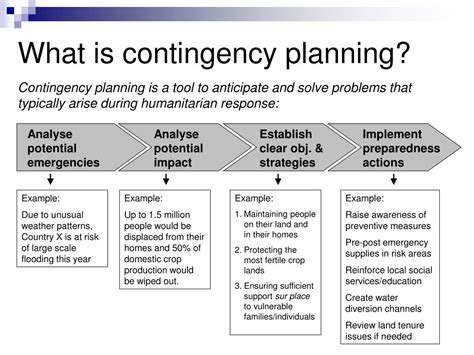
Key Principles of Zero Trust
Several core tenets define successful Zero Trust implementations. Network micro-segmentation proves indispensable, creating isolated zones that prevent threat lateral movement. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) serves as the gatekeeper, adding critical verification steps beyond simple credential checks.
Continuous behavior monitoring forms the nervous system of Zero Trust, enabling rapid detection of anomalous activities. Perhaps most crucially, the principle of least privilege ensures users and devices receive only the bare minimum access required, dramatically reducing the blast radius of potential compromises.
Zero Trust vs. Traditional Security Models
Legacy security approaches operated on outdated assumptions, treating internal networks as safe havens. This perimeter-centric thinking crumbles against today's sophisticated threats and complex organizational structures. Zero Trust introduces a dynamic security paradigm where verification happens continuously, regardless of network location.
The paradigm shift from trust but verify to never trust, always verify represents the fundamental evolution in cybersecurity thinking. This proactive stance proves particularly effective against insider threats, external attackers, and the ever-changing landscape of digital vulnerabilities.

How Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge Interrelate

Zero Trust: A Foundation for Secure Access
At its core, Zero Trust eliminates implicit trust assumptions across an organization's digital ecosystem. The requirement for continuous authentication creates a dynamic security barrier that adapts to each access request. This approach proves especially valuable in today's distributed work environments where traditional network boundaries have dissolved.
Adopting Zero Trust demands a cultural shift in security thinking. Organizations must transition from location-based trust models to identity-centric verification frameworks, enabling precise control over resource access at the most granular levels.
Zero Knowledge: Proof Without Disclosure
Zero-knowledge proofs represent a cryptographic breakthrough where one party can validate information without exposing the underlying data. Through carefully constructed mathematical interactions, the prover demonstrates knowledge while maintaining complete confidentiality.
Consider proving you know a combination without revealing the numbers - this encapsulates the power of zero-knowledge proofs. The technique shines in scenarios requiring verification of sensitive information where disclosure would create unacceptable risk.
The Synergy of Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge
When combined, these frameworks create a security powerhouse. Zero Trust establishes the access control framework while zero-knowledge proofs enable secure verification methods. This combination delivers both robust authorization and unparalleled privacy protection.
The integration allows organizations to implement dynamic, context-aware security policies without compromising sensitive data. This dual approach addresses modern security challenges where both access control and data privacy are paramount.
Practical Applications of Zero Knowledge
Real-world implementations span numerous critical areas. In electoral systems, zero-knowledge proofs can validate votes while preserving ballot secrecy, addressing longstanding security and privacy concerns.
Digital identity verification represents another promising application, allowing credential confirmation without exposing personal details. The technology also enables secure authentication protocols and verifiable digital signatures without key exposure.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
Transitioning to Zero Trust presents notable obstacles, particularly in legacy environments. The complexity of managing thousands of identities and devices across hybrid infrastructures can overwhelm unprepared organizations.
Successful deployment requires careful phasing, with particular attention to minimizing operational disruption. Organizations must conduct thorough infrastructure assessments before implementing sweeping changes to authentication and access protocols.
Security Considerations in Zero Trust
Implementation demands rigorous security evaluation at every phase. Comprehensive penetration testing and continuous security audits become non-negotiable requirements in Zero Trust environments.
Maintenance of supporting infrastructure proves equally critical. Regular updates, prompt patching, and real-time monitoring form the bedrock of ongoing Zero Trust security.
The Future of Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge
Emerging advancements promise to expand these technologies' capabilities. Innovations in cryptographic techniques and identity verification will drive the next generation of enterprise security solutions.
As digital threats grow more sophisticated, the integration of Zero Trust and zero-knowledge methodologies will likely become standard practice, creating more resilient and privacy-conscious digital ecosystems.
Beyond the Basics: Practical Applications
Implementing Zero Trust in Cloud Environments
Cloud adoption necessitates rethinking security fundamentals. Zero Trust replaces location-based assumptions with continuous verification, requiring robust authentication mechanisms and granular access controls. The dynamic nature of cloud resources demands automated security policy management to prevent configuration drift.
Micro-segmentation proves particularly valuable in cloud architectures, creating security compartments that contain potential breaches. Cloud-native security tools significantly simplify the implementation and maintenance of Zero Trust policies across distributed environments.
Zero Knowledge Proofs and their Role in Zero Trust
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) enhance Zero Trust by enabling secure verification without data exposure. This cryptographic innovation allows credential validation while maintaining absolute confidentiality, representing a paradigm shift in secure authentication.
The applications extend to secure computation scenarios where data integrity verification occurs without revealing source information. ZKPs enable trust validation on a need-to-know basis, perfectly complementing Zero Trust's granular access philosophy.
Implementation advantages include minimal infrastructure disruption and strong resistance to tampering. The cryptographic foundations ensure verification processes remain secure even against sophisticated attacks, making ZKPs a powerful addition to modern security architectures.