Beyond Encryption: The Importance of Data Integrity
In today's digital landscape, organizations face relentless threats from data breaches, regardless of their size or industry. While encryption remains a cornerstone of data protection, it's crucial to recognize its limitations. Encryption primarily serves as a guardian of confidentiality, restricting access to sensitive information only to authorized individuals. Yet, even the most robust encryption can't prevent breaches if the underlying data integrity is undermined. Data integrity ensures information remains accurate, complete, and consistent throughout its entire lifecycle - from initial entry to storage and eventual retrieval. This requires implementing rigorous validation processes at every stage to prevent unauthorized alterations or corruption.
A truly comprehensive security strategy must extend far beyond encryption alone, incorporating multiple defensive layers to protect data integrity. Effective approaches include strict access controls, thorough data validation protocols, and regular audits to identify and correct inconsistencies. By prioritizing data integrity, organizations can defend against sophisticated attacks that target data manipulation rather than simple theft.
The Critical Role of Data Validation in Leak Prevention
Data validation stands as a fundamental pillar of data integrity. This process involves systematically verifying information against established standards to ensure its accuracy and reliability. Comprehensive validation checks examine data types, acceptable ranges, proper formats, and completeness while identifying inconsistencies or missing values. Implementing rigorous validation procedures from the outset dramatically reduces the risk of corrupted or malicious data entering organizational systems.
Early detection and correction of data errors prevents the propagation of inaccuracies throughout enterprise systems. This proactive approach avoids potentially catastrophic consequences that could emerge if errors remain undetected until much later stages, when remediation becomes significantly more complex and expensive.
Multi-Factor Authentication: Strengthening Defenses Against Data Compromise
While encryption protects data during transmission, robust access controls are equally vital for safeguarding stored information. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) represents a powerful security enhancement that builds upon traditional password protection. This method requires users to provide multiple verification forms - such as passwords, one-time codes, or biometric data - before granting system access. Properly implemented MFA substantially reduces unauthorized access risks, even when passwords are compromised.
The Imperative of Regular Security Audits and Incident Preparedness
Periodic security audits play an essential role in identifying vulnerabilities within an organization's data protection framework. These comprehensive evaluations should assess the effectiveness of encryption implementations, access controls, validation procedures, and other security measures. Regular audits help ensure security protocols remain current and capable of addressing emerging cyber threats. This holistic approach should include testing incident response plans to verify organizational readiness for potential breaches.
Developing and routinely testing an incident response plan is absolutely critical. Such plans must clearly outline procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents including data leaks. Well-structured response plans minimize breach impacts by enabling swift, organized reactions - a crucial factor in damage mitigation and business continuity preservation.
Motivations and Tactics of Double Extortion Groups
Understanding Motivational Drivers
Double agents operate from complex motivational foundations, often blending personal and political factors. These individuals frequently experience disillusionment with current affiliations, seeking changed circumstances or personal advantage. Their motivations demonstrate remarkable diversity, spanning financial incentives to profound ideological transformations. Understanding these complex drivers proves essential for accurately analyzing and anticipating double agent activities.
The Psychological Toll of Betrayal
Double agents endure significant internal conflict from their dual allegiances. They constantly grapple with the ethical implications of betraying one group for another. This psychological strain often manifests as anxiety, guilt, and paranoia. The act of betrayal itself frequently becomes a source of considerable distress, potentially affecting overall mental health and emotional stability.
Financial Motivations and Material Benefits
Monetary rewards commonly drive individuals toward espionage activities, including double agency. The prospect of substantial payments or access to luxury items can prove irresistibly tempting. Financial considerations often dominate decision-making processes, particularly for individuals experiencing economic hardship or desiring improved lifestyles. The promise of wealth can override better judgment, leading individuals down dangerous paths.
Political Aspirations and Power Dynamics
Political ambitions and power-seeking behaviors frequently motivate double agents. These individuals may attempt to manipulate events or influence outcomes to serve personal or political agendas. The relentless pursuit of power can drive otherwise rational individuals into treacherous situations involving deception and significant personal risk.
Network Exploitation and Relationship Manipulation
Double agents skillfully leverage existing relationships and professional networks to access sensitive information. Their intimate knowledge of organizational structures and personnel provides valuable operational advantages. These same networks often serve as channels for spreading disinformation and creating strategic confusion among targets.
Deception Strategies and Psychological Manipulation
Double agents employ sophisticated deception tactics to manipulate their targets. These methods include psychological manipulation, constructing false narratives, and cultivating trust through calculated relationship-building. They must meticulously maintain appearances of loyalty while secretly working against supposed allies. Such high-stakes deception carries substantial personal risk and potential consequences.
Ideological Convictions and Personal Ethics
Deep-seated beliefs and ethical considerations can significantly influence double agent motivations. Individuals may fundamentally disagree with their assigned group's policies or actions, seeking to undermine them from within. The desire for perceived justice or ethical outcomes can compel otherwise loyal individuals to betray their organizations. These internal conflicts often create intense psychological struggles and moral dilemmas.
