Zero Trust: A Foundation for Secure Access
Zero Trust security models represent a fundamental shift in how organizations approach network security. Instead of relying on implicit trust within a perimeter, Zero Trust assumes no inherent trust for any user, device, or application, regardless of location. This granular approach requires continuous verification and authorization for every access request, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized entities can access sensitive resources. Zero Trust principles emphasize strong authentication methods, micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats.
Implementing a Zero Trust architecture necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the organization's resources and access requirements. This involves carefully defining least privilege access policies, establishing robust identity management systems, and integrating security information and event management (SIEM) tools for continuous threat detection.
SASE: Simplifying Network Security
Software-Defined Access Edge (SASE) is a cloud-native approach to network security that combines multiple security functions into a single platform. This consolidated platform encompasses various security services, including secure web gateways (SWGs), cloud access security brokers (CASBs), and secure SD-WAN solutions. SASE enables organizations to centrally manage and orchestrate these security functions, providing a more streamlined and efficient approach to securing their network perimeter.
The key benefit of SASE lies in its ability to deliver secure access to cloud applications and resources, regardless of location. This agility and flexibility are particularly valuable in today's remote work environment.
The Convergence of Zero Trust and SASE
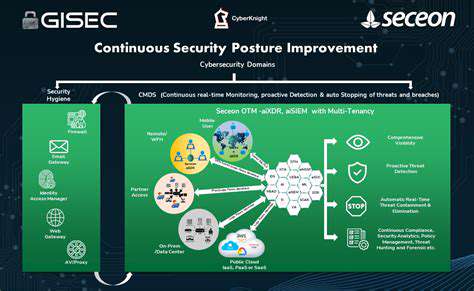
Zero Trust and SASE are not mutually exclusive but rather complementary security strategies. Zero Trust principles provide the foundation for secure access, while SASE delivers the infrastructure and services to support it. By integrating Zero Trust principles into a SASE framework, organizations can create a more comprehensive and robust security posture.
Enhanced Security Posture through Policy Enforcement
A critical aspect of leveraging Zero Trust within a SASE environment is the ability to enforce granular policies. SASE platforms allow for the dynamic enforcement of Zero Trust policies, enabling organizations to adapt security controls based on user, device, and application context. This dynamic policy enforcement ensures that access rights are continuously evaluated and adjusted, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access. Organizations can refine their security controls to best address their specific needs and threat landscape.
Improved Visibility and Control
SASE solutions often provide enhanced visibility into user and device activity, which is crucial for a Zero Trust model. By leveraging the consolidated security platform, organizations gain a holistic view of their network traffic and can identify suspicious activity more quickly. This improved visibility facilitates proactive threat detection and response, enabling organizations to react effectively to evolving security threats.
Simplified Management and Reduced Complexity
The centralized management capabilities of SASE platforms significantly simplify the management of security functions, which is particularly beneficial when implementing a Zero Trust model. Instead of managing multiple disparate security tools, organizations can manage a single platform, reducing complexity and minimizing operational overhead. This simplified management process streamlines security operations, enabling faster response times to threats and reducing the risk of security breaches.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
In addition to the benefits of enhanced security and simplified management, SASE solutions often offer cost-effectiveness and scalability. Centralized management and cloud-native architecture can lead to reduced infrastructure costs. Furthermore, SASE platforms are designed for scalability, enabling organizations to easily adapt their security posture as their needs evolve. This scalability is particularly important in a dynamic and ever-changing threat landscape.