The Rise of Connected Healthcare Equipment and the Security Risks

The Evolution of Remote Monitoring
Connected healthcare is rapidly transforming the way patients are monitored and treated, moving away from traditional, in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems are enabling constant, real-time data collection, allowing healthcare providers to intervene proactively and improve patient outcomes. This shift is driven by advancements in sensor technology, mobile apps, and cloud computing, enabling more accessible and comprehensive patient care.
These advancements are significantly reducing the need for frequent, potentially costly, in-person checkups. This translates to greater convenience for patients and reduced strain on healthcare systems. Furthermore, the ability to track vital signs and other health metrics continuously empowers patients to take an active role in managing their own health.
Enhanced Accessibility and Affordability
One of the most compelling aspects of connected healthcare is its potential to improve accessibility, particularly for patients in underserved communities. Remote monitoring systems can bridge geographical gaps, allowing patients in rural areas or those with limited mobility to receive the same level of care as those in urban centers. This increased accessibility can have a significant impact on health equity, particularly for patients who previously lacked access to regular check-ups and specialist consultations.
Furthermore, connected healthcare can potentially reduce healthcare costs. By enabling proactive interventions, it can prevent hospitalizations and costly emergency room visits. The ability to monitor patients remotely allows healthcare providers to identify potential issues early on, which often leads to more effective and less expensive management strategies.
Data-Driven Insights and Personalized Care
The deluge of data generated by connected healthcare systems offers invaluable opportunities for data analysis and personalized care. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms and machine learning, healthcare providers can gain deeper insights into patient health patterns and tailor treatment plans to individual needs. This data-driven approach can lead to more effective diagnoses, personalized medication regimens, and improved patient outcomes.
Data analysis facilitated by connected healthcare allows for a more comprehensive understanding of patient health, leading to more accurate and timely interventions. This personalized approach to care can significantly improve patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans, further enhancing positive health outcomes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, connected healthcare presents various challenges and ethical considerations. Data security and privacy are paramount concerns, requiring robust safeguards to protect sensitive patient information. Ensuring equitable access to technology and digital literacy among all patient populations is also crucial. Furthermore, the potential for bias in algorithms used for data analysis needs careful consideration.
Interoperability between different systems and devices is critical for seamless data exchange and comprehensive patient care. Addressing these challenges and ethical considerations will be essential for maximizing the benefits of connected healthcare while minimizing potential risks.
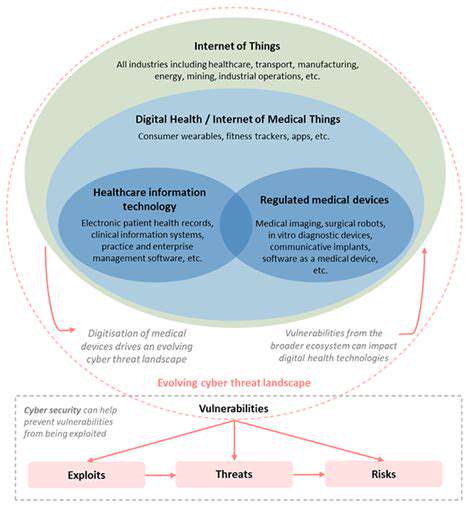
Implementing Robust Security Measures Across the Device Lifecycle
Developing Secure Design Principles
A critical aspect of implementing robust security measures across the medical device lifecycle is the early integration of security principles into the design phase. This proactive approach ensures that security considerations are not an afterthought, but rather an integral part of the device's architecture and functionality. This involves meticulous risk assessments, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and selecting appropriate security controls tailored to the specific device and its intended use. By incorporating security into the design, manufacturers can mitigate risks and create devices that are inherently more secure from the outset, reducing the likelihood of exploits and vulnerabilities emerging later in the development process. A thorough understanding of the potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to medical devices is essential to developing effective design principles.
