The Rise of Double and Triple Extortion

The Phenomenon of Double and Triple Extortion
Recent years have witnessed an alarming escalation in cyber extortion tactics, with criminals now employing double and triple extortion strategies that significantly increase pressure on victims. These sophisticated approaches represent a fundamental shift in the cyber threat landscape, moving beyond simple data encryption to comprehensive attack methodologies.
Modern cybercriminals don't just encrypt data - they steal it, threaten to leak it, and often contact victims' clients and partners to maximize financial pressure. This multi-pronged approach has proven devastatingly effective, with many organizations feeling compelled to pay ransoms they might otherwise refuse.
Understanding the Criminal Methodology
Several factors explain why these advanced extortion techniques have become so prevalent. The primary driver is simple economics - by adding multiple pressure points, attackers dramatically increase their chances of payment. When organizations face not just operational disruption but also reputational damage and regulatory penalties, the calculus changes significantly.
Another critical factor is the professionalization of cybercrime. Today's ransomware groups operate with business-like efficiency, carefully researching targets and tailoring their approaches for maximum impact. They understand exactly which threats will resonate most with different types of organizations.
Impact Across Industries
The effects of these advanced extortion methods vary by sector but are universally damaging. Healthcare organizations face particularly severe consequences, as patient data leaks can trigger regulatory actions and erode public trust. Financial institutions grapple with the potential disclosure of sensitive client information, while manufacturers risk having proprietary designs and processes exposed.
Educational institutions have become frequent targets, with attackers recognizing the value of research data and the sensitivity of student records. No sector appears immune to these evolving threats, requiring universal vigilance and preparation.
Technological Enablers
Several technological developments have facilitated the rise of multi-stage extortion. The availability of sophisticated malware kits on dark web marketplaces has lowered the barrier to entry for would-be attackers. Meanwhile, the proliferation of cloud storage and collaboration tools has created more potential entry points and data exfiltration channels.
The anonymity provided by cryptocurrencies and the dark web has made these crimes both more profitable and harder to trace. These factors combine to create an environment where advanced extortion schemes can flourish.
Defensive Challenges
Organizations face significant hurdles in defending against these multifaceted attacks. Traditional backup strategies, while still essential, no longer provide complete protection when data theft becomes part of the equation. The speed of modern attacks often outpaces detection capabilities, with some ransomware strains able to encrypt entire networks in minutes.
Perhaps most challenging is the psychological dimension - the threat of public exposure creates intense pressure that cloud's rational decision-making. Many security professionals report that these attacks feel fundamentally different from traditional cyber threats in their psychological impact.
The Path Forward
Looking ahead, we can expect these tactics to continue evolving. Some experts predict the emergence of quadruple extortion schemes incorporating additional pressure points. At the same time, improved defenses and international law enforcement cooperation may help mitigate the threat.
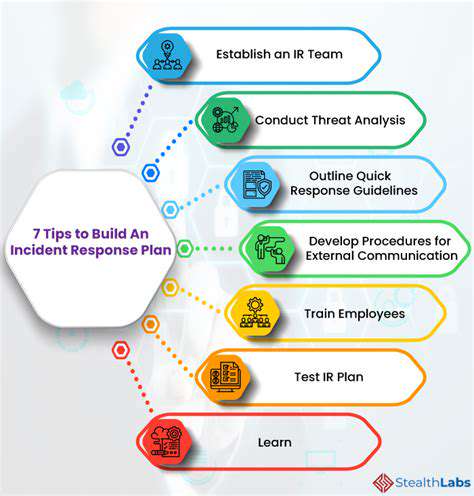
The most effective defense will likely combine advanced technical controls with comprehensive incident response planning and regular staff training. Organizations that prepare holistically will be best positioned to withstand these sophisticated attacks.
Targeted Attacks and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The New Era of Precision Targeting
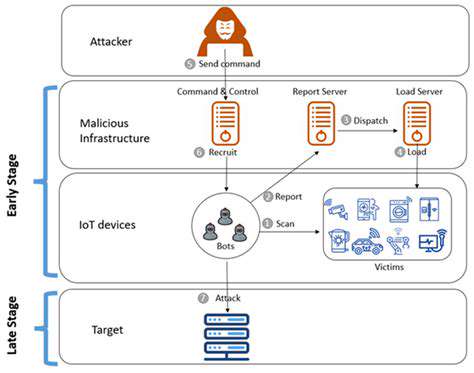
Contemporary ransomware campaigns have shifted dramatically from scattergun approaches to surgical strikes against carefully selected targets. Attackers now conduct extensive reconnaissance, sometimes spending months inside networks before triggering encryption. This patient approach allows them to identify and compromise backup systems, security controls, and critical data stores.
The financial motivation behind this shift is clear - targeted attacks against organizations with strong cybersecurity insurance and ample resources yield significantly higher payouts. Some recent attacks have resulted in eight-figure ransom demands, a far cry from the modest sums demanded in early ransomware campaigns.
Supply Chain as Attack Vector
The interconnected nature of modern business ecosystems creates numerous soft targets for attackers. By compromising a single software vendor or IT service provider, criminals can potentially access hundreds or thousands of downstream organizations. This approach offers tremendous efficiency for attackers, making supply chain attacks particularly attractive.
Recent high-profile incidents have demonstrated how a single vulnerable link can endanger entire industries. The SolarWinds attack revealed how deeply supply chain compromises can penetrate even well-defended networks. These incidents have forced organizations to completely rethink their third-party risk management approaches.
