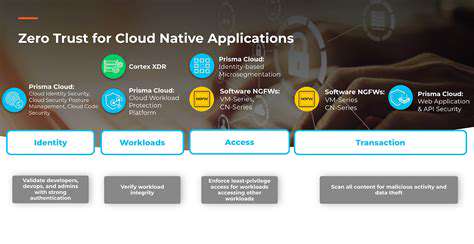
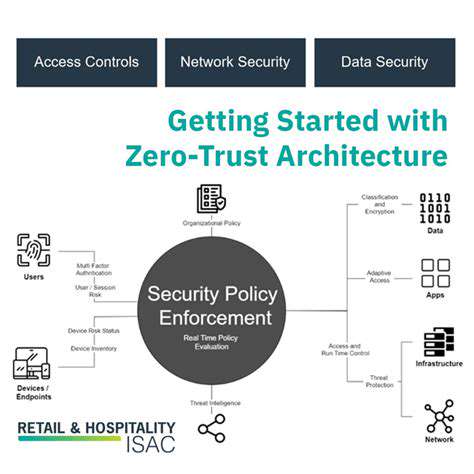
Transitioning to Zero Trust necessitates abandoning outdated perimeter-focused security in favor of precise, identity-driven protocols. The framework prioritizes stringent access governance, minimal privilege allocation Principles, and live surveillance to guarantee that data and applications remain accessible exclusively to vetted entities, irrespective of their physical or network location.
The Growing Need for Zero Trust in Cloud Environments
Cloud adoption continues accelerating, erasing conventional security perimeters and amplifying Zero Trust's relevance. Modern cloud ecosystems introduce unique complexities - diverse user populations, elastic workloads, and decentralized infrastructure that routinely outmaneuver traditional defensive measures.
As cyber threats grow increasingly sophisticated, perimeter defenses like firewalls prove inadequate alone. Zero Trust delivers a holistic security architecture for safeguarding cloud workloads, APIs, and user pathways through persistent verification and rigorous policy enforcement across all cloud assets.
Challenges in Adopting Zero Trust in Cloud Settings
Organizations frequently encounter integration hurdles when implementing Zero Trust within existing cloud frameworks. Legacy systems often lack native support for granular access controls, necessitating substantial modernization investments.
Moreover, effective Zero Trust deployment demands robust identity management infrastructure, sophisticated analytics for immediate threat identification, and comprehensive visibility spanning multiple cloud providers. These prerequisites can introduce operational complexity and initial cost barriers that may deter some enterprises.
Key Technologies Enabling Zero Trust in the Cloud
Several cutting-edge technologies facilitate Zero Trust implementation in cloud contexts. Advanced identity providers, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and unified login solutions strengthen user verification, diminishing impersonation risks.
Micro-segmentation and software-defined perimeters (SDP) enable creation of isolated cloud environments, dramatically shrinking potential attack surfaces. Continuous monitoring systems and security information/event management (SIEM) platforms prove indispensable for anomaly detection and rapid threat response.
Best Practices for Implementing Zero Trust in Cloud Security
Successful Zero Trust adoption begins with thorough asset discovery and classification to identify protection priorities. Developing context-aware access policies grounded in least-privilege principles ensures proper control enforcement.
Enterprises should implement phased rollouts, initially securing high-risk workloads before expanding Zero Trust protocols cloud-wide. Regular audits, continuous training, and security integration into DevOps workflows remain critical for maintaining Zero Trust efficacy.
Zero Trust and CSPM Synergies: A Powerful Combination
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture and Its Core Principles
Zero Trust architecture represents a security philosophy built on perpetual verification. It presumes threats exist everywhere - inside and outside network boundaries - mandating rigorous authentication for all resource access attempts. This methodology reduces insider threat risks and contains lateral movement by enforcing least-privilege access principles.
Zero Trust implementation requires ongoing surveillance, adaptive access controls, and robust authentication like MFA. Organizations typically employ identity/access management (IAM) tools to execute policies verifying user identities and device health pre-access. This transition from perimeter-focused to data-centric security substantially enhances protection in complex cloud ecosystems.
What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) encompasses tools and methodologies for identifying/resolving security risks across cloud platforms. CSPM solutions provide continuous monitoring of cloud configurations, compliance statuses, and security policies, offering visibility into potential weaknesses. They automate compliance verification against standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, ensuring persistent secure configuration.