Furthermore, adhering to industry standards and best practices is crucial for maintaining a high level of security. These standards often outline recommended security controls, such as data encryption, access control mechanisms, and secure communication protocols. Adherence to these guidelines not only enhances the overall security posture of the device but also facilitates interoperability and compliance with regulatory requirements. This adherence can significantly enhance the trust and confidence in the medical device, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare professionals.
Implementing Secure Development Practices and Testing
The development process itself plays a significant role in ensuring the security of medical devices. Implementing secure development practices throughout the entire lifecycle, from requirements gathering to deployment, is paramount. This includes training developers on secure coding techniques, employing secure coding guidelines, and conducting regular code reviews to identify and address potential vulnerabilities early in the process. Utilizing security testing methodologies, such as penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, is equally important to uncover and remediate any security flaws that may have been introduced during the development phase.
Effective testing strategies are crucial for proactively identifying and mitigating security risks. Rigorous testing throughout the development process, including penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, can expose potential weaknesses in the device's security mechanisms. These testing efforts should encompass not only the software components but also the hardware and communication interfaces. By thoroughly testing the device under various simulated attack scenarios, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into its resilience and improve its overall security posture.
Implementing robust security testing procedures, including penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security audits, is vital to identify and address potential vulnerabilities proactively. These tests should simulate real-world attack scenarios to evaluate the device's ability to withstand various threats and exploits. Comprehensive testing, coupled with continuous monitoring and updates, ensures that the medical device remains secure throughout its operational lifecycle.
Security should be integrated into the entire software development life cycle (SDLC), not just as an afterthought. This includes secure coding practices, rigorous testing, and incorporating security feedback into the design and development process. By adopting a proactive and iterative approach, manufacturers can significantly enhance the overall security posture of their medical devices.
Maintaining a strong security posture requires continuous monitoring and updating of the device's security mechanisms. Regular security assessments and vulnerability patching are crucial to address emerging threats and exploits, ensuring the device remains resilient against evolving cyber risks. This ongoing vigilance is essential in the rapidly changing threat landscape.
Protecting Patient Data and Privacy Through Secure Data Transmission and Storage
Implementing Robust Encryption Protocols
Secure data transmission relies heavily on robust encryption protocols. These protocols scramble data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access sensitive patient information during transit. Advanced encryption standards, such as AES-256, are crucial for safeguarding data confidentiality. Implementing these protocols across all communication channels, including email, file transfers, and online portals, is paramount for protecting patient privacy.
Furthermore, the use of end-to-end encryption ensures that only the intended recipient can decrypt the data. This is particularly important for protecting patient data exchanged between healthcare providers and patients. By encrypting data at both ends of the communication pathway, the risk of unauthorized access is minimized.
Utilizing Secure Data Storage Solutions
Data storage security is equally critical. Implementing secure data storage solutions, such as encrypted databases and cloud storage services with advanced access controls, is essential. These solutions should employ multi-factor authentication to verify user identities and limit unauthorized access to sensitive data. Regular audits and security assessments of these systems are necessary to detect and address potential vulnerabilities.
Establishing Strict Access Control Measures
Implementing strict access control measures is vital to limit access to patient data. This includes assigning appropriate permissions based on the roles and responsibilities of individuals within the healthcare organization. Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific patient data. Regular reviews of these access controls are necessary to adapt to changing organizational needs and maintain data security.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and addressing potential security weaknesses in data transmission and storage systems. These assessments should cover all aspects of the system, from the hardware to the software, and from the network infrastructure to the user authentication processes. Proactive security measures, such as penetration testing, can help identify and mitigate potential threats before they can be exploited.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee training and awareness programs play a crucial role in maintaining a strong security posture. Educating employees about the importance of data protection, the risks associated with phishing attacks, and the proper handling of sensitive patient information is essential. Regular training sessions can reinforce best practices and ensure that all staff members understand their responsibilities in safeguarding patient data.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Adherence to relevant data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, is paramount for protecting patient data. Understanding and implementing the specific requirements of these regulations, including data minimization, data retention policies, and breach notification procedures, is critical. This ensures that the organization is compliant with legal and ethical obligations, thereby protecting patients' rights and privacy.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Robust data backup and recovery strategies are essential for mitigating the impact of data loss or system failures. Regular backups of patient data, stored in secure offsite locations, can restore data in case of disaster or cyberattacks. Having a well-defined disaster recovery plan, including clear procedures for data restoration, is critical for maintaining business continuity and minimizing disruption to patient care. Regular testing of these backup and recovery procedures is necessary to ensure their effectiveness.
