The Zero Trust model represents a dramatic departure from conventional network security practices. Rather than assuming safety behind a perimeter, it demands rigorous verification for every access attempt, whether from inside or outside the network. This methodology proves essential in our current digital environment where threats emerge from multiple vectors - including employees, external attackers, and system vulnerabilities. Establishing Zero Trust involves far more than firewall configurations; it requires a complete overhaul of authentication protocols, authorization processes, and constant surveillance of network operations.
This transformation stems from the shortcomings of traditional security measures. Perimeter-based defenses struggle to accommodate modern work arrangements involving remote employees, cloud platforms, and sophisticated attack methods. The Zero Trust framework offers a flexible solution that secures all access points equally, eliminating the outdated distinction between trusted internal networks and untrusted external ones.
Segmentation as a Cornerstone of Zero Trust
Effective network segmentation forms the backbone of any successful Zero Trust implementation. By compartmentalizing networks into discrete zones, companies can contain potential breaches to limited areas. Should an intruder infiltrate one segment, their capacity to spread through other network sections becomes severely restricted. This focused approach enables more precise security controls and swifter reactions to incidents, dramatically reducing potential harm from security events.
Well-executed segmentation also facilitates strict adherence to the principle of least privilege access. Under this system, individuals and devices obtain access strictly to resources necessary for their immediate functions. This practice shrinks potential attack vectors while reinforcing overall security. Maintaining an effective segmentation strategy demands thoughtful design and regular updates to address evolving requirements.
Enhancing Security Posture with Segmentation
Segmentation's value extends well beyond breach containment. It allows organizations to implement customized security protocols for different network sections based on data sensitivity. For instance, segments housing confidential financial information might employ more rigorous controls than those containing general operational data. This precision in security management leads to better compliance with regulations and more effective risk mitigation.
Additionally, segmentation improves security monitoring and incident response capabilities. Isolated segments enable security personnel to pinpoint and address threats more efficiently. Granular logging and continuous surveillance within each segment offer critical data about potential security incidents or unusual behavior, enabling faster detection and resolution.
Ultimately, segmentation constitutes an indispensable element of any thorough Zero Trust approach. When properly implemented, it creates a more secure and adaptable infrastructure, safeguarding critical systems and sensitive information from diverse threats.
Quantum computing leverages the unconventional principles of quantum mechanics to address challenges that traditional computing systems cannot approach. Unlike conventional computers that process information in binary states (0 or 1), quantum systems employ qubits capable of existing in multiple states simultaneously. This fundamental distinction enables quantum computers to analyze innumerable scenarios concurrently, paving the way for revolutionary advances in healthcare, materials science, and machine intelligence.
Enhancing Security Posture Through Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Continuous Monitoring for Early Threat Detection
Uninterrupted surveillance stands as a fundamental pillar of Zero Trust security, empowering organizations to identify and counteract threats as they emerge. This process entails perpetual observation of network communications, user behaviors, and system settings for irregularities and potential dangers. Contemporary threat detection systems incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms prove particularly valuable, as they can recognize and adapt to new attack methodologies. When security teams detect departures from normal operational patterns, they can intervene before minor issues escalate into major crises, thereby minimizing operational disruption and recovery periods.
Establishing comprehensive logging and auditing mechanisms proves essential for effective continuous monitoring. These records offer critical visibility into system operations, enabling thorough incident investigations and vulnerability assessments. The capacity to connect events across various platforms and applications proves invaluable for understanding attack trajectories and implementing timely corrective actions. Such detailed examination helps uncover underlying causes and supports the development of preventive strategies to bolster overall security.