Through comprehensive dashboards and alert systems, CSPM empowers security teams to rapidly address misconfigurations or policy deviations. These tools become increasingly vital as cloud environments grow in complexity, proactively reducing attack surfaces and simplifying standards adherence.
Synergies Between Zero Trust and CSPM in Cloud Security
Combining Zero Trust principles with CSPM tools creates a formidable security framework addressing both access control and configuration risks. While Zero Trust enforces strict access policies and continuous verification, CSPM maintains compliant, secure cloud configurations. Together, they form comprehensive defenses against evolving cloud threats.
This integration enables adaptive security controls responding to real-time cloud configuration and user behavior changes. When CSPM detects vulnerabilities, Zero Trust policies can dynamically restrict access or impose additional authentication layers, establishing multi-layered protection.
The combined approach enhances visibility and control, accelerating incident response and preventing unauthorized access. This strategic integration marks significant progress in cloud security management.
Practical Benefits of Integrating Zero Trust with CSPM
Integrating Zero Trust with CSPM yields substantial security posture improvements, decreasing breach likelihood and unauthorized access incidents. Organizations gain granular access control while continuously monitoring cloud configurations, adopting proactive security stances.
Operational efficiency improves through security policy automation and real-time alerts, reducing manual intervention and accelerating response times. The combination also facilitates regulatory compliance by streamlining adherence to industry standards through automated checks and strict access governance.
Furthermore, this integration promotes organizational security awareness as continuous monitoring and verification reinforce accountability and best practices among users and administrators.
Implementing Zero Trust and CSPM: Best Practices
Effective Zero Trust/CSPM integration begins with establishing clear identity/access policies aligned with Zero Trust principles. This involves deploying robust authentication, role-based access controls, and contextual authorization mechanisms to validate all access requests.
Concurrently, implementing comprehensive CSPM solutions ensures secure configurations across all cloud assets. Routine audits, automated remediation, and compliance reporting should integrate into daily operations to maintain security standards alignment.
Cross-functional collaboration between security, operations, and development teams proves essential for consistent policy application and updates. Ongoing training programs further reinforce the importance of maintaining Zero Trust mentalities alongside vigilant configuration management.
Challenges and Considerations in Zero Trust and CSPM Adoption
Despite advantages, Zero Trust/CSPM integration presents challenges including policy management complexity across diverse cloud platforms and ensuring tool interoperability. Organizations must also address potential performance impacts from continuous verification processes and configuration scanning.
Data privacy and compliance considerations emerge when monitoring user activities and configurations across multiple regions. Balancing security with user experience remains critical, as excessively restrictive policies may impede productivity.
Enterprises should adopt incremental implementation strategies, beginning with high-value assets before extending Zero Trust/CSPM practices organization-wide. Careful planning, vendor selection, and change management prove vital for overcoming these obstacles.
Future Trends in Zero Trust and CSPM Integration
Cloud security's future lies in increasingly integrated, autonomous systems capable of real-time threat adaptation. AI and machine learning advancements will empower Zero Trust/CSPM solutions to predict vulnerabilities and automatically enact protective measures without human involvement.
The rise of zero-trust network access (ZTNA) and secure access service edge (SASE) architectures will further unify network security and cloud management, delivering seamless, policy-driven access controls across distributed environments.
Emerging standards will enhance security tool interoperability, fostering cohesive ecosystems. As Zero Trust/CSPM synergy recognition grows, expect more integrated platforms simplifying deployment and management, ultimately yielding stronger, more resilient cloud security strategies.
Fusion cocktails, a vibrant and ever-evolving genre, represent a global culinary fusion in miniature. They seamlessly blend ingredients and flavors from diverse cultures, often surprising and delighting palates with unexpected combinations. This mixing of traditions transcends geographical boundaries, creating a unique and exciting drinking experience that reflects the increasingly interconnected world we inhabit.
Beyond Compliance: CSPM for Enhanced Cloud Security Operations

Beyond Basic Security: CSPM's Role in Enhanced Protection
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions transcend mere compliance fulfillment. They represent proactive strategies for fortifying cloud security and protecting sensitive information. CSPM identifies and resolves vulnerabilities often invisible to conventional security approaches, enabling organizations to mitigate risks pre-exploitation. These solutions empower enterprises to maintain resilient cloud environments, significantly reducing breach and data loss probabilities.
