Defining Zero Trust in a Hybrid Cloud Landscape
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
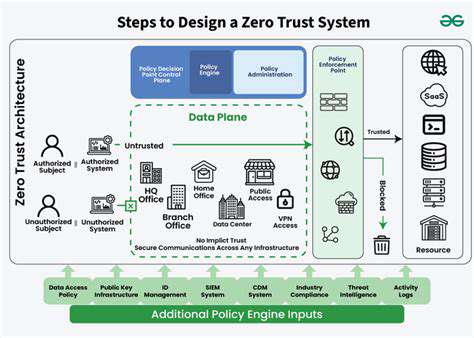
Modern security frameworks increasingly adopt the Zero Trust model, which fundamentally rejects the notion of implicit trust. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security, Zero Trust requires rigorous verification for every access attempt, regardless of origin. This paradigm proves particularly valuable in hybrid cloud deployments where resources span multiple locations and network boundaries.
The principle of least privilege access forms the bedrock of effective Zero Trust implementation. By strictly limiting user permissions to only essential resources, organizations dramatically reduce potential attack vectors and minimize blast radius during security incidents.
Implementing Zero Trust Across Hybrid Cloud Environments
Successful Zero Trust deployment in hybrid clouds demands a comprehensive strategy that accommodates diverse infrastructure components. Identity and access management (IAM) systems serve as the cornerstone, providing unified visibility across all users and devices irrespective of their physical or cloud location. Network segmentation emerges as another critical component, creating logical barriers that contain potential breaches.
Data governance receives heightened importance under Zero Trust, requiring detailed tracking of information access patterns. This granular visibility not only strengthens security but also simplifies compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Role of Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Zero Trust
IAM solutions occupy center stage in Zero Trust architectures by enabling real-time authentication and authorization decisions. These systems verify the legitimacy of every access request before granting permissions, eliminating reliance on network location as a trust indicator.
Cross-platform IAM integration presents both a challenge and necessity for hybrid cloud environments. Consistent identity management across on-premises and cloud resources prevents security gaps while simplifying administrative overhead.
Security Segmentation and Micro-segmentation in a Hybrid Cloud
Micro-segmentation transforms network security by creating fine-grained security zones within hybrid cloud environments. This approach isolates workloads and applications, preventing lateral movement by potential attackers. When properly implemented, micro-segmentation significantly enhances an organization's defensive posture against sophisticated threats.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection in Zero Trust
Effective Zero Trust implementations require persistent vigilance through advanced monitoring solutions. Security teams leverage SIEM platforms, intrusion detection systems, and real-time threat feeds to identify and respond to anomalous activities. This ongoing surveillance ensures security controls remain effective against evolving threats.
The Importance of Context-Aware Access Control
Dynamic access policies represent a key innovation in Zero Trust security. By evaluating multiple contextual factors - including user location, device security posture, and behavioral patterns - systems can make nuanced access decisions that balance security with usability.
Overcoming Challenges and Best Practices for Hybrid Cloud Zero Trust Implementation
Transitioning to Zero Trust in hybrid environments requires careful planning and execution. Organizations benefit from phased rollouts that allow for testing and adjustment. Cross-functional collaboration between security and operations teams proves essential for successful implementation.
Comprehensive documentation and user education form the foundation for sustainable Zero Trust adoption. Clear policies and regular training ensure all stakeholders understand their roles in maintaining security. Tailoring controls to specific application requirements yields more effective protection than one-size-fits-all approaches.
Enhancing Security Posture with Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection

Strengthening Authentication Mechanisms
Modern authentication frameworks increasingly incorporate multiple verification factors to combat credential-based attacks. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has transitioned from optional enhancement to security necessity across all organizational levels. Password hygiene remains critical despite advanced authentication methods, with regular rotation and complexity requirements forming basic safeguards.
Improving Network Security
Defense-in-depth strategies dominate contemporary network security approaches. Layered protections combining firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and regular vulnerability assessments create resilient infrastructures. Segmentation strategies complement these controls by limiting potential breach impact through logical isolation of network segments.
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions have evolved to address modern data protection challenges across hybrid environments. These systems monitor data flows while enforcing policies that prevent unauthorized transfers. Effective DLP implementation requires careful policy definition aligned with business needs and regulatory requirements.
Enhancing Endpoint Security
The expanding attack surface created by mobile devices demands robust endpoint protection strategies. Modern endpoint security solutions combine traditional antivirus capabilities with advanced detection and response features. Consistent endpoint policy enforcement across all device types remains paramount for maintaining security posture.
Developing Security Awareness Training
Human factors continue to represent significant security vulnerabilities. Ongoing education programs that address emerging threats like sophisticated phishing campaigns help transform employees into security assets rather than liabilities. Training effectiveness improves when incorporating real-world examples and interactive elements.
Implementing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM platforms have become indispensable for security operations, providing centralized visibility across diverse systems. Advanced correlation capabilities enable detection of complex attack patterns that might evade simpler monitoring solutions. Properly tuned SIEM implementations significantly reduce mean time to detection and response for security incidents.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Proactive security validation through audits and testing identifies vulnerabilities before exploitation occurs. Comprehensive assessment programs incorporate automated scanning, manual penetration testing, and configuration reviews. Regular evaluation cycles ensure security controls remain effective against evolving threats and changing business requirements.
The Role of Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) in Hybrid Cloud Zero Trust
Understanding Hybrid Cloud Environments
Hybrid cloud architectures combine operational flexibility with security challenges. The distributed nature of these environments complicates consistent security policy enforcement across different platforms. Successful implementations require careful planning to maintain visibility and control while leveraging cloud benefits.
The Need for Zero Trust in Hybrid Clouds
Zero Trust principles address hybrid cloud security challenges by eliminating trust assumptions. This approach proves particularly valuable when resources span multiple environments with varying security postures. Implementation requires detailed asset inventory and comprehensive access control mechanisms that function consistently across all platforms.
CSPM as a Critical Component of Hybrid Cloud Zero Trust
CSPM solutions bridge the visibility gap in complex hybrid environments. These tools continuously assess configuration compliance and identify security deviations. Automated remediation capabilities help maintain consistent security postures across dynamic infrastructures.
Enhancing Security and Compliance with CSPM
CSPM platforms streamline security operations through policy automation and centralized monitoring. The resulting efficiency gains allow security teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual configuration reviews. Detailed compliance reporting simplifies audit processes while demonstrating adherence to regulatory requirements.