Collaboration and Standardization for Enhanced Medical Device Security
Collaboration Among Stakeholders
Effective medical device security hinges on collaborative efforts between various stakeholders. This includes manufacturers, regulatory bodies, healthcare providers, and patients. Open communication channels, information sharing, and joint development of security protocols are crucial. Manufacturers need to actively engage with regulatory bodies to understand evolving security threats and implement robust mitigation strategies. Healthcare providers, in turn, must adopt and educate themselves on the latest security measures to ensure proper device implementation and use. Ultimately, fostering a culture of collaboration and transparency is paramount for creating a safer and more secure medical device environment for all.
Standardization initiatives across different medical device types are also essential. This involves establishing universally accepted security protocols and guidelines, ensuring interoperability between devices, and promoting the use of common security architectures. Such standardization efforts will significantly reduce complexity and enhance the overall security posture of the medical device ecosystem. This collaborative approach will contribute to a more secure and reliable healthcare system for everyone.
Standardization of Security Protocols
Establishing standardized security protocols across different medical device types is crucial for bolstering overall security. This involves defining clear security requirements, testing methodologies, and reporting procedures that apply consistently. Standardized protocols will allow for more efficient and effective security assessments, vulnerability management, and incident response. This approach will minimize the risk of disparate security standards leading to vulnerabilities and gaps in protection across different devices. Clear guidelines will ensure that similar security measures are consistently applied, fostering a more secure healthcare ecosystem.
The standardization of security protocols should encompass the entire lifecycle of a medical device, from design and development to manufacturing, deployment, and maintenance. This comprehensive approach will help ensure that security considerations are integrated into every stage of the device's life, leading to a more robust and resilient security posture. This includes establishing clear procedures for reporting vulnerabilities, conducting regular security audits, and updating protocols as new threats emerge. Such a comprehensive approach is essential to maintain a high level of security throughout the device's operational life.
Security Measures for Specific Device Types
Different medical devices present unique security challenges that necessitate tailored security measures. For example, implantable devices require robust protection against unauthorized access and tampering, while connected devices need safeguards against cyberattacks. Specific security protocols and procedures must be developed and implemented for each device type to address its unique vulnerabilities. This involves considering factors such as the device's intended use, the data it handles, and the potential impact of a security breach. For instance, implantable devices may need to be designed with enhanced physical security features, while connected devices should be equipped with multiple layers of network security.
Implementing robust encryption and access control mechanisms is another critical aspect of device-specific security measures. This applies to both the data transmitted and stored by the devices. Additionally, regular security assessments and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address vulnerabilities. This approach ensures that security measures are tailored to the specific needs and characteristics of each device type, thereby reducing the overall risk of a security breach. This approach also includes the development of comprehensive training programs for healthcare professionals on the proper use and maintenance of these devices.
Importance of Ongoing Training and Education
Ongoing training and education are essential to maintain and enhance the security of medical devices. Healthcare professionals must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to properly configure, operate, and maintain these devices, while adhering to security protocols. Regular updates on emerging threats and best practices are crucial to keeping professionals informed. This proactive approach will ensure that security is not an afterthought but an integral part of the device's lifecycle. Continuous improvement of security practices is essential in the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape.
Regular security awareness training for all personnel involved in the medical device ecosystem—from manufacturers to healthcare providers—is vital. This includes training on identifying potential security threats, implementing appropriate security measures, and reporting any suspicious activities. This will contribute to a strong security culture and help prevent security breaches. Training also covers the importance of incident response procedures and emergency protocols, so personnel are prepared to handle security incidents effectively.