Challenges Specific to Medical Device Security
Regulatory Hurdles
Securing medical devices presents a distinct set of regulatory obstacles, primarily due to the strict requirements that govern these devices. While these regulations aim to guarantee safety and effectiveness, they can inadvertently hinder the implementation of strong security measures. Device manufacturers must carefully navigate intricate guidelines and standards, such as those established by the FDA in the United States or similar regulatory bodies worldwide, all while incorporating security features into their designs. This process typically demands comprehensive documentation, rigorous testing, and thorough validation procedures, which may lead to increased development expenses and extended timelines.
The regulatory environment surrounding medical devices remains in constant flux. As new threats and vulnerabilities emerge, regulatory bodies frequently introduce updated standards and guidelines. Manufacturers must remain vigilant in tracking these changes, maintaining compliance with shifting requirements, and demonstrating proactive security measures. Neglecting to adapt to these evolving regulations can result in substantial penalties, delays in bringing products to market, and reputational damage within the healthcare sector. This dynamic landscape requires ongoing education, training, and a flexible approach to implementing security measures within the regulatory framework.
Interoperability and Data Management
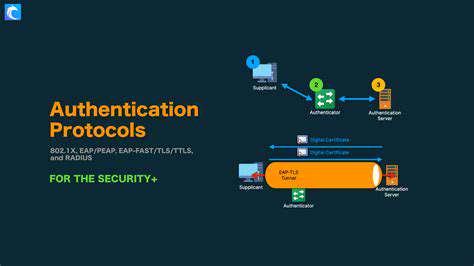
The growing interconnectivity of medical devices through networks and cloud-based systems introduces significant security concerns. Establishing secure communication channels and ensuring safe data exchange between various devices and systems while protecting patient privacy and maintaining data integrity presents a major challenge. Medical devices frequently need to interface with other healthcare systems, including electronic health records (EHRs), imaging systems, and laboratory equipment. While this interoperability enhances efficiency and care coordination, it simultaneously expands potential vulnerabilities if not properly secured.
Handling sensitive patient data generated by medical devices represents another critical issue. This information, often containing highly confidential details, requires strong encryption methods, strict access controls, and secure storage solutions. Compliance with data privacy regulations like HIPAA in the United States is absolutely essential. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse has become increasingly challenging as cyberattacks against healthcare organizations grow more sophisticated.
Collaboration and Continuous Improvement
Fostering a Culture of Collaboration
An effective medical device security program requires a collaborative environment where diverse stakeholders—including engineers, security experts, regulatory professionals, and clinical staff—work together cohesively. This cooperative approach ensures that security considerations are incorporated throughout every phase of the device lifecycle, from initial design through development, manufacturing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
Continuous Security Assessments and Audits
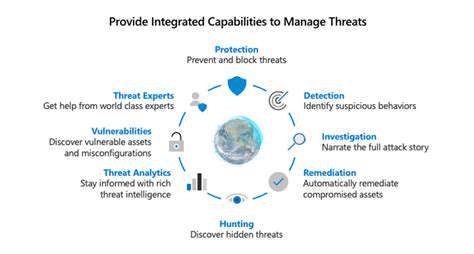
Maintaining medical device security demands ongoing attention rather than a one-time implementation. Regular security evaluations and comprehensive audits are vital for promptly identifying and addressing vulnerabilities. These assessments should encompass the complete device lifecycle, from design and development to deployment and maintenance. Rigorous testing and evaluation of security measures are crucial for verifying their effectiveness in preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
Implementing and Maintaining Security Controls
Robust security controls are fundamental for protecting medical devices from potential threats and vulnerabilities. These protective measures should be implemented and consistently maintained throughout the device's entire operational lifespan. Strong access controls, secure communication protocols, and advanced data encryption techniques form the foundation of a comprehensive security strategy.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
The security threat landscape continues to evolve rapidly, requiring medical device security programs to remain adaptable. Staying informed about emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and technological advancements is essential for maintaining strong security defenses. This includes actively monitoring industry developments, participating in relevant professional events, and seeking external expertise to better understand new security challenges.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Security
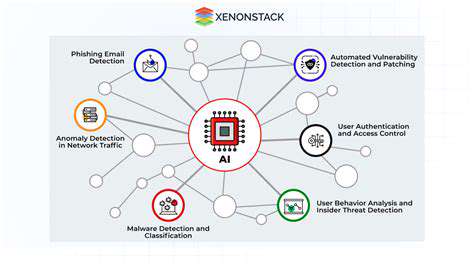
Technological innovations can significantly contribute to strengthening medical device security. Implementing advanced cybersecurity tools—such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption protocols—can substantially improve the overall security of devices and networks. Secure communication channels and remote access protocols are particularly important for ensuring safe data transmission and protecting sensitive patient information.