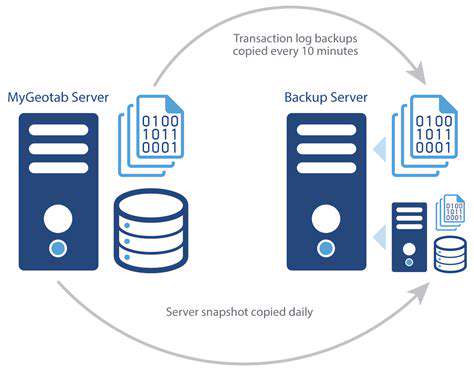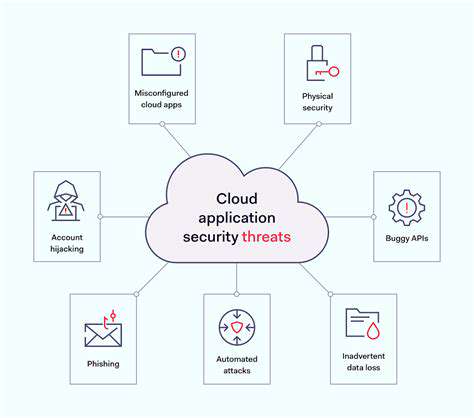
Understanding the Hybrid Cloud Landscape
Securing hybrid cloud environments requires navigating a labyrinth of interconnected systems, where traditional security perimeters dissolve. Unlike monolithic infrastructures, these setups blend legacy on-premises hardware with elastic cloud services, creating a patchwork of potential entry points for attackers. Security teams must map every digital touchpoint across this fragmented terrain before deploying Zero Trust safeguards. Comprehensive audits of data flows, API connections, and cross-platform dependencies form the essential groundwork for effective protection.
Defining Zero Trust Principles
The Zero Trust paradigm shatters decades-old assumptions about network security. Rather than operating on inherited trust from network location, this model treats every access request as a potential threat until verified. Each login attempt, API call, or system handshake undergoes rigorous scrutiny regardless of origin. This philosophical shift demands continuous validation of credentials, device health checks, and context-aware authorization protocols throughout every digital interaction.
Establishing a Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) System
Modern IAM solutions act as the gatekeepers of Zero Trust architectures. Beyond basic multi-factor authentication, they incorporate behavioral biometrics, device fingerprinting, and risk-based adaptive controls. Privileges aren't static grants but dynamic permissions that adjust based on real-time risk assessments. For instance, a finance team member accessing sensitive records from an unrecognized device might trigger additional verification steps or temporary access restrictions until identity confirmation.
Implementing Micro-segmentation
Network segmentation in Zero Trust environments resembles a high-security facility with multiple airlock chambers. Each segment operates as an isolated security zone, with traffic flows strictly governed by policy engines. When properly configured, these digital compartments contain threats like biological containment units, preventing malware outbreaks from spreading across network segments. The implementation requires meticulous mapping of application dependencies to avoid creating availability bottlenecks while maintaining stringent access controls.
Enhancing Security Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust transforms security operations centers into high-alert monitoring hubs. Next-generation SIEM platforms now incorporate machine learning to detect anomalous patterns across hybrid environments. Security teams must balance automated alerts with human expertise to distinguish between false positives and genuine threats in these complex ecosystems. Regular purple team exercises help validate detection capabilities while exposing blind spots in monitoring coverage.
Implementing Secure Remote Access
The modern workforce's mobility demands reinvented remote access strategies. Zero Trust remote solutions replace legacy VPNs with identity-aware proxy services that evaluate multiple risk factors before granting access. Each session establishes ephemeral connections with just-in-time privileges that disappear after task completion, significantly reducing the attack surface. These systems integrate with endpoint detection platforms to verify device security posture before permitting any resource access.
Regular Security Assessments and Continuous Improvement
Maintaining Zero Trust efficacy requires perpetual evolution. Quarterly penetration tests should probe defenses from both external and internal vantage points, simulating sophisticated attack scenarios. Red teams increasingly employ adversarial machine learning to uncover novel exploitation paths that bypass traditional security controls. These findings feed into iterative improvement cycles, ensuring defenses stay ahead of emerging threats in the hybrid cloud landscape.
Leveraging Cloud Native Security Tools for Enhanced Protection
Understanding the Need for Enhanced Security in Hybrid Environments
The distributed nature of hybrid clouds creates a security paradox - while offering operational flexibility, they exponentially increase the potential attack surface. Traditional security tools designed for static datacenters struggle to protect fluid workloads migrating across cloud boundaries. Modern threats exploit these transitional gaps, requiring security solutions that understand both legacy and cloud-native architectures. Security teams now need tools that provide unified visibility across this fragmented landscape while automatically adapting to configuration changes.
Cloud-Native Security Tools: A Comprehensive Approach
Purpose-built cloud security platforms employ API-first architectures that seamlessly integrate with cloud provider services. These solutions move beyond simple monitoring to actively enforce security policies across containerized workloads and serverless functions. Their distributed agents form a protective mesh around cloud assets, enabling real-time policy enforcement regardless of workload location. This architectural approach proves particularly effective in hybrid scenarios where security policies must span multiple infrastructure generations.
Zero Trust Principles in Cloud-Native Security
Cloud-native security tools operationalize Zero Trust through continuous authorization mechanisms. Instead of one-time authentication, these systems constantly reevaluate access privileges based on changing contexts. A developer's container might lose database access when moved from a secure build environment to a less-controlled testing zone. Such dynamic policy enforcement represents the pinnacle of Zero Trust implementation, where trust is never assumed and always verified at microsecond intervals.
Enhanced Visibility and Control with Cloud-Native Tools
The telemetry capabilities of modern cloud security platforms create a living map of the hybrid environment. Security teams gain X-ray vision into cross-cloud communications, spotting abnormal data flows that might indicate compromise. Advanced tools correlate events across infrastructure layers, revealing attack patterns that would remain invisible to siloed monitoring systems. This comprehensive visibility enables proactive threat hunting rather than reactive incident response.
Automation and Orchestration for Efficiency
Security automation in hybrid clouds extends far beyond scheduled scans. Intelligent platforms now automatically quarantine compromised workloads, rotate exposed credentials, and patch vulnerable systems without human intervention. These self-healing capabilities prove invaluable when managing thousands of ephemeral cloud resources that might only exist for minutes or hours. Orchestration workflows ensure consistent policy application across diverse environments while maintaining detailed audit trails for compliance purposes.
Integration and Scalability for Future Growth
Leading cloud security platforms employ open architectures that simplify integration with existing toolchains. Standardized APIs allow seamless connectivity with CI/CD pipelines, ITSM systems, and custom applications. This interoperability becomes crucial as organizations expand their hybrid footprints, preventing security tool sprawl. The platforms' elastic scaling capabilities ensure performance remains consistent as workloads fluctuate, avoiding the security gaps that often emerge during rapid cloud expansion cycles.