For decades, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have served as the backbone of secure remote access. These systems create encrypted connections between user devices and corporate networks, facilitating protected data transmission. Yet their relevance in our current cybersecurity environment, marked by sophisticated threats, has become increasingly doubtful. The fundamental constraints of VPN technology, especially when contrasted with zero-trust principles, often create security gaps that advanced attackers can exploit. This vulnerability grows more concerning as remote work expands, simultaneously broadening potential attack vectors.
The primary weakness lies in VPNs' blanket-access methodology. They generally provide uniform network privileges to all authenticated users, regardless of device security status or location context. This approach proves dangerously inadequate when facing modern threats that might emerge from hijacked employee devices or malicious insiders. Contemporary security demands precise, context-aware access controls that far surpass traditional VPN capabilities. Moreover, the centralized architecture of VPN systems frequently creates operational bottlenecks and complicates security monitoring, hindering rapid threat detection and response.
The Zero Trust Imperative: Moving Beyond VPN Limitations
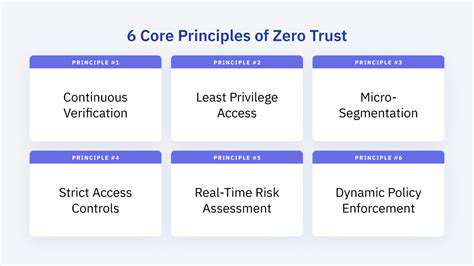
Zero Trust security represents a paradigm shift from network-based trust to universal verification. It mandates continuous authentication of every user, device, and application, irrespective of their network position or access history. This detailed security framework proves essential in an era where perimeter defenses alone can't provide adequate protection. Zero Trust principles deliver the flexibility and responsiveness required to counter modern cyber threats, empowering organizations to manage risks in constantly changing digital environments.
Adopting zero-trust architecture enables substantial security improvements. Techniques like network micro-segmentation, context-aware access controls, and adaptive multi-factor authentication demonstrate how this model overcomes VPN shortcomings. Organizations can dramatically shrink their attack surface by enforcing strict least-privilege access policies. This strategy not only prevents unauthorized access but also contains potential breaches by limiting lateral movement within networks. The transition to zero trust represents an essential advancement for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining business operations against increasingly complex cyber attacks.
Modern network complexity and attack sophistication demand security solutions more robust and flexible than conventional VPNs can provide. Zero Trust architecture meets these challenges by building security on continuous verification rather than static permissions. This shift toward zero trust isn't merely reactive to current threats; it's a forward-looking strategy to protect against future risks while ensuring ongoing security for critical data and systems.
By transcending VPN limitations, businesses can effectively manage the challenges of distributed workforces and dynamic threat environments. Zero trust establishes a more secure and resilient framework for asset protection, operational efficiency, and uninterrupted business processes.
Implementing zero-trust principles allows organizations to simplify security operations, minimize vulnerabilities, and develop more responsive protection strategies. This proactive stance becomes indispensable for staying ahead of evolving threats and securing sensitive information in today's intricate cybersecurity landscape.
The Future of Remote Access Security: Embracing Zero Trust

Enhanced Security Protocols
The evolution of remote access security depends on developing dynamic, intelligent protection systems. Modern solutions must replace outdated, rigid security measures with adaptive technologies capable of identifying and neutralizing emerging threats instantaneously. Incorporating multi-layered authentication as standard practice represents a critical enhancement, moving security beyond vulnerable password-only systems. These improvements will substantially reduce unauthorized access risks while elevating overall protection for remote connectivity.
Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing zero-trust architecture has become essential for modern remote access security. This model operates on continuous verification principles, authenticating every access attempt regardless of origin. Network segmentation and precision access controls form the foundation of this security approach. By enforcing strict resource-specific permissions, businesses can contain security incidents and dramatically reduce potential damage from breaches.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Next-generation security systems must incorporate intelligent threat identification and mitigation capabilities. These solutions need real-time detection and response mechanisms that adapt to new attack methodologies. Advanced analytics and pattern recognition technologies will become indispensable for processing security data and identifying subtle indicators of compromise. This predictive security model will significantly improve organizations' ability to prevent and control security events.
Improved Endpoint Security
Endpoint protection requires urgent enhancement in distributed work environments. The variety of devices and applications used by remote employees creates numerous potential entry points for attackers. Comprehensive endpoint security must include behavioral monitoring, vulnerability management, and automated patch deployment. Businesses should implement advanced endpoint detection platforms that continuously monitor device activity and automatically quarantine suspicious systems.
Secure Cloud Integration
As cloud services become integral to remote operations, their security integration grows increasingly critical. Implementing end-to-end encryption and secure connectivity protocols remains paramount for data protection. Additionally, organizations must rigorously manage cloud access permissions and enforce strict compliance with industry security frameworks to prevent data leaks and unauthorized access.
Employee Training and Awareness
Human factors continue to represent a major security vulnerability. Ongoing security education programs prove essential for developing workforce cyber awareness. Regular training sessions combined with realistic security simulations can significantly improve employees' ability to recognize and avoid potential threats. This continuous learning approach strengthens organizational security culture and reduces risk exposure.