Vulnerabilities in Existing Infrastructure
Many retail establishments operate with outdated infrastructure not designed for today's IoT-driven landscape. Older systems, including POS terminals and network hardware, frequently lack the necessary protections, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. A single compromised legacy component can jeopardize the entire network, leading to financial harm and eroded consumer trust.
Merging new IoT devices with aging systems often introduces security blind spots. Without proper integration, critical data pathways remain exposed. Conducting thorough security evaluations helps pinpoint these gaps, allowing businesses to implement targeted safeguards.
The Impact of Data Breaches
When smart retail systems suffer data breaches, the fallout extends beyond immediate financial losses. Stolen customer information—from payment details to purchase histories—can trigger regulatory penalties and long-term brand damage. Implementing multilayered defenses like end-to-end encryption and real-time threat detection is no longer optional.
The true cost of a breach often manifests in dwindling customer confidence and reduced sales. Proactive security investments and well-rehearsed incident response protocols significantly mitigate these risks.
Addressing the Evolving Threat Landscape
Combatting modern cyber threats requires agility and vigilance. Retailers must stay informed about emerging risks through ongoing monitoring and threat intelligence sharing. A defense-in-depth strategy—combining firewalls, access controls, and regular penetration testing—creates robust protection.
Human error remains a critical vulnerability point. Comprehensive staff training, coupled with systematic software updates and strict access management, forms the foundation of a secure retail ecosystem. Prevention-focused security cultures outperform reactive approaches in today's threat environment.
Securing Inventory Management Systems
Implementing Robust Access Controls
Inventory systems demand strict access governance. Role-based permissions, mandatory multi-factor authentication, and periodic credential rotations prevent unauthorized system entry. Detailed activity logs enable rapid detection of suspicious behavior, allowing immediate response to potential breaches.
Protecting Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Encrypting inventory data—both stored and transmitted—forms the first line of defense against compromise. Regular automated backups ensure business continuity during disruptions, while validation protocols maintain information accuracy. These measures collectively preserve the reliability essential for operational decision-making.
Securing Physical Access to Inventory
Digital protections must extend to physical inventory locations. Biometric access systems, 24/7 surveillance, and GPS tracking for high-value items create comprehensive security coverage. Regular facility audits identify and rectify physical security gaps before exploitation.
Implementing Secure Supply Chain Management
Vendor networks represent potential vulnerability points. Secure data exchange protocols and thorough partner vetting processes minimize supply chain risks. Regular security assessments of all supply chain participants ensure continued alignment with organizational security standards.
Ensuring Data Integrity Throughout the Retail Experience

Data Validation Strategies
Automated validation checks at every data touchpoint prevent error propagation. Continuous validation processes, rather than periodic reviews, maintain consistent data quality across retail operations.
Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Geographically dispersed backup storage with regular restoration testing ensures operational resilience. Documented recovery time objectives guide efficient incident response when disruptions occur.
Access Control Mechanisms
Principle of least privilege implementation significantly reduces insider threat risks. Behavior-based access monitoring detects anomalies that traditional controls might miss.
Data Logging and Auditing
Immutable audit trails with blockchain verification provide tamper-proof activity records. Automated alerting on unusual access patterns enables rapid security response.
Regular Data Quality Assessments
Cross-departmental data quality task forces identify systemic issues. Machine learning algorithms increasingly assist in detecting subtle data anomalies.
Data Security Protocols
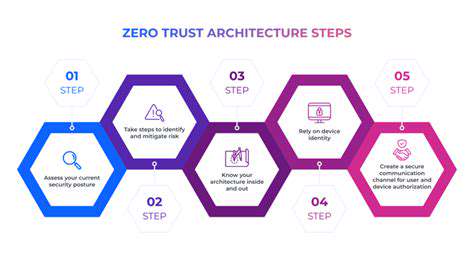
Zero-trust architectures replace perimeter-based security models. Quantum-resistant encryption prepares retailers for future cryptographic challenges.