The Rise of Connected Devices
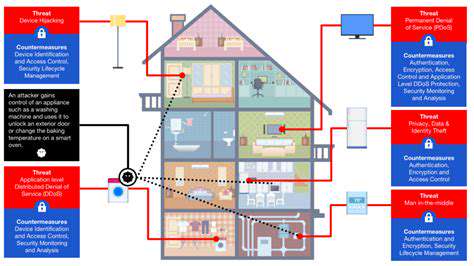
Modern enterprises now face unprecedented cybersecurity challenges due to the widespread adoption of internet-connected devices. From household appliances to industrial control systems, these technologies have created new vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit. What makes this particularly concerning is that many IoT devices ship with default credentials and minimal security protections, effectively creating an open invitation for attackers. The rapid deployment of these technologies often outpaces the implementation of proper security measures, leaving organizations scrambling to secure their networks.
Consider how hospitals now rely on connected medical devices or how manufacturing plants use networked equipment. A single compromised device in these environments could disrupt critical operations or expose sensitive data. Security teams must adopt holistic strategies that account for both the technical and operational aspects of these emerging threats.
The Shadow IT Challenge
Employee-driven technology adoption presents another growing concern for security professionals. When staff members use unauthorized cloud services or personal devices for work purposes, they create invisible gaps in organizational defenses. These shadow IT systems typically lack the security controls and monitoring capabilities that enterprise IT departments implement, making them prime targets for exploitation.
Forward-thinking organizations are addressing this issue through a combination of employee education and improved internal IT offerings. By understanding why employees bypass official channels and providing secure alternatives that meet their needs, companies can significantly reduce this hidden risk.
Cloud Security Considerations
The migration to cloud platforms has transformed traditional security paradigms. While cloud providers offer robust infrastructure protections, customers must understand they retain responsibility for securing their data and applications within these environments. This shared responsibility model requires organizations to implement additional controls for identity management, data encryption, and access governance.
Financial institutions handling sensitive customer data, for example, must implement extra layers of protection when using cloud services. They need to carefully evaluate their cloud provider's security certifications and ensure their internal controls complement the provider's safeguards.
Human Vulnerabilities in Cybersecurity
Despite technological advancements, people remain the weakest link in most security chains. Attackers increasingly rely on sophisticated social engineering techniques that exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Recent studies show that over 90% of successful breaches start with phishing attacks, demonstrating the critical need for comprehensive security awareness training.
Organizations that invest in continuous employee education see measurable reductions in security incidents. Effective programs go beyond annual training sessions, incorporating simulated phishing tests and real-world examples to reinforce learning. When employees can recognize and report suspicious activity, they become an organization's strongest defense rather than its greatest vulnerability.
Identifying and Assessing Vendor Risks: A Multi-Layered Approach

Understanding Vendor Risk
Third-party risk management has become a board-level concern as organizations recognize how vendor relationships can impact their security posture. A comprehensive evaluation process should examine not just a vendor's technical controls, but also their financial health, geographic risks, and compliance history. Particular attention should be paid to vendors who handle sensitive data or provide critical services, as their failures could have cascading effects.
For instance, a payroll processing vendor experiencing a breach could expose employee financial information, while a cloud hosting provider outage might take down multiple customer systems. These scenarios demonstrate why rigorous vendor assessments are no longer optional but essential components of enterprise risk management.
Assessing Potential Impacts
Effective vendor risk analysis requires evaluating both likelihood and potential consequences. Security teams should consider worst-case scenarios: How would a vendor bankruptcy, data breach, or service disruption affect operations? Quantifying these risks helps prioritize mitigation efforts and allocate resources effectively. Some organizations use scoring systems to rate vendors based on their criticality and risk profile.
The financial sector provides instructive examples. Banks must assess whether their payment processors maintain adequate fraud controls, while investment firms need to verify their data providers' information security measures. In each case, the potential financial and reputational damage from vendor failures justifies thorough due diligence.
Implementing Risk Mitigation Strategies
After identifying vendor risks, organizations should implement appropriate controls. These might include contractual requirements for security audits, performance bonds, or security incident notification procedures. Establishing clear service level agreements with measurable benchmarks helps maintain accountability throughout the vendor relationship.
Some companies adopt a defense-in-depth approach, maintaining secondary vendors for critical functions to ensure business continuity. Others implement continuous monitoring solutions that track vendor security postures in real-time. The most effective programs combine contractual protections with active oversight and regular reassessment.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Staying Ahead of the Curve

The Importance of Ongoing Vigilance
Modern security operations require constant attention rather than periodic reviews. Advanced monitoring tools can detect anomalies in user behavior, network traffic, and system performance that might indicate emerging threats. By analyzing these patterns, security teams can identify potential issues before they cause significant damage.
Performance Optimization Through Data
Comprehensive monitoring generates valuable operational intelligence. IT departments can use this data to identify inefficient processes, underutilized resources, or potential capacity constraints. Data-driven decision making allows organizations to optimize their technology investments while maintaining high availability.
Building Responsive Security Postures
The most resilient organizations treat security as an evolving process rather than a fixed state. They regularly update controls based on new threat intelligence and adjust configurations in response to changing business needs. This adaptive approach helps maintain strong defenses against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Integrating Automation
Automated alerting systems play a crucial role in modern security operations. By configuring rules that trigger notifications for specific events, teams can respond to issues more quickly and consistently. When properly implemented, automation reduces response times while minimizing human error in routine security processes.