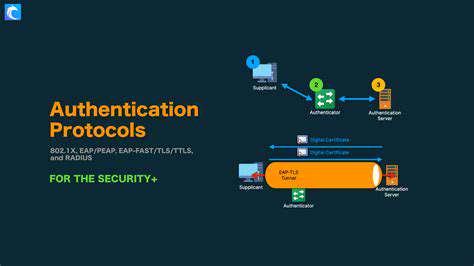
Successful implementation hinges on developing ironclad identity verification systems. Multi-factor authentication becomes non-negotiable, required for all personnel regardless of seniority or department. Even if hackers obtain password credentials, MFA creates an additional barrier that's notoriously difficult to bypass. Equally critical is implementing precision access controls that follow the principle of least privilege - granting employees only the minimum system permissions required for their specific duties.
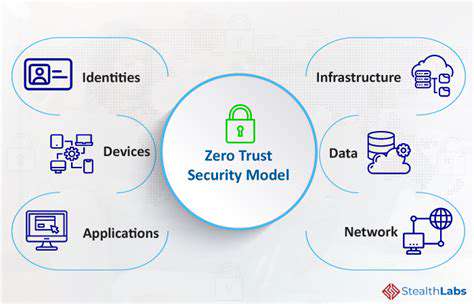
Key Benefits of Zero Trust Security
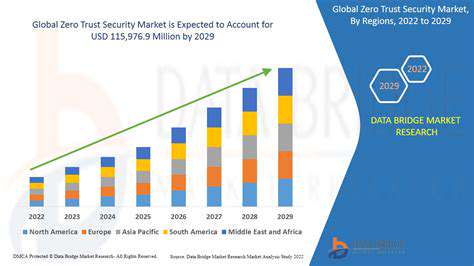
The advantages of adopting zero trust extend far beyond basic protection. Organizations gain an unprecedented level of security sophistication, creating digital environments that can withstand modern cyber threats. By eliminating automatic trust and requiring continuous verification, companies dramatically reduce their vulnerability to both external attacks and internal threats.
Real-time monitoring capabilities reach new heights under zero trust frameworks. Security teams gain microscopic visibility into network activities, allowing them to spot suspicious patterns immediately. This hyper-awareness enables lightning-fast responses to potential breaches, often stopping attacks before they cause damage. The detailed audit trails also provide invaluable forensic data for investigating incidents and strengthening future defenses.
Perhaps most importantly, zero trust architecture future-proofs organizations against evolving cyber threats. As attack methods grow more sophisticated, the verify-first approach ensures security measures remain effective. This proactive stance not only protects sensitive data but also maintains uninterrupted business operations - a critical advantage in today's digital economy.
Challenges and Considerations for Zero Trust Adoption
While the benefits are substantial, implementing zero trust presents several hurdles. The technical complexity can overwhelm IT teams, requiring specialized knowledge to properly integrate with existing systems. Many organizations find they need to upgrade legacy hardware and software to support the stringent verification requirements, potentially leading to significant upfront costs.
User experience often suffers during the transition period. Employees accustomed to seamless access may chafe at additional authentication steps. Successful implementations require careful change management, including comprehensive training programs that explain the security benefits while addressing user concerns. Temporary productivity dips should be expected and planned for during the adjustment phase.
Compatibility issues frequently emerge, particularly with older systems designed for perimeter-based security. Some applications may require substantial modifications or even replacement to function within a zero trust environment. Organizations must conduct thorough infrastructure assessments and develop phased migration plans to avoid operational disruptions during the transition.
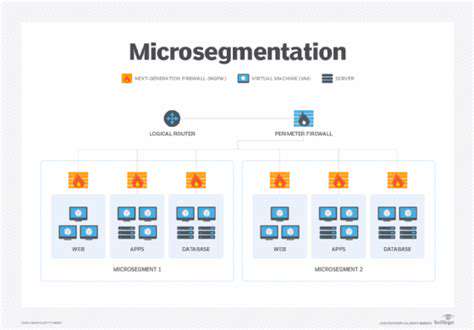
Enhancing Data Protection Through Microsegmentation
Implementing Robust Access Controls
Effective data protection begins with surgical precision in access management. The principle of least privilege isn't just recommended - it's mandatory for true security. This means conducting regular audits of user permissions and eliminating any unnecessary access rights. Department managers should collaborate with IT security to define exact access requirements for each role, creating customized permission sets that support workflow needs without creating security gaps.
Permission reviews shouldn't be annual events, but rather ongoing processes tied to organizational changes. When employees change roles or leave the company, their access privileges should be modified or revoked immediately. Automated provisioning systems can help maintain tight control while reducing administrative burdens on IT staff.
Employing Strong Encryption Techniques
In today's threat landscape, encryption serves as the last line of defense against data breaches. Modern encryption standards like AES-256 have become the gold standard, providing virtually unbreakable protection when properly implemented. Organizations must encrypt data both during transmission (using TLS protocols) and at rest (through full-disk or database encryption).
Key management deserves equal attention to the encryption itself. Cryptographic keys should be stored separately from the encrypted data, with strict access controls governing who can retrieve them. Regular key rotation adds another layer of security, ensuring that even if keys are compromised, their usefulness is time-limited.
Establishing Secure Data Storage Procedures
Data storage security requires a multi-layered approach. Physical security measures like biometric access controls for data centers complement digital protections such as encrypted storage arrays. Comprehensive backup strategies must account for both security and availability, with offline backups protected against ransomware and other malware threats.
Retention policies should be carefully calibrated to operational needs and regulatory requirements. Automatic deletion procedures for obsolete data reduce both storage costs and potential attack surfaces. For highly sensitive information, consider implementing data masking techniques that preserve utility while minimizing exposure.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
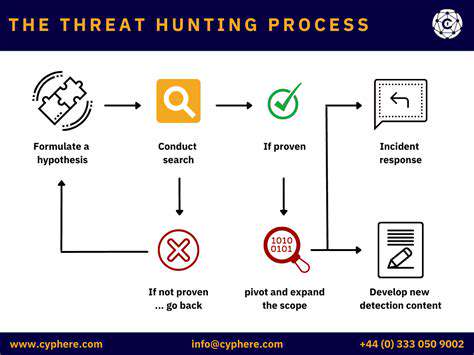
Security isn't a one-time project but an ongoing process requiring constant vigilance. Quarterly penetration testing provides realistic assessments of defensive capabilities, simulating the tactics of actual attackers. These tests should cover all system components, from network infrastructure to individual applications.
Vulnerability scanning should occur even more frequently, ideally as a continuous monitoring process. Automated tools can detect known vulnerabilities, while manual reviews by security experts uncover more subtle weaknesses. All findings should be prioritized based on potential impact and addressed through a formal remediation process.
Training and Awareness Programs
Human factors remain the weakest link in security chains. Effective training programs go beyond annual compliance seminars, incorporating regular phishing simulations and security awareness updates. Employees should learn to recognize not just obvious scams but sophisticated social engineering attempts that bypass technical controls.
Department-specific training helps staff understand security protocols relevant to their work. Finance teams need different emphasis than engineering groups, for example. Gamification elements and recognition programs can boost engagement, transforming security from an annoyance to a point of organizational pride.