Selecting the right container for coffee storage plays a pivotal role in preserving freshness while keeping unwanted kitchen odors at bay. Opt for containers made of glass, ceramic, or high-quality plastic that offer durability and resist damage from daily use. The key lies in selecting a container with an airtight seal - this barrier prevents moisture, air, and pests from compromising your coffee's quality while maintaining its rich aroma and flavor profile over time.
Advanced Zero Trust Implementation Strategies
Adapting Zero Trust to Varied Infrastructure
While the core concepts of zero trust remain constant, their application demands careful customization across different technological environments. Security teams must address the distinct requirements of cloud platforms, traditional data centers, and hybrid systems separately. Each environment presents unique security challenges that require tailored solutions while maintaining the fundamental principle of least privilege access throughout the organization's digital ecosystem.
Evolving Security in Response to Modern Threats
Today's cybersecurity threats demonstrate unprecedented sophistication, often exploiting overlooked vulnerabilities. A dynamic zero trust framework must incorporate real-time threat intelligence and adaptive risk evaluation to counter emerging attack vectors effectively. Organizations should complement these technical measures with regular security training programs to mitigate risks stemming from human error, which remains one of the most common entry points for cyberattacks.
The Critical Role of Network Microsegmentation
Implementing microsegmentation transforms network security by creating isolated zones that contain potential breaches. This approach dramatically reduces the attack surface area while enabling more precise monitoring and control of network traffic. Security teams gain the ability to quickly identify and respond to suspicious activities within specific segments without compromising the entire network infrastructure.
Unifying Identity Management with Zero Trust
Robust identity verification forms the backbone of effective zero trust implementation. Modern IAM systems must authenticate both users and devices with multiple verification factors before granting resource access. While integrating these systems with existing infrastructure may require substantial modifications, the enhanced security benefits justify the investment for organizations handling sensitive data.
Real-Time Security Monitoring Systems
Continuous surveillance represents a non-negotiable component of zero trust security frameworks. Advanced monitoring tools provide immediate alerts about unusual activities, enabling security personnel to respond to potential threats before they escalate. Automated response mechanisms further strengthen defenses by rapidly containing security incidents with minimal human intervention.
Cloud-Specific Zero Trust Solutions
The distributed nature of cloud computing creates unique security challenges that demand specialized zero trust solutions. Security policies must maintain consistency across multiple cloud platforms while accommodating the inherent flexibility of cloud environments. This requires innovative approaches to access control that protect data regardless of its physical or virtual location.
Human Factors in Security Implementation
Technological solutions alone cannot guarantee comprehensive security. Regular training programs that educate staff about phishing attempts, password security, and threat recognition create an essential human firewall. Fostering a company-wide culture of security awareness significantly enhances an organization's overall defensive posture.
The Path Forward: Zero Trust as Standard Practice

Artificial Intelligence in Modern Cybersecurity
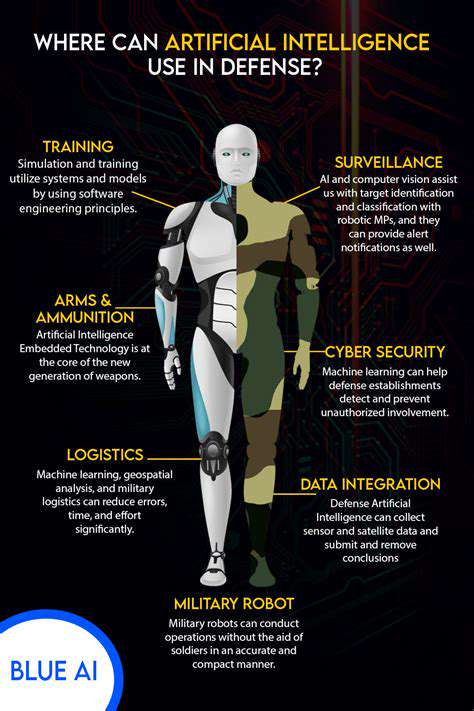
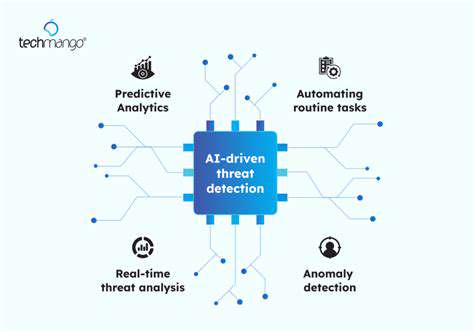
The cybersecurity field is undergoing radical transformation through AI integration. Advanced AI systems can process enormous security datasets to detect subtle threat patterns, revolutionizing how organizations identify and respond to potential breaches. These intelligent systems automate routine monitoring tasks while flagging anomalies that might escape human notice. However, the complexity of AI algorithms introduces challenges regarding decision transparency and vulnerability to specialized attacks targeting the AI systems themselves.
The Necessity of Zero Trust Frameworks
Traditional perimeter-based security models prove increasingly inadequate against contemporary threats. Zero trust architectures operate on the fundamental principle of never trust, always verify, subjecting every access request to rigorous scrutiny regardless of origin. Implementing this approach requires comprehensive identity verification systems and behavior monitoring that extend across all digital assets, including cloud resources and mobile devices. The transition demands significant organizational commitment but delivers substantially improved protection against modern cyber threats.
Data Protection in Regulatory Environments
Evolving privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA compel organizations to strengthen their data protection measures. Compliance involves implementing robust security controls and establishing transparent data handling procedures. The global nature of digital information flows necessitates international cooperation to develop consistent privacy standards that protect users across jurisdictions. Beyond regulatory requirements, ethical considerations about data usage are gaining prominence, influencing corporate policies and consumer expectations alike.