Developing a Robust Mitigation Strategy: Addressing Identified Risks
Understanding the Scope of Supply Chain Risks
Effective mitigation strategies require thorough comprehension of potential supply chain risks spanning geopolitical instability, natural disasters, supplier financial distress, and transportation network disruptions. Comprehensive vulnerability identification enables development of appropriate countermeasures. Clear risk categorization (operational, financial, reputational) permits targeted mitigation efforts.
Analyzing historical patterns, industry developments, and emerging global challenges proves essential. This evaluation should address both immediate concerns and future possibilities, facilitating proactive rather than reactive responses.
Identifying Critical Supply Chain Nodes
Pinpointing the most vulnerable supply chain points is crucial. This includes recognizing critical suppliers, key transportation routes, and essential production facilities. Evaluating each node's dependencies reveals potential disruption ripple effects. Cross-departmental stakeholder involvement ensures holistic understanding of supply chain interconnectivity.
Developing Contingency Plans for Disruptions
After identifying critical nodes, creating contingency plans becomes imperative. These should specify alternative suppliers, backup transportation options, and downtime minimization procedures. Scenario planning, disruption simulation, and plan refinement based on results form key components of this phase.
Implementing Robust Monitoring and Alert Systems
Proactive monitoring detects potential issues early. Systems tracking KPIs, supplier performance, and market trends enable rapid risk identification. Real-time data feeds and early warning mechanisms help mitigate potential disruptions before escalation. Scalable system design accommodates growth and changing conditions.
Diversifying Supply Sources and Transportation Routes
Reducing dependence on single suppliers and transportation routes enhances resilience. Source diversification minimizes impact from individual supplier failures or disruptions. Exploring alternative transportation methods and routes decreases vulnerability to regional or mode-specific problems. Diversification strategies should align with each product or service's unique requirements.
Strengthening Supplier Relationships and Collaboration
Strong supplier relationships enable smooth operations and early risk detection. Open communication, shared risk assessment, and joint planning initiatives promote collaboration. This facilitates proactive problem-solving and mutually beneficial solution development, increasing transparency and shared responsibility throughout the supply chain.
Regular Risk Assessments and Training
Ongoing risk evaluations and employee training maintain mitigation strategy effectiveness. Assessments should evaluate current measures and identify new vulnerabilities from changing market conditions. Training programs equip staff with risk identification and response skills, ensuring organizational preparedness. Continuous improvement adapts strategies to evolving global threats.
Implementing Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: A Dynamic Approach
Defining the Scope of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring requires customized solutions. Understanding specific supply chain components and processes is essential. This involves identifying KPIs impacting business objectives like order fulfillment time, inventory turnover, and supplier lead times. Clear metric definition and baseline establishment enable effective progress tracking and improvement identification. The scope should align with specific needs and resources, focusing initially on the most impactful elements.
Careful evaluation of available data sources is crucial. This includes internal data from ERP, warehouse management, and transportation management systems, plus external supplier and logistics partner data. Integrating these diverse sources into a unified platform provides comprehensive supply chain visibility and enables real-time monitoring, ensuring all relevant aspects receive coverage.
Leveraging Technology for Real-Time Insights
Modern supply chains depend on technology for efficient operations and data analysis. Implementing real-time tracking, advanced analytics, and predictive modeling provides valuable disruption and bottleneck insights. These technologies enable anomaly detection, facilitating proactive responses that minimize delays or disruptions.
Technology integration with existing systems must ensure seamless data flow. Technology selection should match supply chain needs and consider integration requirements with current platforms. Strong data security protocols protect sensitive information and ensure regulatory compliance.
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Clear, measurable KPIs form the foundation of continuous monitoring and improvement strategies. These should reflect supply chain priorities including order fulfillment accuracy, on-time delivery rates, inventory levels, and supplier performance. Focus on these critical metrics provides comprehensive performance understanding and identifies improvement areas.
Regular KPI review and adjustment ensures continued relevance to evolving business needs. This iterative process enables adaptation to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities. Effective KPI utilization supports data-driven supply chain management.
Implementing a Feedback Loop for Continuous Improvement
A robust feedback mechanism is essential for continuous improvement. This system should gather input from internal teams, customers, and suppliers. Analyzing this feedback reveals optimization and improvement opportunities, providing insights for proactive problem-solving.
Actively soliciting feedback across all supply chain levels is vital. Methods may include surveys, focus groups, and direct communication channels. Incorporating diverse perspectives yields comprehensive understanding of challenges and opportunities, enabling significant efficiency and responsiveness improvements.
Developing a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Successful continuous monitoring and improvement requires a culture embracing change and learning. This involves creating a collaborative environment where employees at all levels feel empowered to identify and suggest improvements, essential for developing a dynamic, adaptable supply chain.
This improvement culture extends beyond problem identification to encourage proactive solutions and best practice implementation. Regular training and development programs equip employees with necessary skills and knowledge to contribute effectively, fostering proactive problem-solving throughout the supply chain.
Addressing Potential Disruptions and Risks
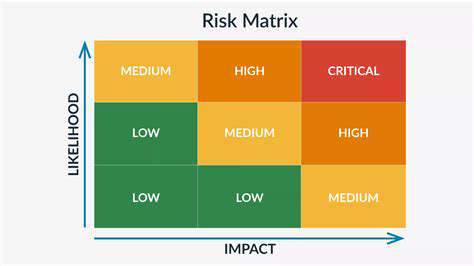
Supply chains naturally face disruption risks ranging from natural disasters to geopolitical events. Implementing a strong risk management framework identifies potential disruptions and develops contingency plans. Understanding various risks' potential impacts enables appropriate mitigation strategy development.
Comprehensive risk assessment processes proactively identify and address potential issues. These evaluations should consider multiple factors from natural disasters to economic fluctuations. Anticipating and preparing for potential disruptions maintains resilience and ensures ongoing supply chain stability.