Data Minimization Principles
Data minimization is a core principle of data protection, advocating for collecting and processing only the minimum amount of personal data necessary to achieve a specific, legitimate purpose. This means carefully considering what data is truly required and rejecting the temptation to hoard excessive information. Thorough planning and a clear understanding of the intended use cases are crucial for effective data minimization. This approach not only respects individual privacy rights but also enhances operational efficiency by reducing storage costs and complexity.
By limiting the data collected, organizations significantly reduce the potential for misuse or unintended consequences. A data-minimization strategy ensures that personal information is not overly broad or encompassing, thereby minimizing the risk of breaches and inappropriate disclosures. Furthermore, this principle promotes transparency and accountability within data handling processes, as it highlights the need for justification of every piece of data collected.
Purpose Limitation
Purpose limitation, a closely related concept, emphasizes the importance of processing personal data only for the specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes for which it was collected. This principle stresses that data should not be used for purposes beyond those originally stated. Organizations need to clearly define the intended use cases from the outset and document them meticulously.
This approach promotes transparency and accountability, ensuring data subjects understand how their information will be used. It also prevents the potential for misuse and inappropriate processing, thereby safeguarding individual rights and promoting trust in data handling practices. Furthermore, it facilitates compliance with data protection regulations, which often require organizations to clearly articulate the purpose of data collection.
Implementing Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Effective implementation of data minimization and purpose limitation requires a proactive and systematic approach. Organizations should develop comprehensive data inventories to understand the types and volumes of personal data they hold. This will allow them to identify areas where data collection can be streamlined and unnecessary data can be discarded.
Establishing clear data policies and procedures is also essential. These policies should outline the specific purposes for collecting data, the types of data allowed, and the retention periods. Regular reviews of data processing activities are crucial to ensure ongoing compliance with these principles. Regular audits and assessments are vital for maintaining the effectiveness of these measures and proactively addressing any potential risks. Training employees on data protection principles is an integral part of this process, fostering a culture of data privacy awareness and responsibility.
Personalized care plans are crucial for tailoring healthcare interventions to individual needs and preferences. These plans go beyond a generic approach, acknowledging that each patient's journey is unique. By taking into account a patient's specific medical history, lifestyle, and preferences, a personalized care plan can lead to better adherence to treatment regimens and improved overall health outcomes. This customized approach empowers patients, fostering a sense of ownership and control over their health. It also facilitates better communication between patients and healthcare providers, leading to a more collaborative and effective treatment strategy.
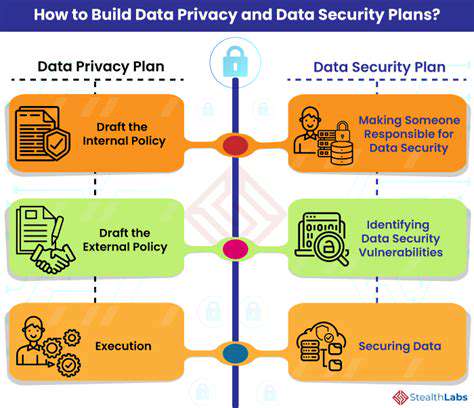
Data Security and Privacy Policies: Clear and Comprehensive
Data Encryption Techniques
Data encryption is a crucial aspect of data security, transforming readable data into an unreadable format, known as ciphertext, to protect sensitive information. This process, often employed to safeguard sensitive data during transmission, relies on cryptographic algorithms. Strong encryption algorithms are essential for preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data confidentiality. Employing robust encryption methods across various platforms and systems is paramount in today's digital landscape.
Various encryption techniques exist, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Symmetric-key encryption, like AES, uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, offering speed but potentially raising key management challenges. Asymmetric-key encryption, exemplified by RSA, employs separate keys for encryption and decryption, enhancing security but potentially introducing performance trade-offs. Choosing the right encryption method depends on the specific security requirements and the nature of the data being protected.
Access Control Mechanisms
Implementing robust access control mechanisms is vital for safeguarding sensitive data. These mechanisms control who can access specific data and what actions they can perform on that data. Strict access controls are paramount in preventing unauthorized access and misuse of confidential information. Defining clear roles and responsibilities within an organization is crucial to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data.
Different access control models, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC), can be implemented. RBAC defines access privileges based on user roles, while ABAC considers various attributes, such as location, time, and user attributes, to determine access rights.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for proactively identifying and addressing potential security vulnerabilities. These audits involve a systematic review of security policies, procedures, and controls to ensure their effectiveness and compliance with industry standards. Regular audits identify weaknesses before they are exploited, preventing potential breaches and safeguarding sensitive data. Thorough audits help maintain a strong security posture and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are proactive measures designed to prevent the unauthorized disclosure or loss of sensitive data. These strategies often involve implementing policies and technologies to monitor data access and movement, ensuring that sensitive data is handled securely. DLP solutions can identify and block sensitive data from leaving the organization's network, reducing the risk of data breaches. Robust DLP systems can play a crucial role in minimizing the potential impact of data breaches.
Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Establishing comprehensive data backup and recovery procedures is critical for ensuring business continuity and data availability. These procedures involve regularly backing up data to offsite locations to safeguard against data loss due to various factors, such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. Regular backups are essential for restoring data in case of a disaster or a security incident. Effective data recovery plans are crucial for maintaining business operations and minimizing downtime.
Privacy Policy Compliance
Ensuring compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is paramount in today's data-driven world. Organizations must develop and implement privacy policies that clearly outline how personal data is collected, used, and protected. Organizations need to be transparent about their data handling practices and comply with the relevant regulations. Failing to comply with privacy regulations can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage.
Incident Response Plan
Establishing a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for effectively handling security incidents. This plan should outline the procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security breaches. A robust incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of security breaches and ensuring business continuity. Having a clear incident response plan in place can help organizations mitigate the damage caused by security incidents. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure its effectiveness.