Implementing Robust Security Measures Across the Entire Chain
Understanding the Criticality of a Secure Supply Chain
In today's globalized economy, a resilient supply chain isn't just an advantage—it's a necessity. While many organizations focus on internal protections, true security demands a holistic view encompassing every link from raw material procurement to customer delivery. This integrated approach requires anticipating disruptions before they occur, safeguarding not just profits but also brand trust and operational reliability.
The consequences of supply chain breaches extend far beyond temporary inconveniences. We've seen how single vulnerabilities can trigger cascading failures, resulting in product recalls, regulatory penalties, and in extreme cases, endangering public safety. Recognizing how each participant and process interconnects forms the foundation for effective risk management.
Identifying Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities
Effective security begins with rigorous threat mapping across all supply chain touchpoints. This means scrutinizing not just your immediate suppliers but their suppliers as well—the so-called fourth-party risk that many overlook. Transportation routes, temporary storage nodes, and even digital information flows all represent potential attack surfaces requiring evaluation.
Seasoned security professionals know audits shouldn't be annual events, but continuous processes adapting to new threats. Whether it's political unrest affecting shipping lanes or newly discovered software vulnerabilities, maintaining current threat intelligence separates reactive organizations from proactive ones.
Implementing Strong Authentication and Access Control
The principle of least privilege becomes particularly crucial in supply chain contexts. Beyond basic password policies, modern systems implement context-aware authentication that considers location, device health, and behavioral patterns before granting access. Biometric verification and hardware security keys now supplement traditional credentials for high-value transactions and sensitive system modifications.
Enhancing Data Security and Encryption
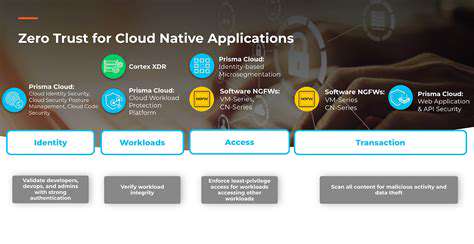
Data protection extends far beyond compliance checkboxes. Forward-thinking organizations employ end-to-end encryption that persists throughout the data lifecycle, coupled with robust key management practices. The most secure networks assume breach scenarios, implementing zero-trust architectures where every access request gets validated regardless of origin.
While technology provides the tools, human factors often determine success. Regular, engaging security training that goes beyond PowerPoint slides helps transform staff from potential vulnerabilities into active defenders.
Establishing Secure Logistics and Transportation
Physical security measures have evolved dramatically with IoT advancements. Modern tracking systems combine GPS with environmental sensors monitoring temperature, humidity, and even unexpected container openings. Blockchain-enabled shipment tracking creates immutable audit trails, while AI-powered anomaly detection flags suspicious patterns in real-time.
Warehouse security now integrates biometric access controls with smart surveillance systems capable of distinguishing between routine activity and potential threats. These layered defenses create overlapping protection zones that deter both opportunistic and targeted attacks.
Promoting Collaboration and Communication
Security silos create dangerous blind spots. Leading organizations establish joint security operations centers where partners share threat intelligence through secure channels. Standardized incident reporting protocols ensure rapid response coordination when threats emerge, while regular tabletop exercises build muscle memory for crisis situations.
The most resilient supply chains cultivate security as a shared value rather than a contractual obligation. This cultural alignment, supported by transparent performance metrics and mutual accountability frameworks, creates self-reinforcing security ecosystems.

Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation to Evolving Threats

Real-Time Data Acquisition
Modern monitoring systems ingest data streams from thousands of edge devices, each serving as a sentinel for potential issues. The art lies in distinguishing signal from noise—implementing smart filtering that surfaces meaningful anomalies without alert fatigue. Distributed ledger technologies now provide tamper-evident records of sensor readings, creating trustworthy audit trails for regulatory and forensic purposes.
Latency kills effectiveness in time-sensitive scenarios. Edge computing architectures process critical data locally when milliseconds matter, while maintaining synchronization with central systems for comprehensive analysis.
Adaptive Algorithms and Models
The most effective systems employ ensemble modeling techniques, where multiple algorithms cross-validate findings to reduce false positives. Self-learning systems now automatically tune their sensitivity based on environmental context, becoming more vigilant during high-risk periods while reducing unnecessary alerts during stable operations.
Model drift represents an insidious challenge in dynamic environments. Continuous validation against ground truth data, coupled with automated retraining pipelines, ensures detection capabilities don't degrade over time.
Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Advanced simulation environments allow security teams to stress-test their supply chains against hypothetical scenarios. Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical networks, enabling safe experimentation with mitigation strategies before implementing them in the real world.
Performance Metrics and Evaluation
Beyond traditional KPIs, mature organizations track leading indicators that predict future security posture. Metrics like mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR) get supplemented with more nuanced measurements of system resilience and adaptive capacity.
Integration with Feedback Loops
The most resilient systems incorporate human expertise through hybrid decision-making frameworks. AI handles routine pattern recognition at scale, while human analysts focus on edge cases and strategic improvements. This symbiotic relationship creates continuous improvement cycles where machine learning models get refined by operational insights, and human operators benefit from AI-powered decision support.