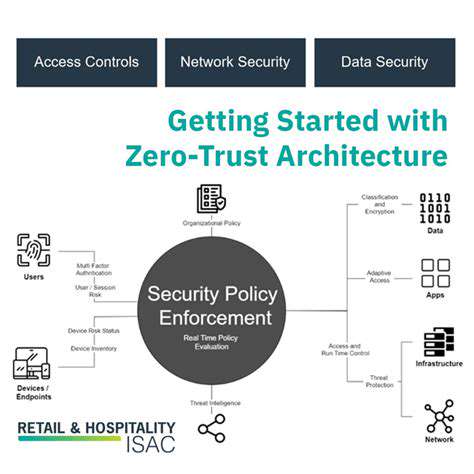
The Evolving Landscape of Supply Chain Threats

The Rise of Global Supply Chains
The global landscape of supply chains is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting geopolitical dynamics, and increasing consumer demands. This evolution has led to a more complex and interconnected web of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Companies are now increasingly reliant on international partnerships and collaborations to ensure efficient and cost-effective production and delivery of goods to consumers worldwide. This interconnectedness, while offering numerous advantages, also presents new challenges in terms of risk management and resilience.
Global supply chains have become incredibly intricate and interdependent, making them vulnerable to disruptions from various sources, including natural disasters, political instability, and pandemics. Managing these risks requires a proactive and adaptable approach, encompassing contingency planning, diversification of suppliers, and robust communication channels.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustainability
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern but a critical factor shaping supply chain strategies. Companies are increasingly under pressure to adopt environmentally friendly practices throughout their supply chains, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and logistics. This includes reducing their carbon footprint, minimizing waste, and promoting ethical labor practices. Meeting these demands requires significant investments in technology and process improvements.
Implementing sustainable practices in supply chains presents significant challenges, but also substantial opportunities. Companies that effectively integrate sustainability into their operations can gain a competitive advantage by attracting environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing their brand reputation, and potentially reducing operational costs in the long run. Sustainable practices can also foster a culture of social responsibility and ethical conduct throughout the entire supply chain, benefiting all stakeholders involved.
Environmental regulations are also becoming more stringent across the globe, impacting sourcing decisions and manufacturing processes. Consequently, companies must adapt to these changes to avoid penalties and maintain compliance.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
technological advancements are revolutionizing the way supply chains operate, from automation and data analytics to blockchain technology and artificial intelligence. Automation is streamlining processes, improving efficiency, and reducing labor costs. Data analytics is providing valuable insights into real-time performance, enabling companies to identify bottlenecks and optimize their operations.
The integration of these technologies is enabling businesses to create more agile and responsive supply chains, capable of adapting to changing market demands and unexpected disruptions. Blockchain technology is enhancing transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain, improving trust and accountability among all stakeholders. Artificial intelligence is further enhancing supply chain prediction and optimization.
These advancements are constantly evolving, and companies must stay abreast of these developments to maintain a competitive edge. Adopting a proactive approach to technological innovation will be crucial for navigating the ever-changing landscape of supply chains.
The use of advanced technologies can lead to increased efficiency and reduced costs, but requires significant investment and expertise to implement effectively.
Proactive Threat Intelligence Gathering and Analysis

Proactive Threat Intelligence Gathering Strategies
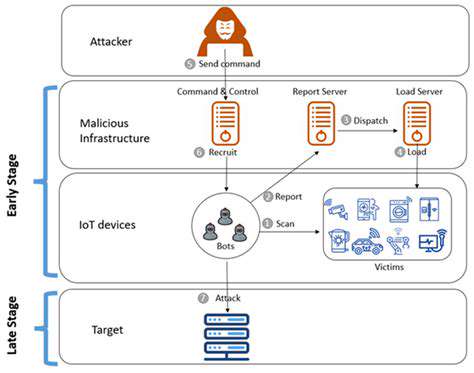
Proactive threat intelligence gathering is crucial for organizations to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats. It involves actively seeking out and analyzing information about potential risks, rather than simply reacting to incidents. This proactive approach allows organizations to identify vulnerabilities and develop preventative measures before attackers exploit them. By understanding the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by threat actors, organizations can tailor their security strategies to mitigate specific risks.
A key aspect of this approach is the implementation of robust threat intelligence platforms and tools. These platforms provide the framework to collect, process, and analyze data from various sources, including open-source intelligence (OSINT), security feeds, and internal logs. Effective threat intelligence gathering also necessitates the establishment of clear procedures and protocols for sharing and disseminating the gathered information across the organization.
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) Techniques
Leveraging open-source intelligence (OSINT) is a vital component of proactive threat intelligence gathering. This involves scouring publicly available information sources such as social media, news articles, forums, and websites to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. By analyzing this information, organizations can gain valuable insights into attacker motivations, targets, and methods.
OSINT research can reveal valuable details about emerging threats, such as new malware families, attack campaigns, or compromised credentials. This information allows security teams to anticipate potential threats and develop effective countermeasures. Furthermore, OSINT can be instrumental in identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) and patterns associated with specific threat actors.
Threat Hunting and Data Analysis
Implementing threat hunting strategies is essential for proactively identifying and responding to advanced threats. This involves actively searching for suspicious activity within an organization's network and systems using various tools and techniques. Threat hunting should be guided by a detailed understanding of the organization's specific attack surface, operational procedures, and potential vulnerabilities. This investigation often involves the use of advanced analytics to spot anomalies and patterns that might indicate malicious activity.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration
Integrating security information and event management (SIEM) systems into the threat intelligence framework is critical. SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources within the organization, providing valuable insights into potential threats. By correlating events and identifying patterns, SIEM systems can help pinpoint suspicious activity and trigger alerts to security personnel.
The data collected from SIEM systems can be combined with other threat intelligence sources to provide a comprehensive view of the threat landscape. This holistic approach allows organizations to make more informed security decisions and implement appropriate countermeasures.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective threat intelligence gathering relies heavily on collaboration and communication across different teams and departments within an organization. Sharing threat intelligence information with relevant stakeholders, such as security operations, incident response, and IT teams, is crucial for a timely and coordinated response to potential threats. Clear communication channels and protocols are essential for ensuring that the gathered intelligence is effectively disseminated and acted upon.
Building relationships with external partners, such as security researchers and industry experts, can also significantly enhance threat intelligence capabilities. This collaborative approach fosters a broader understanding of emerging threats and allows for a more comprehensive threat intelligence strategy.