A Paradigm Shift in Security
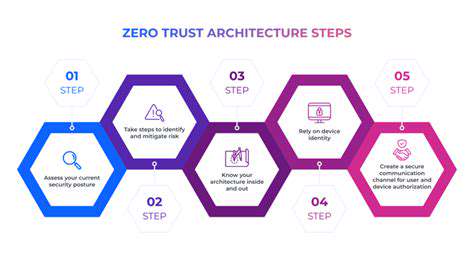
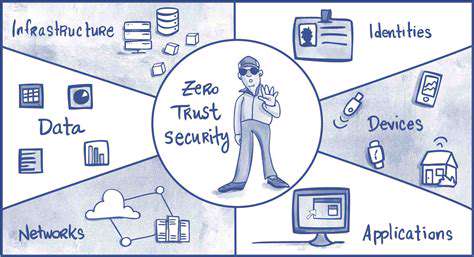
In recent years, the zero trust model has emerged as a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity, fundamentally altering how organizations protect their digital assets. Gone are the days when perimeter defenses alone could suffice; zero trust operates on the principle that no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location within the network. This radical departure from traditional security models demands a thorough reassessment of existing policies to ensure every access request undergoes rigorous verification.
The driving forces behind this shift include increasingly complex network infrastructures, the rise of remote work, and more sophisticated cyber threats. Older security frameworks often fall short in addressing these challenges, creating an urgent need for more dynamic solutions. By adopting zero trust principles, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture while better safeguarding sensitive information against modern threats.
The Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero trust is built on a simple yet powerful mantra: Never trust, always verify. Every user, device, and application must prove its authenticity before gaining access to resources. This verification process extends far beyond traditional network boundaries, covering cloud applications, mobile devices, and other endpoints.
The Role of Identity and Access Management
Effective identity and access management (IAM) serves as the backbone of any zero trust architecture. Comprehensive IAM solutions verify user identities, enforce access controls, and maintain security policies across all systems. Deploying robust IAM systems is essential for establishing trust and preventing unauthorized data access.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other strong verification methods play a critical role in confirming user and device identities while minimizing the risks associated with compromised credentials.
Implementing Zero Trust in Practice
Transitioning to a zero trust framework requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must evaluate their current security measures, identify critical assets, and develop tailored strategies that align with their specific needs. This process includes defining clear security policies, implementing strict access controls, and continuously monitoring network activity for anomalies.
The Benefits of Zero Trust
Organizations that successfully implement zero trust enjoy numerous advantages, including reduced breach risks and enhanced overall security. This approach allows businesses to adapt more effectively to evolving threats while providing stronger defenses against sophisticated attacks. Additionally, zero trust fosters a more secure and productive work environment by minimizing unnecessary access privileges.
The framework also enables organizations to gain deeper insights into user and device activities, facilitating proactive threat detection and faster response times. In today's complex digital landscape, this level of visibility is invaluable for maintaining robust security.
Future Trends and Considerations
Looking ahead, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize zero trust implementations. These technologies can enhance access controls, automate security processes, and improve threat detection capabilities. Equally important is the integration of zero trust with other security solutions like cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems to create comprehensive protection strategies.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and adaptable. Continuous refinement of zero trust methodologies will be essential for maintaining effective security in the face of emerging challenges.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Encryption for Personal Devices

Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Fundamentals
In today's digital landscape, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) has become an indispensable component of cybersecurity strategies. These solutions employ various technologies and methodologies to prevent sensitive data from leaving organizational control, whether through intentional or accidental means. Effective DLP implementations involve identifying, classifying, and monitoring sensitive information to apply appropriate protective measures. Techniques like encryption, access controls, and user behavior analysis help mitigate potential risks.
With various DLP solutions available, understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right approach based on organizational needs and risk profiles. A successful DLP program extends beyond breach prevention to establish comprehensive data protection throughout the information lifecycle.
