactively identify potential issues before they escalate into major incidents. This proactive approach allows for swift responses and minimizes the impact of disruptions on users and operations. Implementing robust monitoring tools and dashboards is essential for effective continuous monitoring. These tools provide real-time visibility into system health and enable quick identification of anomalies.
A key component of effective continuous monitoring is the establishment of clear baselines and thresholds. These baselines represent the normal operating parameters for various system components. By establishing these parameters, deviations from the norm can be quickly detected and analyzed. Regularly reviewing and updating these baselines is crucial to reflect changes in system usage and performance characteristics.
Incident Response Planning
A well-defined incident response plan is vital for effectively managing and resolving incidents. This plan should outline the procedures for identifying, containing, and resolving incidents. The plan should clearly define roles and responsibilities for each team member or stakeholder involved in the incident response process. A robust plan ensures that everyone knows what to do in the event of an incident, minimizing delays and maximizing efficiency.
Furthermore, the incident response plan should include specific procedures for communication and escalation. This ensures that relevant stakeholders are informed promptly about the incident's status and severity. Having clear communication channels in place helps maintain transparency and collaboration during the resolution process.
Incident Detection and Analysis
Early detection of incidents is crucial for minimizing their impact. Implementing automated monitoring tools and alerts for critical system metrics is essential. These tools can detect anomalies and trigger alerts in real-time, enabling quick response and containment. Alert fatigue can occur if notifications are overly frequent or lack context. Effective incident detection and analysis require a combination of automated tools and manual review to ensure false positives are minimized.
Analyzing incident data is equally important. Understanding the root cause of incidents is key to preventing similar issues in the future. Thorough analysis of logs, metrics, and other relevant data can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of the incident. This process involves identifying patterns, correlations, and potential vulnerabilities that contributed to the incident.
Incident Management and Recovery
Effective incident management encompasses the steps taken to resolve the incident and restore normal operations. This includes containing the incident's spread, isolating affected components, and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence. A well-defined incident management process is critical to quickly restoring services and minimizing downtime. The process should include steps for communicating with stakeholders, documenting the incident, and performing post-mortem analysis.
Recovery strategies should be integral to the incident management process. This involves having backup and recovery plans in place to restore critical systems and data quickly. Implementing proactive disaster recovery measures can significantly reduce the impact of incidents and minimize data loss.