While the Soviet space program took a different approach than NASA's Apollo missions, their Luna projects made invaluable contributions to lunar exploration. These robotic missions, which included the first successful soft landings on the Moon, gathered crucial data about surface conditions and composition. Though the Soviets didn't develop true rovers comparable to America's Lunar Roving Vehicles, their achievements informed subsequent rover designs by revealing the Moon's environmental challenges.
The Impact on Businesses and Individuals
Increasing Sophistication of Ransomware Threats
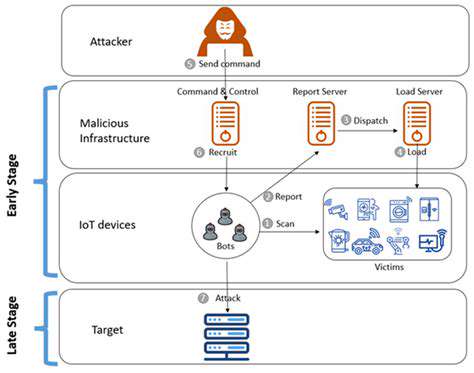
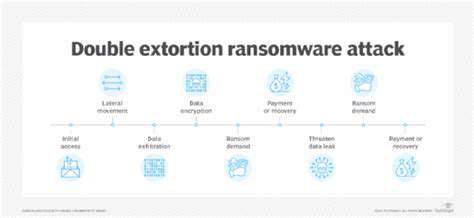
The ransomware threat landscape continues evolving rapidly, advancing beyond basic encryption to more complex, damaging attack methodologies. Attackers now routinely employ sophisticated techniques to infiltrate networks, exfiltrate sensitive data, and deploy multiple extortion mechanisms. Modern attacks not only encrypt files but also threaten public data release if ransom demands go unmet - the defining characteristic of double extortion. This escalation in attack complexity presents serious challenges for businesses across all sectors, compelling substantial investments in advanced cybersecurity solutions.
This evolution owes much to the proliferation of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platforms. These services enable relatively unskilled attackers to launch sophisticated operations, dramatically expanding the threat landscape and attack frequency. The accessibility of these tools represents a major factor in the rise of double extortion incidents.
The Double Extortion Paradigm
Double extortion represents a significant escalation in ransomware tactics. This approach combines traditional data encryption with threats to publish stolen information, creating additional pressure on victims. The added psychological and operational pressure significantly increases the likelihood of ransom payment. Organizations often perceive reputational damage and potential operational disruptions as more severe consequences than the ransom cost itself.
Many attackers now maintain dedicated data leak websites where they publicly post stolen information, creating additional leverage against victims while potentially causing lasting brand damage and eroding customer trust.
Critical Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Ransomware threats no longer exclusively target small businesses. Critical infrastructure sectors - including healthcare, energy, and government agencies - increasingly face sophisticated attacks. These incidents can disrupt essential services with potentially life-threatening consequences, necessitating heightened protective measures for vital systems.
Ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure often result in substantial financial losses and prolonged operational challenges. Recovery processes prove both costly and time-intensive, while public safety implications can be severe and far-reaching.
Financial Consequences for Businesses
Beyond direct ransom payments, businesses face substantial costs related to incident response, data recovery, legal expenses, and reputational harm. Lost productivity, operational disruptions, and potential regulatory penalties can quickly accumulate, making ransomware a potentially existential threat for many organizations. Even when companies pay ransoms, they often incur significant financial burdens.
The financial impact extends beyond immediate response costs. Organizations must invest in enhanced security infrastructure, employee training programs, and comprehensive incident response planning to prevent future attacks - creating ongoing financial pressures.
Personal Privacy Implications
Ransomware attacks frequently compromise sensitive personal information including financial records, medical histories, and identification documents. The potential for subsequent data breaches and identity theft represents serious concerns for affected individuals. These incidents contribute to the ongoing erosion of personal privacy in the digital age.
Individuals face growing vulnerability as ransomware attacks increasingly target sensitive personal data. Implementing strong authentication methods, practicing secure online behaviors, and maintaining threat awareness become essential personal protection measures. The psychological and practical impacts on affected individuals can be profound and long-lasting.
Proactive Security as a Necessity
The escalating sophistication of ransomware attacks demands proactive cybersecurity approaches. Organizations must prioritize robust security measures including multi-factor authentication, prompt software updates, comprehensive network protections, and ongoing employee education. Implementing complete security solutions and adopting forward-looking strategies becomes essential for mitigating future attack risks. This requires both technical solutions and cultural shifts toward security awareness.
Proactive measures should include implementing comprehensive security protocols, conducting regular system audits, and maintaining continuous network monitoring. Additionally, organizations must develop and regularly test detailed incident response plans to ensure preparedness for potential attacks.