Zero Trust: A Fundamental Shift in Security
Zero Trust security is a paradigm shift from the traditional network-centric security model. Instead of assuming trust within a perimeter, Zero Trust operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. This means every user, device, and application, regardless of location or access method, must be authenticated and authorized before gaining access to resources. This granular level of control significantly enhances security posture, especially in the context of increasing remote work and evolving threat landscapes.
Strengthening Government Agency Security
Government agencies face unique security challenges due to sensitive data handling and complex regulatory environments. Zero Trust significantly improves security posture by reducing attack surface, preventing unauthorized access, and enhancing data integrity. This approach is crucial for safeguarding classified information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Implementing Zero Trust principles allows government agencies to proactively address emerging threats and maintain a robust security posture in today's dynamic environment. This approach is vital for protecting critical infrastructure and sensitive government data from various attack vectors.
Enhanced Access Control and Authentication
Zero Trust relies on rigorous access control and authentication mechanisms. This means verifying the identity of each user and device before granting access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords are crucial components of this approach, ensuring a higher level of security compared to traditional perimeter-based models. By incorporating these measures, government agencies significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Improved Visibility and Threat Detection
Zero Trust architectures provide enhanced visibility into network activity and user behavior. This visibility enables proactive threat detection and response. Advanced analytics and security information and event management (SIEM) tools can be integrated to identify suspicious activities and respond effectively to potential threats, thus maintaining a robust security posture.
The Importance of Segmentation and Isolation
Zero Trust emphasizes the segmentation and isolation of network resources. This compartmentalization restricts the impact of a breach, preventing lateral movement by attackers. By isolating sensitive data and resources, government agencies can minimize the potential damage from a security incident and maintain business continuity.
Addressing the Challenges of Implementation
Implementing Zero Trust in government agencies requires careful planning and execution. Transitioning from traditional security models to a Zero Trust framework involves significant organizational changes, including policy updates, infrastructure adjustments, and staff training. Careful consideration of these factors is essential to ensure a successful and secure implementation.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Zero Trust security is not a one-time implementation; it's an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring, threat intelligence gathering, and adaptation to evolving security threats are crucial to maintaining a strong security posture. Agencies must regularly review and update their Zero Trust policies and procedures to address emerging vulnerabilities and maintain optimal security. This proactive approach is essential for staying ahead of cyber threats.
Implementing Zero Trust in Government Agencies
Understanding the Zero Trust Model
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no implicit trust, either for users or devices, within an organization's network. Instead of relying on traditional network segmentation, it verifies every user and device attempting to access resources. This approach is crucial for government agencies, which often handle highly sensitive data and face significant threats from both internal and external actors. Zero Trust emphasizes continuous verification and authentication, ensuring that only authorized individuals and devices can access specific resources.
This fundamental shift in security thinking demands a reassessment of current security protocols. It moves beyond the traditional perimeter-based security approach, recognizing that threats can arise from anywhere within or outside the network. A Zero Trust environment establishes trust on a granular level, based on continuous authentication and authorization.
Benefits for Government Agencies
Implementing Zero Trust offers numerous advantages for government agencies. Enhanced security is paramount, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Improved compliance with regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, is another significant benefit, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected. Zero Trust also promotes agility and scalability, allowing agencies to adapt quickly to evolving security threats and changing operational needs.
The potential for cost savings through reduced incident response and recovery efforts is also a major consideration. By proactively preventing breaches and minimizing damage, agencies can significantly reduce financial burdens associated with security incidents.
Challenges in Implementation
While Zero Trust offers substantial benefits, there are inherent challenges in its implementation. Migrating from traditional security models to a Zero Trust architecture requires significant investment in new technologies, processes, and expertise. The complexity of managing identities and access across various systems and applications can be overwhelming, requiring careful planning and meticulous execution.
Integrating existing systems with a new Zero Trust framework can be complex and time-consuming. Training staff on new security protocols and procedures is also critical for successful implementation. Furthermore, maintaining ongoing vigilance and adapting to emerging threats is essential for sustaining a robust Zero Trust environment.
Key Technologies for Zero Trust
Several key technologies are crucial for implementing Zero Trust in government agencies. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential for verifying user identities. Network segmentation and micro-segmentation effectively isolate sensitive data and applications, reducing the impact of potential breaches.
Advanced threat detection and response systems are vital to identify and mitigate emerging threats. Identity and access management (IAM) solutions play a critical role in managing user permissions and access controls.
Data Protection and Compliance
Data protection and regulatory compliance are paramount considerations in a Zero Trust environment. Government agencies must ensure that their Zero Trust implementation aligns with relevant data protection regulations and industry standards. This includes ensuring that sensitive data is encrypted and protected at all stages of the data lifecycle.
Implementing robust logging and monitoring mechanisms is critical for tracking user activity and detecting suspicious behavior. Regular audits and assessments are essential to verify compliance and identify potential vulnerabilities.
Building a Culture of Security
Implementing Zero Trust is not just about technology; it's also about fostering a culture of security awareness and responsibility within the agency. Employees need to be educated and empowered to identify and report potential security threats. Regular security training and awareness campaigns are essential for promoting vigilance and proactive security measures.
Encouraging a strong security culture is a continuous process that demands ongoing communication, education, and engagement from all levels of the organization. This approach fosters a shared responsibility for security, ensuring that everyone understands their role in protecting sensitive information.
