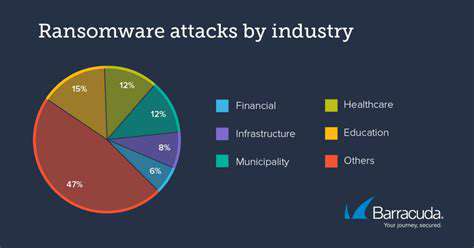
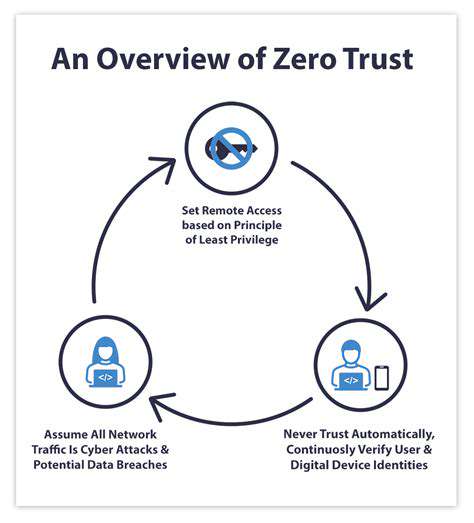
The interconnected nature of these systems creates a domino effect - a single compromised device can jeopardize an entire network. This complexity transforms what should be simple security measures into intricate challenges requiring specialized knowledge. The danger isn't limited to individual device weaknesses but extends to how these components interact and share data across the agricultural ecosystem. One security breach could ripple through multiple systems, potentially crippling an entire farming operation.
Malicious Actors and Motivations
Cybercriminals targeting agricultural operations have evolved beyond simple financial motives. Today's threats include attempts to disrupt food production, industrial espionage, and theft of proprietary agricultural data. The consequences of successful attacks extend far beyond individual farms, potentially causing regional food shortages and economic instability. As farming systems become more interconnected, the risk of deliberate sabotage grows exponentially.
The financial rewards for compromising agricultural systems have never been greater. By disrupting supply chains or stealing sensitive data, attackers can inflict massive financial damage to farming operations. Potential impacts include destroyed crops, broken distribution networks, and extortion opportunities. Some attackers may even have political motivations or simply seek to create chaos in agricultural markets.
Data Breaches and Information Security
Precision agriculture generates enormous quantities of valuable data - sensor readings, weather patterns, crop performance metrics, and more. This information goldmine attracts malicious actors looking to steal trade secrets or disrupt operations. A single breach could expose planting schedules, yield projections, or even the exact locations of valuable equipment. The fallout from such incidents includes financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal consequences. Implementing ironclad data protection measures isn't optional - it's a business necessity for modern farms.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Smart farming systems typically involve multiple vendors and suppliers, each potentially introducing security risks. The agricultural supply chain's complexity makes it difficult to monitor every component's security status, creating opportunities for attackers to slip compromised hardware or software into the system. Farmers need better visibility and verification processes throughout their supply chains to prevent these hidden threats. Regular third-party security audits should become standard practice for all agricultural technology providers.
The Need for Enhanced Security Measures
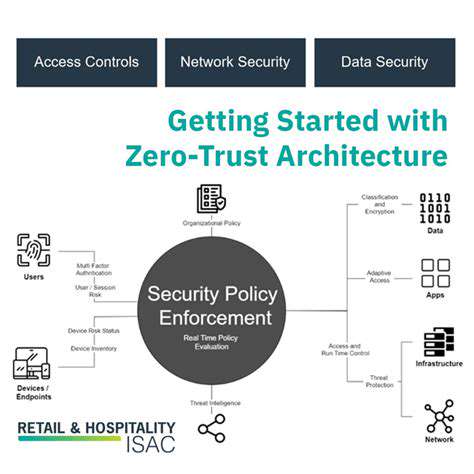
Protecting modern agricultural operations requires a comprehensive security strategy. This includes implementing military-grade encryption, strict access controls, and regular system audits. Continuous network monitoring and advanced threat detection systems help identify potential breaches in real-time. Perhaps most importantly, farmers and agricultural workers need ongoing security education to recognize and respond to emerging threats. Only through proactive, multilayered security can the agricultural sector hope to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Protecting Data Integrity and Confidentiality: A Multi-Layered Approach
Ensuring Data Accuracy in Agricultural Practices
Reliable data forms the foundation of modern agricultural decision-making. From yield predictions to resource allocation, accurate information drives efficiency and profitability. Farmers must implement rigorous data collection protocols, use high-quality sensors, and establish strict quality control measures. In agriculture, bad data can be as destructive as bad weather - both can ruin an entire season's work.
Protecting Sensitive Information in the Supply Chain
The agricultural supply chain's complexity creates numerous opportunities for data leaks. Protecting proprietary information - from crop yields to customer lists - requires robust encryption, secure data storage, and strict access controls. Every participant in the supply chain must prioritize data security to prevent breaches that could compromise entire agricultural networks.
Implementing Robust Data Security Measures
Basic security practices form the first line of defense against data breaches. Strong, unique passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security training for all employees significantly reduce vulnerability. The human element remains the weakest link in most security systems, making comprehensive staff training essential for protecting sensitive agricultural data.
Utilizing Advanced Encryption Technologies
Modern encryption methods provide powerful protection for agricultural data. End-to-end encryption for communications and strong hashing algorithms for stored data create formidable barriers against unauthorized access. These technologies not only secure data but also build confidence among farmers, suppliers, and customers throughout the agricultural ecosystem.
Importance of Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Comprehensive backup systems and disaster recovery plans are insurance policies for agricultural data. Whether facing equipment failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks, the ability to quickly restore critical data can mean the difference between business continuity and catastrophic loss. Automated off-site backups should be standard practice for all farming operations.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Regular security training transforms employees from potential vulnerabilities into active defenders. Effective programs cover password security, phishing recognition, and proper data handling procedures. A well-trained workforce provides the most cost-effective security measure available to agricultural businesses.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Adhering to regulations like GDPR isn't just about avoiding fines - it's about building trust. Proper data handling procedures, clear consent protocols, and transparent data practices demonstrate respect for privacy while protecting business interests. In today's data-driven world, regulatory compliance is a competitive advantage for agricultural operations.

Blockchain technology offers revolutionary security benefits that could transform agricultural data protection. Its decentralized verification system creates an immutable record that's extremely resistant to tampering. Blockchain's distributed nature eliminates single points of failure while maintaining transparent access for authorized users.
Addressing the Human Element: Training and Awareness Programs

Training and Development: Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Effective training programs should evolve beyond basic skill development to foster continuous learning cultures. Organizations that invest in employee development reap benefits in engagement, retention, and performance. Tailored training programs that address specific role requirements ensure employees gain immediately applicable skills.
Successful training strategies employ diverse methods - from hands-on workshops to digital learning platforms - accommodating various learning preferences. By creating engaging, supportive learning environments, businesses empower employees to drive their own professional growth.
Building Strong Communication Channels
Clear communication forms the backbone of successful organizations. Regular team meetings, transparent information sharing, and accessible feedback systems create cohesive work environments. When employees feel heard and informed, they become more engaged and productive.
True communication requires active listening and empathy. Encouraging open dialogue where all voices are valued builds trust and strengthens team dynamics. These soft skills often prove as valuable as technical abilities in creating high-performing teams.
Cultivating a Positive and Supportive Work Environment
Positive workplaces directly impact both employee well-being and business outcomes. Fostering mutual respect and trust among colleagues creates foundations for success. Team-building activities and recognition programs reinforce positive behaviors while strengthening workplace relationships.
Addressing and Resolving Conflicts Proactively
Workplace conflicts are inevitable but manageable with proper protocols. Clear resolution processes and conflict management training help minimize disruptions. Neutral mediation often reveals solutions that satisfy all parties while preserving working relationships.
Promoting Employee Well-being and Work-Life Balance
Employee wellness programs and flexible work arrangements demonstrate organizational commitment to staff welfare. Supporting work-life integration leads to more focused, productive employees who feel valued beyond their job performance.