CSPM provides panoramic visibility across cloud infrastructures, detecting misconfigurations and weaknesses spanning multiple platforms and services. This comprehensive perspective proves indispensable in today's intricate cloud ecosystems. Through continuous monitoring and analysis, CSPM helps prevent security incidents proactively, minimizing potential financial and reputational damages.
Proactive Threat Detection and Mitigation
Exceptional CSPM solutions incorporate proactive threat identification and neutralization capabilities. These features help organizations anticipate emerging threats and respond swiftly to potential incidents. Continuous surveillance for suspicious activities and anomalies adds critical defensive layers against evolving cyber threats, narrowing vulnerability windows and strengthening overall security postures.
Effective threat detection involves recognizing unusual user behavior or system activity patterns - analyzing access logs, identifying anomalous login attempts, and detecting irregular data access. This functionality proves essential for countering sophisticated threats that might otherwise evade detection.
Additionally, CSPM solutions scrutinize security configurations for deviations from best practices, alerting administrators to potentially exploitable weaknesses. Prompt identification and resolution of these issues substantially reduces attack surfaces and enhances cloud security.
Optimizing Cloud Security Posture
Proper CSPM implementation extends beyond vulnerability remediation to continuous security posture optimization. This involves regular policy/procedure reviews, alignment with industry best practices, and staying informed about threat landscape developments. Continuous evaluation and refinement remain imperative for maintaining adaptable, resilient security strategies.
Integration with other security tools/platforms represents a crucial optimization aspect, enabling comprehensive security visibility and coordinated threat responses. Organizations can leverage CSPM-derived insights to improve overall security postures and proactively address risks.
By cultivating continuous improvement cultures and proactive security measures, enterprises effectively harness CSPM to strengthen cloud security postures, minimizing vulnerabilities and risks. This ensures cloud environments remain not just secure, but adaptable and resilient against evolving threats.
Real-world Implications and Future Trends

Advancements in Technology and Their Impact on Society
Technological innovations persistently transform communication, work, and information access paradigms. Emerging devices and platforms create unprecedented connectivity and cross-border collaboration opportunities, while simultaneously raising privacy, security, and data management concerns. Societal adaptation requires establishing regulations that safeguard users without stifling innovation.
In healthcare, technology enables superior diagnostics and personalized treatments, dramatically improving patient outcomes. However, access disparities to advanced medical tools persist, underscoring the need for equitable distribution. Healthcare's future depends on thoughtful, ethical integration of emerging technologies to ensure universal benefits.
Environmental Challenges and Sustainable Solutions
Escalating climate change and environmental degradation threaten global ecosystems and human livelihoods. Addressing these crises demands immediate action and innovative solutions balancing economic growth with ecological preservation. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power lead sustainable development strategies.
Governments and corporations increasingly adopt carbon reduction and conservation policies. These initiatives' long-term success hinges on public awareness and collective responsibility. Future environmental impact mitigation will rely heavily on green technology advancements and sustainable practice adoption.
Economic Shifts and Job Market Evolution
Automation, artificial intelligence, and digital commerce drive rapid global economic transformations, reshaping job markets by creating new opportunities while rendering traditional roles obsolete. Workforce competitiveness in this evolving landscape necessitates continuous skill acquisition.
Educational systems and policymakers play pivotal roles in preparing workers for future demands. Emphasizing lifelong learning and vocational training can bridge skills gaps. Future employment will likely feature increased work flexibility and heightened technological proficiency requirements.
Ethical Considerations in Innovation
Expanding technological capabilities amplify ethical concerns regarding privacy, consent, and AI decision-making. Developing frameworks guiding responsible innovation and preventing emerging technology misuse becomes imperative. Stakeholder collaboration is essential for establishing standards protecting human rights and promoting fairness.
Public discourse and transparency prove vital in addressing ethical dilemmas. Future developments should prioritize inclusivity and accountability, ensuring technology serves collective good without compromising individual freedoms.
Predictions and Preparations for Future Developments
Accurate trend forecasting requires analyzing current data and anticipating potential breakthroughs across disciplines. Preparing society for impending changes demands proactive strategies and adaptable policies. Research and development investments will prove crucial for staying ahead of technological and environmental challenges.
Building resilience and fostering innovation helps societies navigate uncertainties and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Future success will depend heavily on collaborative efforts between governments, academia, and industry to create sustainable, equitable global systems.