Protecting Sensitive Data with Data Loss Prevention (DLP)

Protecting Sensitive Data with Data Encryption
Data encryption is a crucial security measure for safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. By converting readable data into an unreadable format, encryption makes it significantly harder for malicious actors to intercept and decipher sensitive information, such as financial records, personal identifying information, and intellectual property. Effective encryption protocols are essential in today's digital landscape to protect against data breaches and maintain the confidentiality of sensitive data.
Modern encryption techniques rely on complex algorithms and strong cryptographic keys to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. These methods are constantly evolving to counter increasingly sophisticated hacking techniques. Implementing robust encryption protocols is critical for organizations to meet regulatory compliance standards and maintain the trust of their customers.
Implementing Strong Access Controls
Restricting access to sensitive data is paramount. Implementing strong access controls involves carefully defining user roles and permissions to ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data. This granular control limits the potential damage from unauthorized access or malicious insider threats.
Robust access control mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication and regular security audits, are essential to safeguard sensitive information. These measures help prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to data, regardless of their intent.
Utilizing Secure Storage Solutions
Secure storage solutions are vital for protecting sensitive data. Implementing secure storage systems, such as encrypted hard drives and cloud storage with robust security protocols, safeguards data from unauthorized access, even if the physical storage devices are compromised. These measures protect data even in the event of a physical security breach.
Employing encryption and access controls within storage systems is crucial. This approach ensures that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access throughout its lifecycle, from storage to retrieval.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential for identifying vulnerabilities in data protection systems. These assessments help to proactively identify weak points in security protocols and ensure that the systems are regularly updated to address potential threats. Regular testing enhances the overall security posture of the systems.
Penetration testing helps simulate real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of security measures. This process allows organizations to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities before they are exploited by malicious actors. This preventative approach is critical for maintaining a strong security posture.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee training and awareness programs are crucial for fostering a security-conscious culture. By educating employees about the importance of data protection, potential security threats, and best practices for handling sensitive information, organizations can reduce the risk of human error and malicious activity. Such training empowers employees to be proactive in protecting sensitive data.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are essential for preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization's control. These strategies involve implementing policies and technologies that monitor and control data exfiltration, whether through accidental or malicious means. These strategies are critical to preventing sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands, both inside and outside the organization.
Effective DLP solutions often combine technological controls with user awareness and training. This combined approach ensures that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access and accidental disclosure. A comprehensive DLP strategy is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
The Future of Government Security: A Zero Trust Approach
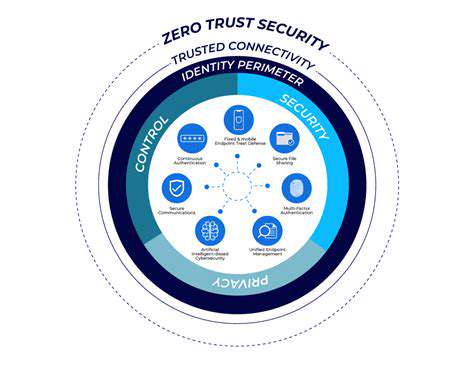
The Rise of AI in Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of cybersecurity, offering governments unprecedented capabilities in threat detection and prevention. AI algorithms can analyze massive datasets of network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify anomalies and potential threats with remarkable speed and accuracy. This proactive approach allows for early intervention and significantly reduces the window of vulnerability.
The potential for AI to automate many aspects of security operations is substantial. This automation frees up human analysts to focus on more complex and nuanced threats, ultimately improving response times and the overall effectiveness of security measures. AI-powered systems can also adapt to evolving threats in real-time, learning and improving their detection capabilities over time.
Enhanced Cyber-Resilience Strategies
Governments are increasingly focusing on building cyber-resilience as a core tenet of national security. This involves implementing a layered approach to security, incorporating robust data protection measures, robust incident response plans, and comprehensive training for personnel. This proactive approach ensures that government systems can withstand and recover from cyberattacks more effectively.
A key component of this strategy is establishing clear communication channels and protocols for responding to cyber incidents. This allows for a coordinated and efficient response, minimizing damage and maximizing the likelihood of a swift recovery. Effective cyber-resilience also necessitates a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation to emerging threats.
The Importance of Data Privacy and Security
With the increasing reliance on digital systems, the protection of sensitive government data has become paramount. Robust data encryption, access controls, and security protocols are crucial to safeguarding information from unauthorized access and malicious use. Maintaining public trust in government institutions hinges on demonstrable commitment to data privacy and security.
Protecting sensitive information not only safeguards national security interests but also upholds the fundamental rights of citizens. Protecting citizen data from breaches and misuse is a critical aspect of effective governance in the digital age.
Strengthening International Cooperation
Cyber threats transcend national borders, requiring international cooperation and information sharing to effectively combat them. Governments must collaborate to develop and implement global standards for cybersecurity, share intelligence about emerging threats, and support each other in responding to cyberattacks. This collective effort is essential in mitigating the risks posed by malicious actors operating across multiple jurisdictions.
International cooperation is vital for achieving a truly secure digital environment for all nations. Sharing best practices and developing joint strategies are critical to bolstering collective resilience against evolving cyber threats.
The Role of Human Factors in Security
While technology plays a crucial role in enhancing government security, the human element remains paramount. Investing in robust cybersecurity training programs for government employees, fostering a culture of awareness and vigilance, and promoting ethical conduct are essential to mitigate human error and ensure the effectiveness of security measures. A strong security posture requires a comprehensive approach that considers the role of human factors in the face of sophisticated cyberattacks.
Human error is a significant vulnerability, and this can be mitigated with thorough training and awareness programs. A culture of security awareness must be cultivated across all levels of government to ensure that individuals are equipped to recognize and report potential threats.