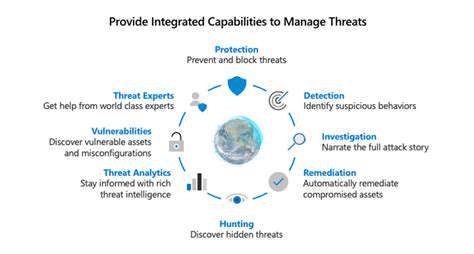
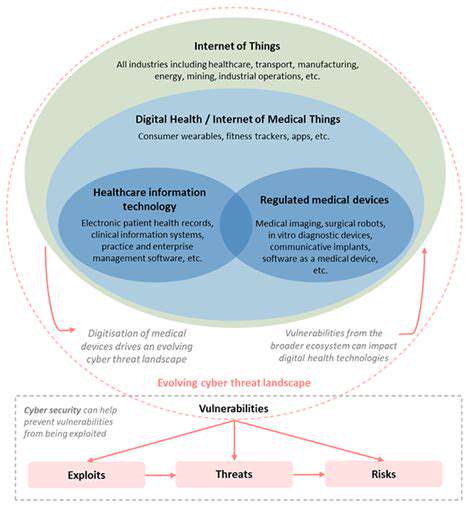
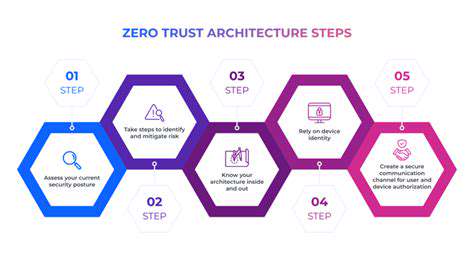
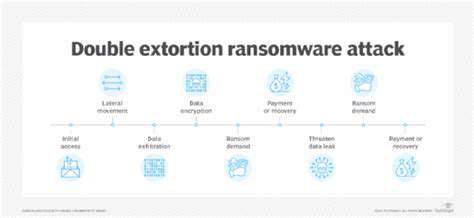
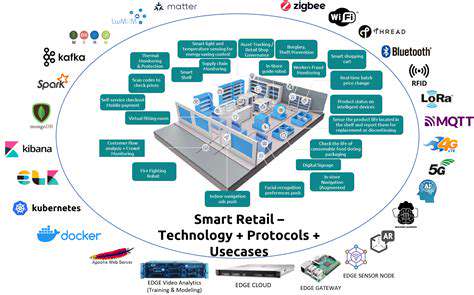
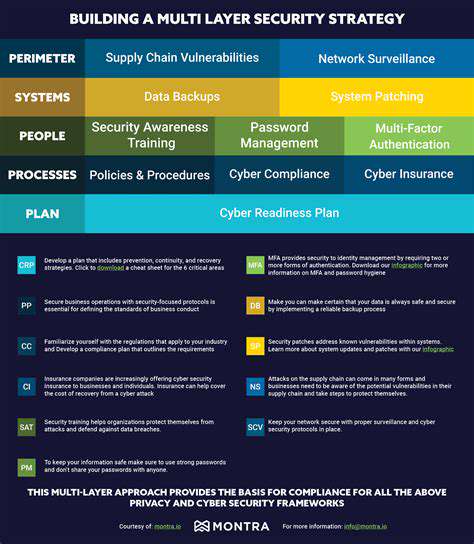
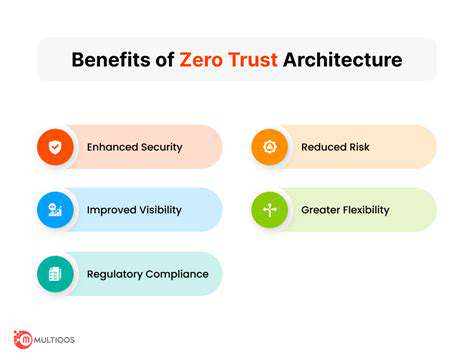
Direct Financial Losses
When ransomware strikes, the ransom payment is just the beginning. Organizations grapple with substantial direct financial hits that ripple through every department. The true cost includes forensic teams working around the clock, regulatory fines piling up, and operations grinding to a halt. Smart businesses don't just react - they build these potential expenses into their risk management strategies from day one.
Recovery isn't quick or cheap. Between specialized decryption tools, data reconstruction experts, and retraining staff, costs often dwarf the original ransom demand. IT teams spend weeks rebuilding systems while revenue streams dry up - a double whammy for the balance sheet.
Downtime and Lost Productivity
When systems freeze, so does business. Critical operations stop dead, shipments delay, and customers grow impatient. The hidden killer? Missed opportunities that never appear on spreadsheets - deals that evaporate when you can't respond quickly. Productivity nosedives as employees resort to manual workarounds, creating new errors while fixing old ones.
Calculating downtime costs is like predicting weather - estimates vary wildly but everyone agrees it's expensive. Sales teams lose commissions, factories miss quotas, and customer service queues balloon. The organizational domino effect touches every department differently but hurts equally.
Data Recovery and Restoration Costs
Rebuilding after encryption is digital archaeology. Specialists painstakingly reconstruct databases while executives sweat over missing files. Those without recent backups face six-figure recovery bills - if recovery is possible at all. Smart companies test their backup systems quarterly because finding out they don't work during a crisis is financial suicide.
