Implementing Zero Trust in Your Cloud Environment
Understanding the Zero Trust Model
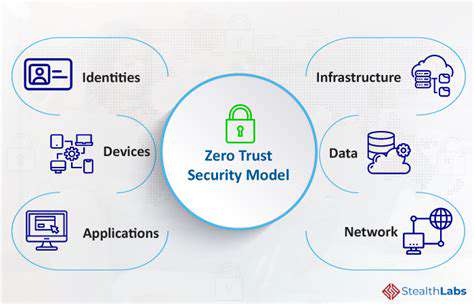
The Zero Trust model fundamentally shifts security thinking from outdated perimeter-based defenses to a modern approach where no user or device is trusted by default, whether inside or outside the network. Rather than depending on traditional firewalls, this strategy employs micro-segmentation and precise access controls to scrutinize every interaction within cloud environments.
This methodology offers a significant advantage by minimizing potential attack vectors. When a breach occurs in one segment, the damage remains contained due to strict compartmentalization. Traditional security frameworks often fail here by treating entire networks as trusted zones.
Implementing Zero Trust Access Controls
Transitioning to Zero Trust requires transforming access management systems. Organizations must implement identity-centric security measures that validate both users and devices before granting application or data access. Multi-factor authentication becomes mandatory for all access attempts, irrespective of user location.
Resource segmentation plays an equally vital role. By establishing detailed access policies, companies ensure that individuals and devices only reach necessary data and functions. This strategic limitation prevents attackers from moving laterally through systems after initial penetration.
Building a Secure Cloud Infrastructure with Zero Trust
Effective Zero Trust implementation demands comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. These platforms aggregate and analyze security logs from multiple sources, enabling real-time identification and response to threats. Continuous behavior monitoring proves essential for spotting unusual patterns that may indicate compromise attempts.
Enhancing Security Posture Through Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Sustaining a Zero Trust environment necessitates ongoing vigilance. Regular security evaluations and penetration tests help maintain defenses against evolving threats. Detailed logging of all user actions, system events, and access requests enables rapid detection and resolution of security incidents.
Proactive vulnerability management remains critical in this framework. Timely patching and thorough documentation of these processes not only strengthen security but also support compliance requirements. Comprehensive audit trails serve as valuable evidence during security reviews and regulatory examinations.
Key Technologies for Zero Trust Cloud Security
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a cornerstone technology in modern security architectures. This approach isolates network resources, permitting access exclusively to verified users and devices. ZTNA's rigorous authentication framework dramatically shrinks the attack surface by preventing unauthorized contact with sensitive systems.
Effective ZTNA deployment typically incorporates multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls. These measures work synergistically to confirm user identities while restricting access to necessary resources only. Such implementation significantly enhances organizational security by minimizing potential breach points.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Comprehensive Identity and Access Management systems form the backbone of successful Zero Trust implementations. These centralized platforms manage user identities, authentication processes, and access privileges with precision. Granular control over resource access ensures that only properly authenticated entities reach sensitive information.
Sophisticated IAM solutions employ advanced authentication techniques to prevent unauthorized access attempts. When properly configured, these systems create security environments where verification precedes every interaction with network resources.
Software Defined Perimeter (SDP)
Software-Defined Perimeter technology revolutionizes network security by establishing dynamic perimeters based on user context rather than static network boundaries. This adaptive approach grants access to specific resources only when needed, representing a significant advancement over traditional segmentation methods.
SDP's real-time evaluation of user credentials and context enables continuous security adjustments. This dynamic capability makes SDP particularly valuable for organizations implementing Zero Trust principles, as it provides responsive protection against evolving threats.
Beyond the Basics: Moving Towards a Secure Cloud Future
Understanding the Core Concepts
Advanced security implementation requires thorough comprehension of foundational principles. Mastering these fundamentals enables professionals to address complex challenges and develop innovative security solutions that stand the test of time.
Exploring Advanced Techniques
Building upon core knowledge, security professionals must investigate sophisticated methodologies. These advanced approaches often distinguish between basic competence and expert-level security proficiency, particularly in complex cloud environments.
Analyzing Real-World Applications
Practical case studies demonstrate how theoretical concepts translate into effective security measures. Examining these implementations provides invaluable insights into real-world security challenges and successful mitigation strategies.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Effective security professionals cultivate analytical abilities to objectively assess threats and solutions. These critical evaluation skills prove essential when navigating complex security scenarios and making informed protection decisions.
Improving Problem-Solving Abilities
Advanced security practice demands refined troubleshooting capabilities. Security teams must identify vulnerabilities, evaluate potential remedies, and implement effective countermeasures based on thorough analysis of each unique situation.
Implementing Effective Strategies
Successful security initiatives require carefully planned execution. Customized security approaches must undergo continuous evaluation and adjustment to maintain effectiveness against evolving cyber threats.
Embracing Continuous Learning
The cybersecurity landscape evolves constantly, necessitating ongoing education. Commitment to professional development ensures security teams remain prepared to address emerging threats and implement cutting-edge protective measures.