Understanding the Limitations of Perimeter Security
For decades, organizations have relied on perimeter-based security models that treat network boundaries as impenetrable fortresses. This outdated approach creates dangerous blind spots in today's interconnected digital ecosystem where threats can originate from anywhere. The reality is that sophisticated attackers routinely bypass traditional defenses, targeting vulnerable endpoints both inside and outside organizational networks.
The perimeter-centric model suffers from three critical flaws:
- It assumes internal networks are inherently safe
- It fails to account for modern mobile workforces
- It provides no protection against compromised credentials
Recent studies by the Ponemon Institute reveal that 68% of breaches involve lateral movement within networks, proving perimeter defenses alone are insufficient against determined attackers.
Embracing the Zero Trust Model
Zero Trust represents a fundamental rethinking of cybersecurity that aligns with today's threat landscape. Rather than assuming trust based on network location, this model requires continuous verification of all access attempts. Every user, device, and application must prove their legitimacy before accessing any resources.
Key principles of Zero Trust include:
- Explicit verification of all entities
- Least privilege access controls
- Microsegmentation of network resources
- Continuous monitoring for anomalies
Implementing Microsegmentation
Network segmentation creates virtual barriers that contain potential breaches. By dividing networks into isolated zones, organizations can:
- Limit attacker movement post-compromise
- Protect sensitive data stores
- Reduce overall attack surface
Gartner predicts that by 2026, 60% of enterprises will phase out VPNs in favor of Zero Trust Network Access solutions that enable granular segmentation.
Establishing Strong Authentication and Authorization
Modern authentication frameworks must go beyond simple passwords. Effective implementations include:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users
- Behavioral biometrics for continuous verification
- Context-aware access policies
Microsoft reports that MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks, making it essential for Zero Trust architectures.
Enhancing Threat Detection and Response
Advanced monitoring solutions provide:
- Real-time analysis of user behavior
- Automated response to suspicious activity
- Integration with threat intelligence feeds
According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report, organizations with AI-driven security tools detect breaches 28% faster than those relying on manual processes.
Prioritizing User Education and Awareness
Effective security training programs should:
- Simulate real-world phishing attempts
- Teach secure remote work practices
- Encourage reporting of suspicious activity
Proofpoint's 2023 Human Factor report found that training reduces click-through rates on phishing emails by 50%.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Security maturity requires:
- Quarterly penetration testing
- Regular policy reviews
- Benchmarking against industry standards
Organizations that conduct annual security assessments reduce breach costs by 30% according to Forrester Research.
Zero Trust Principles: A Foundation for Robust Security
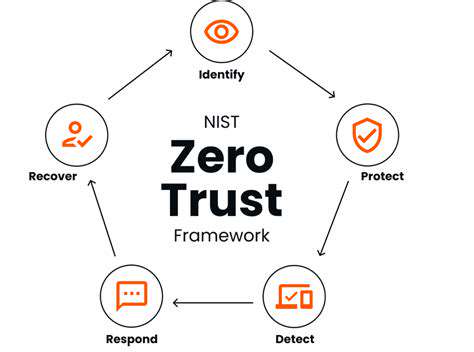
Zero Trust Fundamentals
The core philosophy of Zero Trust challenges traditional security assumptions by:
- Treating all networks as hostile
- Requiring verification for every access attempt
- Granting minimal necessary permissions
Google's BeyondCorp implementation demonstrated 60% fewer security incidents after adopting Zero Trust principles.
Identifying and Verifying Users
Modern identity verification combines:
- Biometric authentication
- Device health checks
- Behavioral analytics
Duo Security reports that 78% of enterprises now use MFA as part of their identity verification strategies.
Micro-segmentation and Network Segmentation
Effective segmentation strategies include:
- Application-level isolation
- Data-centric protection
- Dynamic policy enforcement
Cisco's 2023 Security Outcomes Study found that segmentation reduces breach impact by 45%.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Advanced monitoring solutions provide:
- Real-time anomaly detection
- Automated threat hunting
- Integrated response workflows
Organizations with 24/7 monitoring detect breaches 3x faster than those without continuous surveillance.
Implementing Zero Trust: A Multifaceted Approach
Understanding the Zero Trust Model
Successful implementations require:
- Executive-level sponsorship
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Phased rollout strategy
PwC's Digital Trust Insights survey found that 73% of leaders consider Zero Trust essential for digital transformation.
Implementing Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA solutions offer:
- Application-specific access
- Encrypted connections
- Context-aware policies
Gartner predicts ZTNA will replace 60% of VPNs by 2025 due to superior security and user experience.
Building a Zero Trust Security Posture
Mature implementations incorporate:
- Automated policy enforcement
- Unified visibility tools
- Integrated threat intelligence
Forrester research shows that comprehensive Zero Trust implementations reduce breach costs by 43%.
Measuring and Improving Zero Trust Effectiveness: Continuous Monitoring

Key Metrics for Measuring Zero Trust
Critical success indicators include:
- Mean time to detect (MTTD)
- Mean time to respond (MTTR)
- Policy violation rates
Organizations with mature Zero Trust programs show 50% faster response times to security incidents.
Improving Zero Trust Security Posture
Continuous enhancement requires:
- Regular penetration testing
- Threat modeling exercises
- Security control audits
NIST recommends quarterly security assessments to maintain effective Zero Trust implementations.