Zero-Day Exploits in the Wild
The use of previously unknown vulnerabilities has become a hallmark of advanced ransomware groups. These zero-day exploits provide attackers with a critical advantage, as defenders have no patches or signatures to detect them. The growing market for these exploits on the dark web has made them more accessible to criminal groups.
What makes these particularly dangerous is their ability to bypass traditional security controls. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus solutions typically can't stop attacks leveraging unknown vulnerabilities. This reality has driven increased investment in behavior-based detection systems that don't rely on known signatures.
The Ransomware-as-a-Service Ecosystem
The professionalization of cybercrime has reached new heights with the maturation of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) platforms. These criminal franchises provide would-be attackers with sophisticated malware, payment processing, and even customer support - all for a cut of the profits. This model has dramatically expanded the pool of potential attackers.
Recent law enforcement actions have revealed the industrial scale of some RaaS operations, complete with HR departments, performance metrics, and employee benefits. This level of organization helps explain the relentless pace of ransomware attacks in recent years.
Data Exfiltration as Standard Practice
Where data theft was once the exception in ransomware attacks, it has now become the rule. Nearly all major ransomware groups now routinely exfiltrate data before encryption, using the threat of exposure to compel payment. This practice has created secondary markets for stolen data, with some groups auctioning it to other criminals if the original victim refuses to pay.
The regulatory implications of this trend are significant. Many organizations now face potential fines for data breaches regardless of whether they pay the ransom. This has forced a reevaluation of incident response plans across industries.
Building Resilient Defenses
Effective defense against these advanced threats requires a layered approach. Network segmentation can limit lateral movement, while robust endpoint detection can identify suspicious activity. Perhaps most critically, organizations must assume breach and focus on limiting damage through strict access controls and comprehensive monitoring.
The most resilient organizations are those that regularly test their defenses through red team exercises and continuously update their security postures. In today's threat environment, static defenses simply can't keep pace with evolving attacker tactics.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Defense
AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a critical tool in the fight against advanced cyber threats. Modern security systems leverage machine learning to detect anomalies that might indicate malicious activity. These systems can analyze vast amounts of network traffic, identifying subtle patterns that human analysts might miss.
The most effective AI systems combine supervised learning with unsupervised techniques, allowing them to detect both known attack patterns and novel threats. This dual approach is particularly valuable in identifying zero-day exploits and sophisticated ransomware campaigns.
Practical Applications
In real-world deployments, AI-enhanced security tools have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness. Some systems can now predict potential attack vectors by analyzing an organization's digital footprint. Others use natural language processing to scan for phishing attempts in emails with human-like comprehension.
Behavioral analytics represent another powerful application. By establishing baselines for normal user activity, these systems can flag suspicious behavior that might indicate account compromise. This capability is particularly valuable for detecting the early stages of ransomware attacks.
Ethical and Operational Challenges
While promising, AI security tools aren't without their challenges. False positives remain an issue, with some systems generating numerous alerts that require human verification. There are also concerns about bias in training data and the potential for attackers to manipulate AI systems.
Perhaps most critically, these tools require significant expertise to implement effectively. Many organizations struggle with integration challenges and the need for continuous tuning. AI should augment human analysts, not replace them - the combination of human intuition and machine scale proves most effective.
Future Directions
The next generation of AI security tools will likely focus on predictive capabilities. By analyzing threat intelligence feeds and organizational vulnerabilities, these systems may eventually forecast attack likelihood with surprising accuracy. Some researchers are exploring the use of AI for automated patching and system hardening.
Another promising area involves using AI to simulate attacker behavior, helping organizations identify weaknesses before criminals can exploit them. As these technologies mature, they may fundamentally change how we approach cybersecurity.
Advanced Encryption Techniques and Data Loss Prevention
Modern Encryption Standards
Contemporary encryption methods have evolved significantly to counter increasingly sophisticated threats. Quantum-resistant algorithms are now being developed to prepare for future computing capabilities. Current best practices emphasize not just strong encryption, but proper key management and rotation policies.
The implementation of homomorphic encryption allows some computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption. While still computationally intensive, this approach shows promise for securing sensitive operations in untrusted environments.
Comprehensive DLP Strategies
Effective data loss prevention requires more than just technology solutions. Organizations must develop clear data classification policies, ensuring sensitive information is properly identified and protected. Employee training plays a crucial role, as human error remains a leading cause of data breaches.
The most successful DLP programs combine technical controls with cultural change, creating an environment where data protection becomes everyone's responsibility. Regular audits and testing help ensure these measures remain effective over time.
AI-Enhanced Security
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being deployed to monitor data flows and detect potential exfiltration attempts. These systems can learn normal data access patterns and flag anomalies that might indicate compromise. Some advanced solutions can even automatically respond to potential threats by restricting access or isolating affected systems.
Natural language processing enables these systems to understand context, helping distinguish between legitimate data transfers and potential breaches. This contextual awareness significantly reduces false positives compared to traditional rule-based systems.
Building Security Awareness
Effective security training must evolve beyond annual compliance exercises. Modern programs use engaging, scenario-based training that resonates with employees. Phishing simulations, tabletop exercises, and gamified learning experiences have all proven effective.
The most security-conscious organizations foster cultures where employees feel comfortable reporting potential threats without fear of reprisal. This open approach helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers.