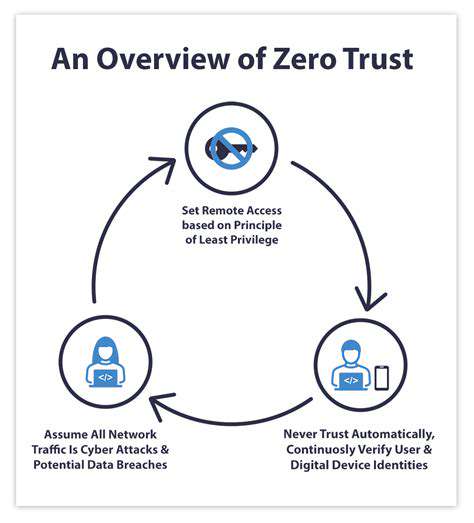
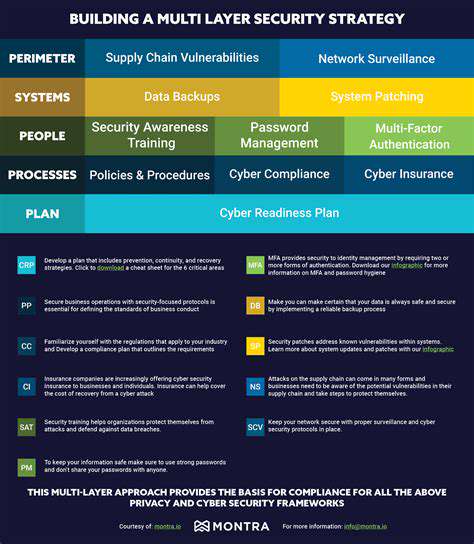
The Early Days of Remote Access
While many assume remote access is a modern innovation, its origins trace back to the infancy of computing. Early mainframe systems relied on remote terminals, demonstrating the potential for distributed computing long before the internet era. These primitive systems, though limited in capability, established foundational concepts that would later evolve into today's advanced remote solutions.
Network infrastructure advancements proved instrumental in transforming remote access capabilities. As connectivity improved, geographical barriers diminished, enabling more sophisticated remote interactions. Early adopters faced technical hurdles, but their pioneering efforts established protocols that remain relevant in contemporary systems.
The Rise of VPNs and Secure Connections
Virtual Private Networks revolutionized secure remote access by establishing encrypted tunnels between users and private networks. This cryptographic protection became essential for safeguarding sensitive data traversing public networks. The growing value of digital assets necessitated increasingly robust security frameworks for remote operations.
The Cloud Computing Era and Scalability
Cloud technology dramatically reshaped remote access paradigms by introducing elastic, on-demand resource allocation. This shift eliminated traditional infrastructure constraints, enabling universal accessibility with minimal setup requirements. The cloud's flexibility catalyzed widespread adoption across diverse sectors, democratizing access to enterprise-grade solutions.
The Emergence of RaaS (Remote Access as a Service)
As IT ecosystems grew increasingly complex, demand surged for streamlined remote access solutions. RaaS emerged as a cloud-hosted service providing managed, secure connectivity to applications and data. By abstracting infrastructure management complexities, RaaS enables organizations to concentrate on strategic priorities rather than technical maintenance.
Future Trends and Innovations in RaaS
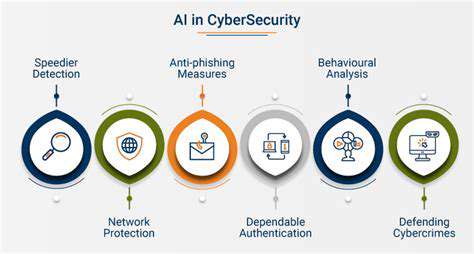
RaaS evolution continues unabated, with artificial intelligence and machine learning driving transformative improvements. These technologies promise enhanced security protocols, refined user experiences, and unprecedented scalability. Emerging capabilities like predictive maintenance and automated threat mitigation will likely become RaaS industry standards. Such advancements will empower organizations to preemptively address vulnerabilities while optimizing operational efficiency.
The RaaS Business Model: A Detailed Look at the Components

Understanding the RaaS Model
The Revenue as a Service framework represents a paradigm shift from traditional licensing to subscription-based engagement. This model prioritizes sustained customer relationships over transactional sales, creating mutually beneficial ecosystems. Mastering the RaaS approach is vital for businesses pursuing sustainable revenue growth and enduring partnerships.
By converting single transactions into continuous value streams, RaaS fosters ongoing collaboration between providers and clients. This perpetual engagement cycle incentivizes both parties to maximize long-term success.
Key Advantages of RaaS
RaaS delivers financial predictability through recurring revenue, enabling more accurate forecasting and strategic planning. This stable income foundation significantly enhances investment appeal and funding opportunities.
The model cultivates deeper customer relationships through continuous service interactions. These ongoing engagements generate valuable insights for service refinement and product development.
Customer Benefits in a RaaS Environment
Clients gain access to cutting-edge solutions without substantial capital expenditures, dramatically lowering adoption barriers. Comprehensive support packages ensure optimal system performance while reducing operational burdens.
