Understanding Zero Trust
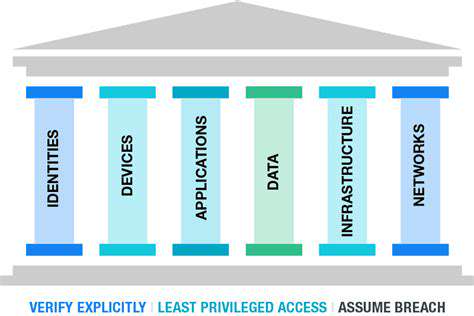
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no implicit trust, regardless of whether an entity is inside or outside a network perimeter. Instead of trusting users or devices automatically, Zero Trust mandates continuous verification and authorization for every access attempt. This approach significantly enhances security posture by requiring strong authentication and continuous validation to verify the identity and trustworthiness of any user, device, or application attempting to access resources within the network.
This fundamental shift in security thinking recognizes that traditional network segmentation isn't enough in today's complex threat landscape. A Zero Trust environment requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond simple network access controls and delves into more granular, dynamic security measures for every interaction. This proactive approach is crucial for mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Zero Trust Principles
Implementing Zero Trust principles involves a multifaceted approach. It's not just about installing new software, but about fundamentally changing how access is managed and controlled. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, like multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify user identity. It also necessitates enforcing granular access controls, permitting only the necessary access for users and devices, and ensuring that these controls are continuously evaluated and updated.
Robust identity management systems are critical components of a Zero Trust architecture. These systems are essential for tracking user activity, detecting anomalies, and ensuring compliance with security policies. The implementation of these measures requires a significant investment in security infrastructure and expertise, but the potential rewards are substantial in terms of enhanced security and reduced risk.
The Importance of Continuous Verification
A critical aspect of Zero Trust is the continuous verification of user and device identities. This dynamic process involves regularly assessing the trustworthiness of all entities attempting to access resources, regardless of their location or prior access history. Such continuous verification is crucial for identifying and responding to potential threats in real-time.
Key Considerations for Zero Trust Adoption
Transitioning to a Zero Trust model requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must assess their existing security infrastructure, identify potential vulnerabilities, and develop a comprehensive implementation strategy. This includes defining clear security policies, implementing appropriate access controls, and establishing robust monitoring and response mechanisms. Effective communication and training are essential to ensure that all stakeholders understand and adhere to the new security protocols. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and adaptation are key to maintaining a robust Zero Trust environment.
Proactive Threat Detection and Response in a Zero Trust Environment
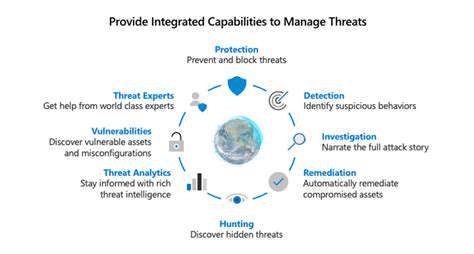
Proactive Threat Hunting Strategies
Proactive threat detection involves actively seeking out potential security risks rather than simply reacting to incidents. This proactive approach is crucial for organizations looking to stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a strong security posture. Identifying potential threats before they can cause significant damage is a key component of a robust security strategy. This approach requires a shift in mindset from reactive security measures to a more aggressive, predictive approach to threat detection.
Implementing advanced threat hunting techniques is essential for proactively identifying and mitigating threats. These techniques often involve using security information and event management (SIEM) tools, threat intelligence feeds, and other analytical methods to detect anomalies and suspicious activity. By actively searching for indicators of compromise (IOCs), organizations can quickly identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited. This proactive approach allows for faster response times and minimizes the potential for significant damage from successful attacks.
Advanced Threat Detection Technologies
Employing advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) is critical for proactive threat detection. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of security data to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activity. The ability to analyze massive datasets and identify anomalies that are often missed by traditional methods is a key advantage of AI-powered threat detection systems. These systems can learn and adapt to new threats, making them crucial in keeping pace with the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Advanced threat detection technologies are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Choosing the appropriate technology depends on an organization's specific needs and resources. Organizations should carefully evaluate different solutions and consider their scalability, integration capabilities, and ease of use before making a decision. Implementing these advanced technologies can significantly enhance an organization's ability to detect and respond to threats.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are essential components of a proactive threat detection strategy. They collect, analyze, and correlate security events from various sources, providing a centralized view of security activity. This holistic view of security events is critical for identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activity. By aggregating and analyzing security logs from various sources, SIEM systems can help organizations identify suspicious behavior quickly.
SIEM systems are often paired with other security tools to provide a comprehensive security solution. The use of SIEM systems combined with other tools such as intrusion detection systems and vulnerability management tools can further enhance the security posture of an organization. This comprehensive approach is essential for proactively detecting and responding to a wide range of threats.
Threat Intelligence and Collaboration
Integrating threat intelligence feeds into security operations is critical for proactive threat detection. Threat intelligence provides valuable insights into emerging threats, tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers. This information is crucial for developing proactive defenses and adapting security strategies to address evolving threats. This intelligence can be gathered from various sources, including open-source intelligence, industry reports, and dedicated threat intelligence providers.
Collaboration with industry peers and security researchers is also vital. Sharing threat intelligence and best practices can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape and enhance proactive threat detection capabilities. Sharing information and insights with other organizations can help identify and mitigate emerging threats more effectively.