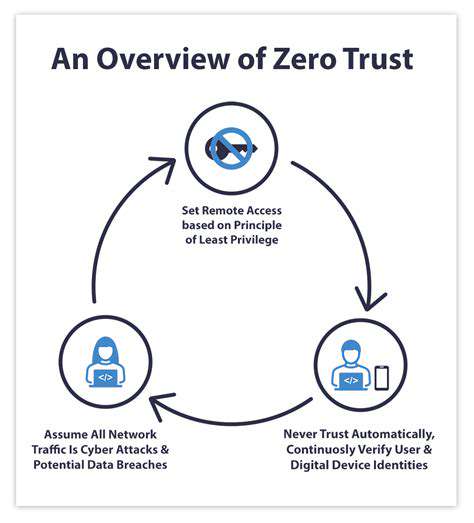
Central to this philosophy is real-time security assessment. Threats evolve constantly, and static defenses become obsolete quickly. Zero trust requires adaptive security measures that continuously evaluate risks and adjust protections accordingly. This dynamic methodology creates a far more resilient security infrastructure.
Implementing Zero Trust in Practice
Transitioning to zero trust isn't about installing new software—it's a complete security overhaul. Organizations must redesign their access frameworks from the ground up, incorporating sophisticated identity verification systems, precise permission controls, and cutting-edge threat detection capabilities.
Employee education forms the human firewall in zero trust implementations. Staff members must become vigilant about authentication protocols and recognize the dangers of careless information sharing. Cultivating this security mindset transforms employees into active participants in cyber defense.
Key Components of a Zero Trust Architecture
Effective zero trust systems incorporate multiple protective layers. Mandatory multi-factor authentication, network micro-segmentation, and routine security evaluations create overlapping defenses. These measures work together to identify and neutralize vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Minimal access privileges represent a critical safeguard. By restricting users to only the resources absolutely required for their roles, organizations dramatically reduce potential damage from compromised accounts.
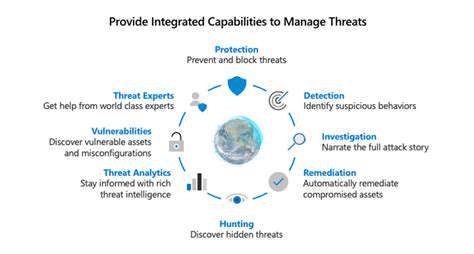
Advanced monitoring solutions provide continuous surveillance, detecting abnormal patterns that might indicate security breaches. These systems enable rapid response to emerging threats before they escalate.
Benefits and Challenges of Zero Trust
The zero trust model delivers substantial security improvements, including minimized attack vectors, stronger data protection, and better regulatory compliance. These enhancements significantly boost stakeholder confidence in the organization's security capabilities.
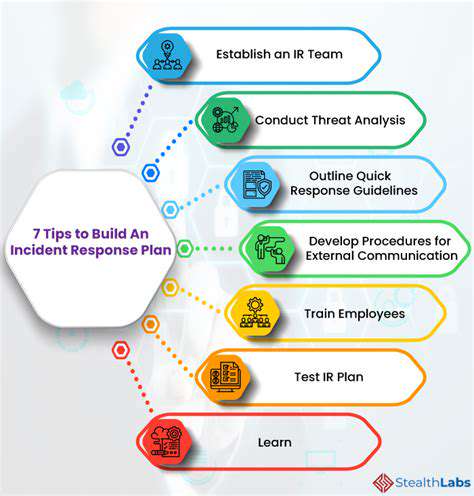
However, adoption hurdles exist. The transformation requires substantial technological investment and careful integration with legacy systems. The complexity of these implementations shouldn't be underestimated.
Cultural adaptation proves equally important as technical implementation. Comprehensive training programs and clear communication help staff understand and embrace the new security protocols, ensuring smooth organizational transition.
Micro-Segmentation and Network Segmentation
Understanding Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation revolutionizes network security by creating ultra-fine security zones, sometimes isolating individual applications. This precision targeting differs fundamentally from conventional broad network divisions, offering superior protection against lateral threat movement during breaches.
This methodology transforms network defense by containing threats at their point of entry. The containment strategy prevents attackers from pivoting to other systems, dramatically reducing potential damage.
Benefits of Implementing Micro-Segmentation
Beyond security enhancements, micro-segmentation delivers operational advantages. The technology provides unprecedented network visibility and accelerates threat response times. Security teams gain real-time insights into network activity, enabling faster anomaly detection and resolution.
The detailed traffic monitoring capabilities allow security personnel to identify suspicious patterns immediately. This proactive monitoring is essential for countering sophisticated, evolving cyber threats.
Network Segmentation Strategies
Effective segmentation employs multiple approaches, from functional divisions to virtual network isolation. Success depends on carefully crafted access policies that match organizational needs. Each segment requires customized security parameters that reflect its specific risk profile and operational requirements.
Precise access control definitions form the backbone of effective segmentation. These rules ensure that only properly authenticated entities can interact with specific network resources, creating multiple security checkpoints throughout the infrastructure.
Zero Trust Principles and Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation embodies Zero Trust philosophy by enforcing strict access validation at microscopic levels. Each request undergoes verification, regardless of origin, creating consistent security enforcement across all network segments. This alignment strengthens the overall security framework through uniform policy application.
Tools and Technologies for Micro-Segmentation
The market offers diverse micro-segmentation solutions, from software-defined networking platforms to purpose-built security appliances. Selection criteria should emphasize compatibility with existing systems, allowing for phased implementation without disrupting current operations.
Solution evaluation must consider long-term operational factors including scalability and management complexity. The ideal platform balances current needs with future growth potential.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
Micro-segmentation introduces administrative complexity, particularly in large-scale deployments. Careful planning and staged rollouts help mitigate operational disruptions. Integration with legacy systems often requires customized solutions to bridge technological gaps.
Implementation teams must prioritize maintaining business continuity during transitions. Thorough testing in controlled environments helps identify and resolve potential issues before they affect production systems.