Data Privacy and Security: A Critical Component
Data Collection Practices
Modern urban monitoring networks gather extensive datasets, ranging from geospatial coordinates and visual recordings to IoT sensor metrics and digital footprint analysis. While this information can optimize municipal services, it simultaneously creates substantial personal privacy dilemmas. Municipalities must rigorously evaluate which data elements require collection, establish strict retention timelines, and implement safeguards against exploitation. Public disclosure of data acquisition methodologies proves fundamental for maintaining community confidence and ethical information utilization.
Precise data lifecycle management protocols become indispensable. Information should persist in storage only for operationally essential durations, directly corresponding to collection objectives, while employing enterprise-grade protection against illicit access. Additionally, advanced de-identification methodologies should be implemented to preserve citizen anonymity without diminishing analytical value.
Data Protection Protocols
Safeguarding information integrity and confidentiality represents the highest priority. Multi-layered defensive architectures become necessary to block unauthorized entry, alteration, or leakage of sensitive records. This necessitates military-grade cryptographic standards, role-based permission systems, and continuous security validation procedures. Consistent software maintenance and hardware firmware updates equally contribute to sustaining robust system defenses.
Proactive threat assessment initiatives including routine penetration testing should identify and remediate potential vulnerabilities before malicious exploitation. Comprehensive breach response blueprints must be operational to rapidly contain and investigate any security incidents.
Operational Transparency
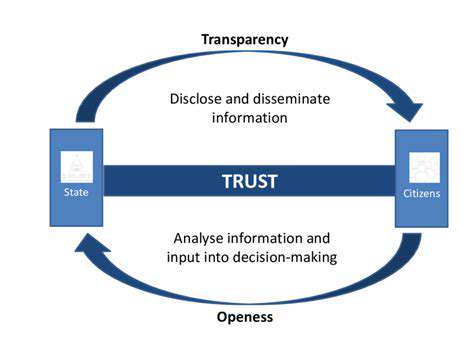
Community education regarding data lifecycle management remains crucial. Detailed, publicly available documentation outlining privacy safeguards and security controls should be developed and disseminated. Third-party compliance verification and regulatory supervision mechanisms further ensure proper adherence to established standards.
Incorporating resident feedback channels transforms passive observation into collaborative governance. Accessible grievance resolution pathways must be created to address privacy concerns and security incidents, including simplified reporting interfaces and guaranteed response timelines.
Ethical Implementation
Urban surveillance deployment demands rigorous moral examination. Algorithmic fairness audits, equitable technology distribution across socioeconomic groups, and fundamental privacy preservation require ongoing evaluation. Continuous ethics committee oversight ensures responsible technological evolution that respects civil liberties.
Legal Compliance
Existing data protection statutes require careful adaptation to address smart city monitoring complexities. International conventions, national legislation, and industry standards must be harmonized, with potential legislative updates to govern emerging surveillance capabilities. Strict alignment with frameworks like GDPR establishes baseline compliance.
Community Partnership
Establishing public confidence proves fundamental for surveillance system acceptance. Transparent policy development, proactive civic dialogue, and participatory design processes cultivate mutual understanding. Regular town hall discussions and technology demonstrations allow direct citizen engagement.
Involving residents in surveillance architecture decisions promotes collective responsibility. This participatory approach yields more inclusive urban solutions that balance security needs with personal freedoms.
Next-generation maritime observation networks revolutionize nautical navigation through persistent tracking and environmental monitoring capabilities. This facilitates instantaneous hazard identification, including meteorological disturbances, oceanic anomalies, or proximate vessel traffic. The uninterrupted availability of precision navigational intelligence enables anticipatory course corrections, minimizing accident probabilities while safeguarding crew and shipments. Persistent maritime domain awareness additionally assists law enforcement in intercepting illicit activities like unauthorized fishing or contraband transport through vessel behavior analytics.
Ethical Governance and Regulatory Compliance
Information Protection
Citizen data safeguarding forms the cornerstone of ethical urban monitoring. End-to-end encryption, statistical anonymization, and granular permission structures prevent data compromise. Explicit retention schedules and certified destruction methods reduce privacy risks. Publicly accessible data usage policies should detail collection purposes and processing methodologies, reinforcing institutional accountability.
Cybersecurity implementation extends beyond technical controls to encompass organizational policies. Scheduled security reviews and threat modeling exercises maintain system integrity. Personnel training programs and security-aware culture development complement technological safeguards.
Public Disclosure
Residents deserve comprehensive understanding of municipal surveillance operations. Technical specifications, operational guidelines, and system capabilities should be published in accessible formats. Community consultation sessions enable direct citizen input during planning and deployment phases.
Effective communication must explain both surveillance capabilities and their operational justification. Clear articulation of public safety benefits, coupled with privacy safeguards, reduces community apprehension. Including diverse stakeholder perspectives during policy formulation enhances system legitimacy.
Oversight Structures
Defined accountability frameworks govern surveillance system usage. Multi-disciplinary review boards comprising technical experts, civil society representatives, and legal professionals should conduct regular system evaluations. Impact assessments measuring demographic effects ensure equitable technology application.
Formal complaint resolution processes must address surveillance-related concerns. Accessible appeal mechanisms and guaranteed investigation timelines demonstrate institutional responsiveness. Transparent resolution of grievances maintains public confidence in oversight systems.
Legal Safeguards
Surveillance operations must conform to constitutional protections and international human rights standards. Legislative frameworks should explicitly define authorized use cases and operational boundaries. Fundamental freedoms including privacy, assembly, and movement require explicit protection in monitoring policies.
Judicial authorization processes for surveillance activities must incorporate proportionality assessments. Chain-of-custody protocols for evidentiary materials ensure legal admissibility. Independent verification of compliance procedures maintains system integrity.
Security-Liberty Equilibrium
Urban monitoring systems must carefully calibrate public safety benefits against individual rights. Surveillance should never create social chilling effects or enable discriminatory practices. Continuous impact monitoring identifies disproportionate effects on vulnerable populations.
Regular effectiveness evaluations ensure surveillance remains minimally intrusive while achieving security objectives. Ongoing civil liberty impact assessments guarantee technology serves democratic values rather than undermining them.