Implementing DLP Strategies
Developing an effective DLP strategy requires meticulous planning. Organizations must first identify and categorize critical data assets by sensitivity level. Establishing clear policies and procedures for handling sensitive information forms the foundation of any DLP initiative. Regular training programs ensure employees understand security best practices and their role in protecting data.
Periodic reviews and updates of DLP policies are equally important to address evolving threats and compliance requirements. This proactive approach helps maintain the effectiveness of data protection measures over time.
Data Classification and Inventory
A well-structured data classification system serves as the cornerstone of any DLP program. This process involves identifying and categorizing data based on sensitivity and potential impact if compromised. Proper classification ensures appropriate protection levels are applied to different data types, forming the basis for effective security controls.
Access Control and Monitoring
Implementing stringent access controls is essential for preventing unauthorized data access. Permissions should be carefully managed, granted only to authorized personnel, and regularly reviewed to ensure alignment with business needs. Monitoring user activities and access patterns helps detect anomalies and potential security incidents.
Regular audits of access logs provide valuable insights into potential security risks and help identify unauthorized access attempts before they escalate into serious breaches.
Encryption and Data Masking
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information by rendering data unreadable without proper decryption keys, whether in transit or at rest. Data masking offers additional protection by replacing actual values with pseudonymous alternatives, particularly useful for testing and reporting scenarios where full data exposure isn't necessary.
User Education and Training
Comprehensive employee training is critical for DLP success. Regular sessions should cover data security importance, organizational policies, and threat recognition. Equipping staff with proper knowledge and skills significantly reduces the risk of accidental data breaches. Continually updating training content ensures awareness of emerging threats and policy changes.
Compliance and Audit
Maintaining compliance with relevant regulations is crucial for effective DLP programs. Organizations must ensure their policies meet all legal and industry requirements. Regular audits assess program effectiveness and identify improvement areas. Detailed record-keeping of DLP activities demonstrates compliance commitment and provides evidence of security measures.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection for Personal Devices
Understanding the Importance of Continuous Monitoring
In our hyperconnected world, continuous device monitoring has become essential for effective security. The traditional approach of installing security software and forgetting about it no longer suffices. A proactive stance involving constant threat scanning, vulnerability identification, and rapid response is necessary to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity. This approach aligns perfectly with zero-trust principles that view every device and user as potentially compromised until proven otherwise.
Ongoing vigilance safeguards personal devices against diverse threats including malware, phishing attempts, and unauthorized access. Beyond prevention, continuous monitoring enables rapid breach detection and response, minimizing potential damage and facilitating swift recovery – critical considerations in zero-trust environments.
Identifying Potential Threats Through Real-Time Analysis
Real-time analysis of device activity forms the foundation of effective monitoring. Advanced algorithms examine network traffic, application behavior, and user actions to detect anomalies indicating potential threats like malware infections or suspicious access patterns. This capability enables immediate response to emerging risks.
The speed and accuracy of real-time analysis are crucial for limiting breach impacts. By quickly identifying and addressing threats, organizations can prevent data loss, maintain operations, and protect sensitive information – particularly important in zero-trust frameworks requiring verification of every access request.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Comprehensive security measures are essential for personal device protection. These include regularly updated antivirus software, strong authentication methods, and enabled multi-factor authentication where available. Such layered defenses significantly increase the difficulty of successful attacks.
The Role of User Education and Awareness
User awareness plays a vital role in threat detection and prevention. Training programs should educate users about common threats like phishing scams and social engineering tactics. Instruction on safe browsing, password management, and suspicious activity recognition helps prevent security lapses stemming from human error.
Integrating Security Tools and Technologies
A holistic monitoring approach requires seamless integration of various security solutions. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection platforms should work together to provide comprehensive coverage. The effectiveness of these tools depends on their ability to share information and coordinate responses.
Responding to Threats and Maintaining Security Posture
Effective threat response protocols are essential for sustaining security. Clear procedures should address incident containment, investigation, and remediation. Regular security assessments and vulnerability scans help identify and address weaknesses before exploitation, maintaining a strong defensive posture.