Implementation Challenges of a RaaS Model
Transitioning to RaaS requires robust subscription management systems and meticulous financial planning. Strategic implementation is critical to minimize attrition risks and ensure sustainable profitability.
Strategies for Success with RaaS
Successful RaaS adoption demands precise market alignment and compelling value articulation. Clearly communicating ongoing benefits differentiates RaaS offerings in competitive landscapes.
Optimal pricing structures must balance affordability with profitability, while marketing strategies should emphasize long-term value propositions over short-term gains.
Scalability and Future Considerations of RaaS
The model's inherent scalability supports exponential growth through customer base expansion. Continuous innovation and service enhancement will determine long-term viability in evolving markets.
The Rise of Targeted Ransomware: Tailored Attacks for Maximum Impact
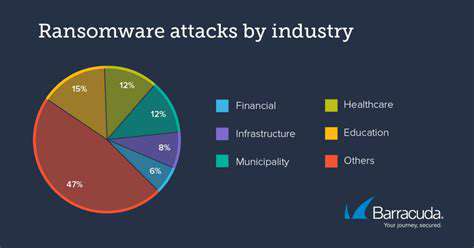
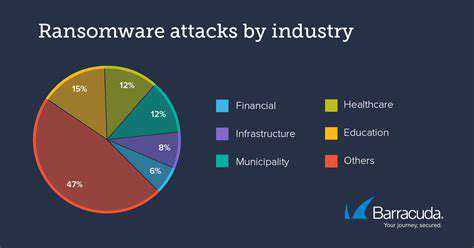
Understanding the Tactics of Targeted Ransomware Attacks
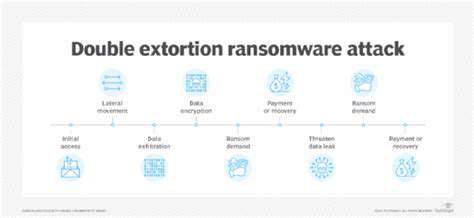
Modern ransomware campaigns have evolved into precision operations, leveraging extensive reconnaissance to identify and exploit specific vulnerabilities. This surgical approach amplifies potential damage, as attackers can customize payloads to maximize disruption.
Attackers conduct comprehensive target analysis, studying network architectures and user behaviors to identify infiltration opportunities. Such meticulous preparation often circumvents conventional security controls designed for generic threats.
The Motivations Behind Targeted Ransomware
While financial incentives remain prevalent, contemporary attacks increasingly pursue strategic objectives including industrial espionage and critical infrastructure disruption. This diversification necessitates comprehensive defensive strategies beyond traditional safeguards.
Vulnerabilities Exploited by Attackers
Attackers frequently leverage unpatched software vulnerabilities and configuration weaknesses to gain footholds. Credential mismanagement represents a particularly pervasive vulnerability, often exacerbated by inadequate security training. These systemic weaknesses provide low-effort, high-impact attack vectors.
The Impact of Targeted Ransomware on Victims
Successful attacks can paralyze operations, incurring substantial recovery costs and lasting reputational harm. The cascading effects often extend beyond immediate financial losses to include regulatory penalties and customer attrition.
Strategies for Mitigating Targeted Ransomware Attacks
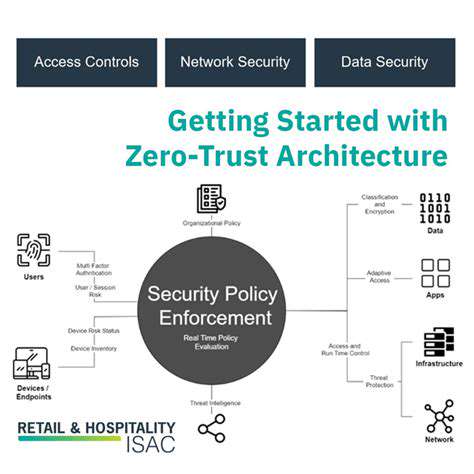
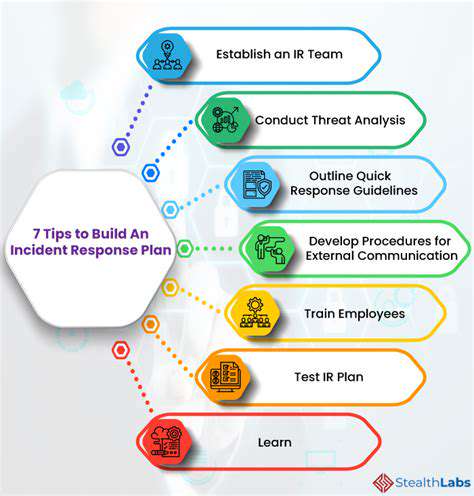
Comprehensive defense requires layered security controls, including privileged access management and continuous monitoring. Proactive threat hunting and incident response planning significantly reduce attack surfaces. Prepared organizations can dramatically mitigate attack impacts through rapid containment protocols.
The Role of Prevention and Detection in Response
Effective ransomware defense combines advanced threat prevention with real-time detection capabilities. Regular security assessments and penetration testing identify potential weaknesses before exploitation occurs.