Validating Access Permissions and User Identities
The Zero Trust model places significant emphasis on continuous verification of access rights and user authentication for every system interaction. This rigorous process differs markedly from traditional security approaches that often provide extensive access privileges by default. Through persistent confirmation of user credentials and access authorizations, organizations can substantially decrease the likelihood of unauthorized system access and data compromise. This verification process must encompass all potential access points, including user devices, applications, and network resources, ensuring strict compliance with established security policies.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) implementation represents a critical element in user identity verification. By requiring multiple independent authentication factors, organizations create additional security layers that significantly raise the difficulty of unauthorized access attempts. Regular audits and updates of access permissions ensure alignment with current business requirements and regulatory obligations, further reducing opportunities for malicious actors and reinforcing security measures.
Automated Validation and Remediation Procedures
Incorporating automated verification and resolution mechanisms into security systems proves vital for effective threat response and vulnerability management. Automated solutions guarantee uniform enforcement of security protocols and immediate attention to policy violations. Specialized tools can continuously scan systems for weaknesses, identify configuration errors, and implement security measures, thereby reducing manual workload and improving response efficiency.
Automated remediation processes hold equal importance. When the system detects vulnerabilities, it should automatically execute countermeasures such as applying security patches, suspending compromised credentials, or blocking suspicious network traffic. This proactive methodology not only limits incident impact but also enhances overall security by preventing recurrent threats.
The Future of MSSP Security: Embracing Zero Trust

The Rise of AI-Powered Threat Detection
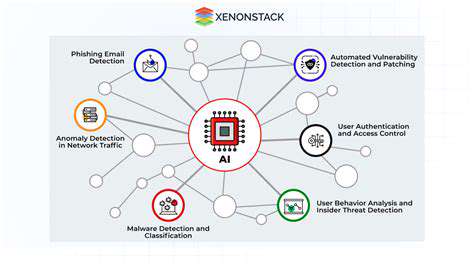
Artificial intelligence continues to revolutionize cybersecurity practices, with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) leading this transformation. Modern AI-driven threat identification systems demonstrate remarkable sophistication, enabling real-time threat recognition and response with exceptional precision. This technological advancement allows MSSPs to anticipate and neutralize emerging vulnerabilities before they can impact client networks. AI systems process enormous volumes of security data to detect subtle patterns and anomalies that might escape human analysts, resulting in more comprehensive and proactive security measures.
Adoption of AI-based security solutions will become mandatory for MSSPs seeking competitive advantage. These technologies enable service providers to offer superior protection to clients, building stronger trust relationships and expanding their market presence. The evolution of MSSP services will increasingly depend on leveraging artificial intelligence for enhanced threat identification and response capabilities.
Expanding the Scope of Managed Services
Future MSSP offerings will extend well beyond conventional network security to include cloud protection, endpoint security, and user security education programs. This broadened approach becomes necessary to counter the constantly changing threat environment.
Security awareness training will emerge as a crucial service component, teaching employees to identify and avoid phishing attempts, malicious software, and other deceptive attacks. MSSPs must assist clients in developing comprehensive security cultures by educating staff about secure computing habits and data protection responsibilities.
The Importance of Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
SOAR platforms are becoming indispensable tools for MSSPs, offering efficient solutions for security incident management. These systems automate numerous security operations including threat investigation, incident handling, and continuous monitoring, allowing MSSPs to address security events more rapidly and effectively.
By automating repetitive tasks, SOAR technology enables security personnel to concentrate on complex, high-priority security challenges. These platforms will significantly improve MSSP operational efficiency and effectiveness, ultimately delivering superior security results for clients.
The Role of Collaboration and Integration
In our interconnected digital ecosystem, cooperative efforts and system integration become vital for cybersecurity success. MSSPs must cultivate strong relationships with security technology vendors and industry partners, exchanging threat information and security methodologies to improve collective defenses. The future of MSSP security will emphasize cooperative strategies that unify diverse security technologies into comprehensive protection frameworks.
Effective integration of security solutions across various environments—including on-site infrastructure, cloud platforms, and mobile devices—proves essential. This holistic approach allows MSSPs to deliver complete security solutions regardless of client IT infrastructure complexity.