Understanding the Importance of Data Backup
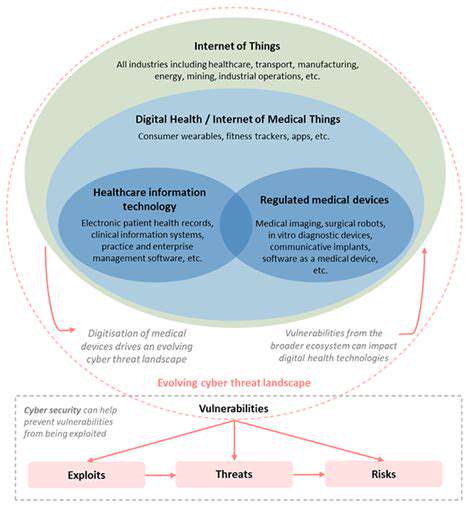
Information loss can cripple organizations and devastate individuals, resulting in financial hemorrhaging, operational collapse, and brand erosion. In our data-driven era, safeguarding digital assets through comprehensive backup solutions isn't optional—it's existential. Truly effective protection requires more than duplicate files; it demands a holistic approach guaranteeing availability, confidentiality, and dependability when disasters strike.
Sophisticated backup methodologies transcend simple file copying. They involve selecting appropriate archival techniques, maintaining consistent schedules, and preserving data authenticity throughout the lifecycle. The backup architecture must reflect data criticality and change frequency to ensure essential information remains perpetually protected.
Types of Data Backup Strategies
Diverse archival approaches serve varying organizational requirements. Complete system snapshots capture everything, while incremental versions only record modifications since previous backups. Hybrid differential methods offer middle-ground solutions by archiving all changes following the last full backup. Selecting the optimal approach requires analyzing data volumes, modification patterns, and recovery time imperatives.
Backup strategy decisions carry significant consequences. Organizations must weigh potential breach scenarios and system failures when determining their archival roadmap. The chosen methodology should align precisely with operational needs and risk tolerances.
Implementing a Secure Backup System
True backup security involves protecting archived data at all stages. Encryption safeguards information during transfers and storage, while strict access controls limit retrieval to authorized individuals. Regular restoration tests verify system reliability before actual emergencies occur. Security measures must be baked into backup architecture from inception, combining digital protections with physical safeguards for storage media.
Continuous system evaluations maintain backup integrity and regulatory compliance. Scheduled audits identify potential vulnerabilities while ensuring alignment with evolving data protection standards.
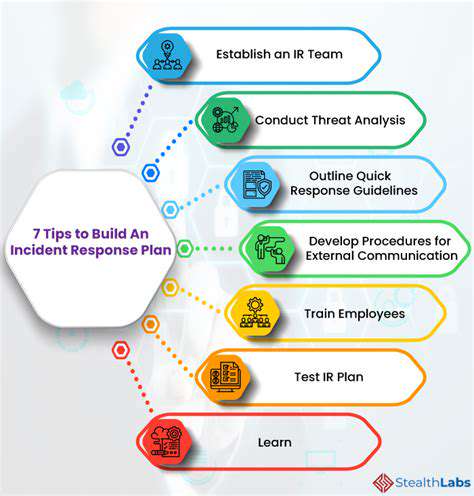
Developing a Disaster Recovery Plan
A thorough disaster recovery framework completes any backup strategy. This playbook outlines data restoration workflows, prioritizes critical functions, and defines team responsibilities during crises. More than paperwork, this plan represents an operational lifeline that reduces downtime and maintains business viability when systems fail.
Evolving threats and organizational changes necessitate regular plan updates. Periodic reviews ensure the recovery strategy remains relevant and effective against emerging digital hazards.
Regular Testing and Maintenance
Consistent backup system validation proves essential for reliability. Restoration trials confirm data recoverability across various failure scenarios, ensuring smooth emergency operations. Proactive system upkeep—including software updates, hardware refreshes, and security enhancements—maintains backup readiness as technologies advance.
Ongoing strategy refinement accommodates technological shifts and business evolution. Regular reassessments guarantee backup solutions continue meeting organizational needs in dynamic digital landscapes.
Post-Incident Analysis and Remediation: Fortifying Security Posture
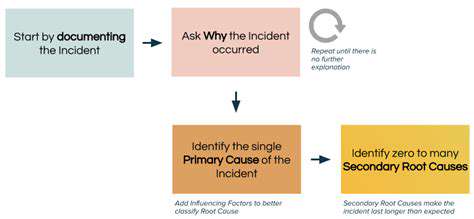
Understanding the Root Cause
Effective incident resolution begins with uncovering fundamental causation. This deep dive examines all contributing elements, from process breakdowns to technical failures. Without identifying why incidents occur, organizations remain vulnerable to recurrent failures. Surface-level fixes often mask systemic problems that will inevitably resurface.
Structured analysis techniques like the 5 Whys method systematically peel back incident layers. This persistent questioning reveals core issues that superficial examinations might overlook.
Documenting the Incident
Thorough incident chronicling provides the foundation for meaningful analysis. Detailed accounts should capture event sequences, affected systems, and organizational impacts. Comprehensive records create institutional memory that informs future incident responses and prevents historical amnesia. Relevant data—system logs, error reports, and firsthand accounts—should be preserved for reference.
Assessing the Impact
Measuring incident consequences determines their true organizational toll. This evaluation encompasses financial costs, reputational harm, operational delays, and business interruptions. Quantified impact analysis guides resource distribution and remediation prioritization. Concrete data helps stakeholders comprehend incident severity and response urgency.
Identifying Contributing Factors
Examining all incident precursors reveals systemic vulnerabilities. This scrutiny should address process gaps, training deficiencies, technical constraints, and environmental conditions. Recognizing these underlying weaknesses enables targeted corrective actions that strengthen overall defenses.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
Analysis findings should inform specific preventative measures. These solutions must address root causes while enhancing processes and security frameworks. Strategic implementation transforms incident lessons into durable protections. Updates may include policy revisions, staff education, and technological upgrades.
Implementing Remediation Actions
Corrective measures must be executed systematically based on priority and practicality. Tracking remediation progress ensures identified issues receive proper attention within defined timelines. This structured approach guarantees comprehensive problem resolution.
Evaluating Effectiveness of Measures
Post-implementation assessment verifies solution efficacy. Continuous monitoring of systems, procedures, and personnel identifies residual vulnerabilities. Ongoing evaluation cycles refine security postures and prevent problem recurrence. Regular adjustments maintain robust defenses against evolving threats.