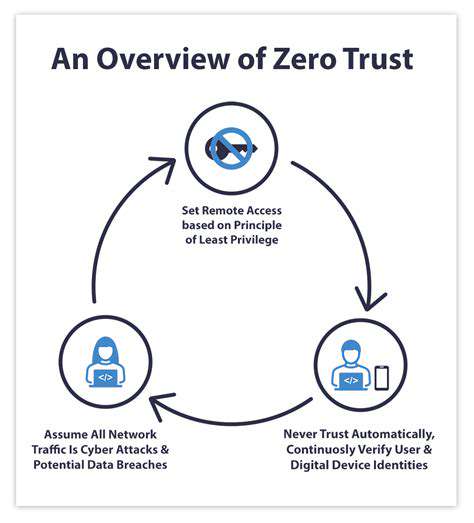
The Rise of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Today's digital world faces an escalating challenge from Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). These aren't your average cyberattacks; they're meticulously crafted campaigns by skilled adversaries aiming for prolonged access to critical systems. What makes APTs particularly dangerous is their ability to remain undetected while exfiltrating sensitive information over months or even years. The accessibility of advanced hacking tools combined with increasingly complex IT environments has created a perfect storm for these threats to flourish.
Organizations must recognize that traditional security measures often fail against these determined attackers. Implementing behavior-based detection systems and maintaining rigorous network monitoring can significantly improve defenses against these stealthy incursions. Regular penetration testing and threat hunting exercises have become non-negotiable in modern cybersecurity strategies.
Cybersecurity in the Cloud Era
Cloud adoption has revolutionized business operations while simultaneously introducing novel security challenges. The dynamic nature of cloud environments, with their ephemeral containers and serverless architectures, demands fundamentally different protection approaches compared to traditional data centers.
Effective cloud security requires embedding protective measures throughout the development lifecycle rather than bolting them on as an afterthought. This includes implementing granular identity management, encrypting data regardless of its state (in transit or at rest), and conducting continuous configuration audits. The shared responsibility model in cloud computing means both providers and clients must actively participate in securing their respective domains.
The Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerability
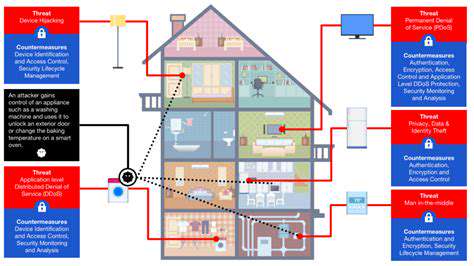
The explosive growth of IoT devices has created a security nightmare. Many manufacturers prioritize time-to-market over security, resulting in devices shipping with weak default credentials, unpatched vulnerabilities, and minimal security features. These shortcomings turn smart devices into convenient entry points for attackers.
The real danger lies in the interconnectivity of these devices - a single compromised smart thermostat could potentially provide access to an entire corporate network. Addressing this requires industry-wide security standards, regular firmware updates, and network segmentation to isolate IoT devices from critical systems. Consumers and businesses alike must demand better security practices from device manufacturers.
The Growing Importance of Data Protection
In an era where data drives business decisions and customer interactions, its protection has never been more crucial. High-profile breaches demonstrate that no organization is immune, whether from external attackers or insider threats.
Modern data protection strategies must extend beyond basic encryption to include comprehensive data governance frameworks. These should address data classification, retention policies, and strict access controls based on the principle of least privilege. Regular employee training on data handling procedures and simulated phishing exercises can significantly reduce human-related security incidents.
The Human Factor in Cybersecurity
Despite technological advancements, people remain both the weakest link and strongest defense in cybersecurity. Social engineering tactics continue to evolve, with attackers crafting increasingly sophisticated phishing campaigns that bypass technical controls.
Creating security awareness isn't about annual training sessions but fostering continuous engagement through interactive learning experiences. Gamification, real-world simulations, and immediate feedback on security incidents help cement good practices. Leadership must model secure behaviors to reinforce their importance throughout the organization.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing threat detection by processing security events at unprecedented scale and speed. Machine learning models can identify subtle patterns indicative of malicious activity that might elude human analysts.
These technologies excel at automating routine security tasks, allowing human analysts to focus on complex investigations and strategic improvements. However, organizations must remain aware that attackers are also leveraging AI, creating an ongoing arms race in cybersecurity capabilities. Continuous investment in these technologies and the skills to implement them effectively will separate resilient organizations from vulnerable ones.
Building a Culture of Security: From the Top Down
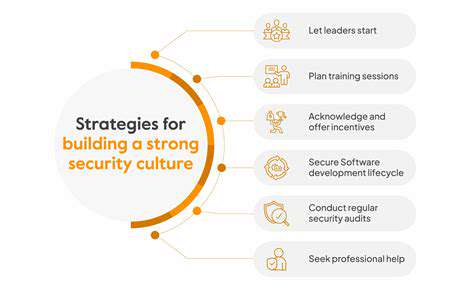
Building a Foundation for Trust
Establishing a security-conscious culture begins with clear expectations from leadership. When executives consistently demonstrate security as a priority through their actions and resource allocation, this mindset permeates throughout the organization. Visible commitment from the C-suite transforms security from an IT concern to a business imperative.
Practical implementation involves integrating security discussions into regular business meetings and tying performance metrics to security compliance. Quarterly security awareness updates and recognition of security champions help maintain focus on these critical issues. Regular penetration test results should be shared across departments to demonstrate real-world vulnerabilities.
Implementing Effective Training Programs
Modern security training must move beyond static presentations to interactive, scenario-based learning. Microlearning modules delivered through mobile platforms allow employees to engage with security concepts in digestible segments when convenient.
The most effective programs incorporate real examples from the organization's history alongside current threat intelligence. Department-specific training ensures relevance, while mandatory certification for access to sensitive systems creates tangible accountability. Metrics on training completion and effectiveness should be regularly reviewed by senior management.
Encouraging Reporting and Feedback
A robust security culture requires psychological safety for employees to report potential issues without fear of reprisal. Anonymous reporting channels alongside public recognition for security-conscious behavior create balanced incentives.
Implementing a structured vulnerability disclosure program with clear response protocols demonstrates organizational commitment to addressing concerns. Regular security innovation contests can tap into employee creativity for improving defenses while reinforcing engagement.
Establishing a Strong Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan serves as the organizational playbook during critical security events. This living document must be tested through realistic tabletop exercises involving cross-functional teams.
The plan should outline precise escalation paths, communication protocols, and business continuity measures tailored to various incident severities. Post-incident reviews must focus on systemic improvements rather than individual blame. Maintaining relationships with legal counsel and law enforcement before incidents occur significantly improves response effectiveness.
Promoting a Security-Conscious Mindset
Cultivating security awareness requires constant, creative reinforcement. Digital signage with security tips, login screen reminders, and even internal social media campaigns can maintain visibility.
Integrating security checkpoints into business processes - like mandatory two-factor authentication prompts or data classification during document creation - builds secure behaviors through repetition. Leadership should share personal security practices to model expected standards at all levels.
Fostering Collaboration and Communication
Breaking down silos between security teams and business units creates a more resilient organization. Regular cross-departmental security briefings ensure all teams understand emerging threats relevant to their operations.
Creating security liaison roles within business units facilitates two-way communication about security requirements and operational constraints. Joint projects between security and development teams bake security into new initiatives from inception. Metrics shared across departments help quantify security's impact on business outcomes.