Forensic Investigations and Legal Fees
Determining the attack's origin requires cyber detectives and corporate lawyers working in tandem. This digital crime scene analysis doesn't come cheap - expect six-digit invoices from security firms before the first court filing. Many organizations discover compliance failures during these investigations, triggering additional regulatory headaches.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
News of a breach travels faster than the malware itself. Clients question whether their data is safe, partners reconsider contracts, and prospects cross your name off vendor lists. The trust deficit often outlasts the technical recovery by years, silently eroding market position. Some businesses never fully regain their pre-attack standing in their industry.
Regulatory Penalties and Compliance Costs
Data protection laws now carry teeth - GDPR fines can reach 4% of global revenue. Post-attack audits often reveal security shortcuts, triggering additional penalties. Compliance becomes a moving target as regulations evolve to address new threats. The smart money invests in proactive compliance rather than reactive damage control.
Employee Training and Security Awareness
Human error causes most breaches, making security training non-negotiable. Effective programs go beyond annual PowerPoints - they simulate phishing attacks and reward vigilance. This ongoing education represents one of the highest ROI security investments a company can make. The right training transforms employees from vulnerabilities into human firewalls.
Operational Disruption and Productivity Loss

Operational Disruptions: A Common Threat
Modern businesses face disruption from all directions - hurricanes, hackers, or simple human mistakes can all trigger chaos. These events expose critical dependencies companies didn't know they had. Survivors prepare by stress-testing their operations before disaster strikes. They map single points of failure and build redundancy into every critical process.
Product Recall: A Critical Management Issue
When products fail, speed saves reputations. The best companies have recall playbooks ready, with cross-functional teams pre-assigned. Every hour counts - hesitation compounds liability while swift action preserves trust. Smart manufacturers track components to pinpoint affected batches within minutes, not days.
Supply Chain Disruptions: A Global Issue
Today's lean supply chains snap under pressure. Wise companies diversify suppliers before shortages strike, even if it costs more upfront. Some maintain strategic reserves of critical components - an expensive insurance policy that pays for itself during crises. The most resilient build regional production capabilities to bypass global bottlenecks.
Customer Service and Operational Interruptions
When systems fail, communication becomes the lifeline. Customers forgive problems but not silence. Proactive status updates via multiple channels prevent frustration from boiling over. The best crisis responders empower frontline staff with alternative solutions and clear escalation paths.
Impact on Product Quality and Safety
Disrupted production often means compromised quality. Smart quality teams increase sampling rates during recovery periods, catching defects before they reach customers. Some implement additional inspection checkpoints when bringing systems back online, accepting slower output for safer products.
Maintaining Customer Trust in Times of Disruption
Transparency builds bridges during crises. Companies that share what they know - and what they're doing about it - emerge with stronger relationships. The most trusted turn recovery efforts into customer communications, showing concrete steps rather than making vague promises.
Financial Implications of Disruptions
Operational hiccups hit the bottom line twice - lost sales today and higher costs tomorrow. Sophisticated firms model various disruption scenarios to understand their financial exposure. They maintain emergency liquidity precisely for these situations, avoiding the added stress of cash crunches during crises.
The Long-Term Implications: Cybersecurity Investments and Preparedness

The Erosion of Trust and Privacy
As digital dependence grows, so does skepticism about data security. Each high-profile breach makes the public more reluctant to embrace new technologies. This chilling effect could delay innovations that require personal data, from personalized medicine to smart cities.
The Rise of Cybercrime as a Global Threat
Cybercriminals operate like multinational corporations, with HR departments and quarterly targets. Their borderless operations exploit legal gray zones, often staying steps ahead of international law enforcement. Some gangs even offer ransomware-as-a-service with 24/7 customer support.
The Importance of Robust Cybersecurity Measures
Basic hygiene prevents most attacks - complex passwords, prompt patching, and employee awareness stop 90% of breaches. Forward-thinking organizations conduct regular fire drills simulating real attacks to test responses. The best security programs measure effectiveness in minutes-to-contain rather than just counting prevented attacks.
The Impact on Critical Infrastructure
When hackers hit power plants or water systems, entire cities feel the pain. Critical infrastructure operators now face resilience audits alongside traditional security checks. Some utilities maintain parallel analog systems as last-resort backups against digital failures.
The Evolution of Cyber Warfare
Nation-state hackers now stockpile zero-day exploits like nuclear arsenals. The most sophisticated attacks leave no fingerprints, creating plausible deniability for sponsoring governments. Cybersecurity firms increasingly work with intelligence agencies to attribute these covert operations.
The Need for International Cooperation
Cyber threats ignore passports, forcing unprecedented global collaboration. Shared threat intelligence networks now span 60+ countries, with real-time alerts about emerging attack patterns. Some nations jointly prosecute cybercriminals, though political tensions often complicate these efforts.
The Future of Cybersecurity
Next-gen defenses will leverage AI to detect anomalies human analysts miss. The cybersecurity skills gap will drive automation, with self-healing networks that contain breaches automatically. Quantum computing will break current encryption, sparking a global race for quantum-resistant algorithms.