Introduction to Zero Trust Architecture
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
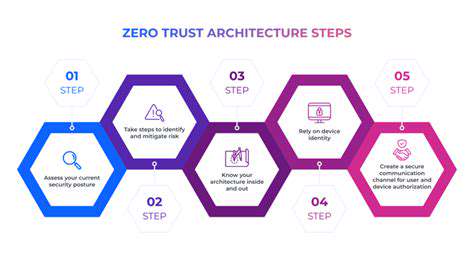
The Zero Trust model represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, abandoning outdated perimeter-based assumptions. Rather than trusting entities inside the network, this framework demands verification at every access attempt. Every device, user, and application must prove its legitimacy before accessing resources, regardless of location. This rigorous approach minimizes potential attack vectors while enhancing overall protection. Unlike reactive security models, Zero Trust anticipates threats before they materialize, creating dynamic barriers against potential breaches.
Transitioning to this model requires more than just upgraded firewalls or VPN solutions. Organizations must implement continuous authentication protocols, sophisticated behavior analysis tools, and comprehensive identity verification systems. These measures ensure that only properly vetted entities interact with critical infrastructure.
Implementing Zero Trust in Azure
Microsoft's cloud platform offers robust capabilities for establishing Zero Trust environments. Azure's integrated services like Azure Active Directory, Virtual Network, and Security Center provide the building blocks for customized security frameworks. These tools enable organizations to create adaptive protection systems that evolve alongside emerging cyber threats.
Key Azure Services for Zero Trust
Azure Active Directory serves as the cornerstone for identity verification. Its comprehensive features support multi-factor authentication, context-aware access policies, and precise permission management. These capabilities ensure that access privileges remain strictly aligned with operational requirements.
Azure Virtual Network facilitates resource isolation through micro-segmentation, while Security Center delivers proactive threat detection. Together, these services form a multi-layered defense system that continuously monitors and protects digital assets.
Benefits and Challenges of Zero Trust in Azure
The Azure implementation offers significant security improvements, including reduced vulnerability exposure and enhanced regulatory compliance. By eliminating implicit trust assumptions, organizations can contain potential breaches more effectively. This creates more reliable cloud ecosystems that inspire confidence among stakeholders.
However, migration complexities shouldn't be underestimated. Legacy system integration and policy management across diverse applications present notable hurdles. Successful adoption requires strategic planning, adequate resource allocation, and phased implementation approaches.

Zero Trust Principles in AWS
Zero Trust Fundamentals in Cloud Environments
AWS security architecture benefits immensely from Zero Trust principles, particularly in hybrid cloud scenarios. The verification-first approach proves essential for combating both internal and external threats. Continuous authentication replaces static perimeter defenses, creating dynamic security postures. This evolution reflects the changing nature of modern IT infrastructures where traditional boundaries no longer exist.
Implementing Zero Trust in AWS
AWS provides extensive tools for implementing least-privilege access models. Identity and Access Management forms the foundation, enabling precise control over resource permissions. Proper configuration ensures users and systems operate with minimal necessary privileges, significantly reducing attack surfaces.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM's granular policy management allows organizations to define exact permission boundaries. Service-specific roles further enhance security by eliminating unnecessary account privileges. These measures prove particularly valuable for preventing lateral movement during security incidents.
Network Security with VPCs and Security Groups
Virtual Private Clouds enable logical isolation of sensitive workloads. Combined with properly configured security groups, they enforce strict traffic flow controls. This network segmentation represents a critical Zero Trust component, limiting potential breach impacts.
Data Protection and Encryption
AWS offers comprehensive encryption solutions for data at rest and in transit. Proper encryption implementation ensures information remains protected throughout its lifecycle. These measures not only secure sensitive data but also support regulatory compliance efforts.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
Real-time monitoring tools provide visibility into user activities and system behaviors. Automated alerts and comprehensive logging enable rapid threat detection and response. This continuous oversight is vital for maintaining Zero Trust integrity over time.
Security Best Practices in AWS Zero Trust
Effective Zero Trust implementations require ongoing attention. Mandatory multi-factor authentication, regular policy reviews, and vulnerability assessments form essential maintenance practices. Proactive security management ensures protection mechanisms remain effective against evolving threats.
Implementing Hybrid Zero Trust Strategies
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
The Zero Trust framework fundamentally transforms security paradigms. By eliminating implicit trust assumptions, organizations achieve more resilient protection across hybrid environments. Every access request undergoes rigorous verification regardless of origin, significantly reducing vulnerability exposure.
Leveraging Azure's Built-in Zero Trust Capabilities
Azure's integrated security features support comprehensive Zero Trust implementations. Conditional Access policies enable dynamic permission adjustments based on contextual factors. These adaptive controls prove particularly valuable for organizations managing distributed workforces.
Implementing a Hybrid Zero Trust Strategy
Successful deployments begin with thorough infrastructure assessments. Detailed mapping of users, devices, and applications informs policy development. This preparatory work ensures security measures align precisely with organizational requirements.
Managing and Monitoring the Zero Trust Architecture
Continuous oversight maintains security effectiveness over time. Azure monitoring tools provide actionable insights into potential threats. Regular policy updates ensure protection mechanisms remain relevant amidst changing business needs and threat landscapes.