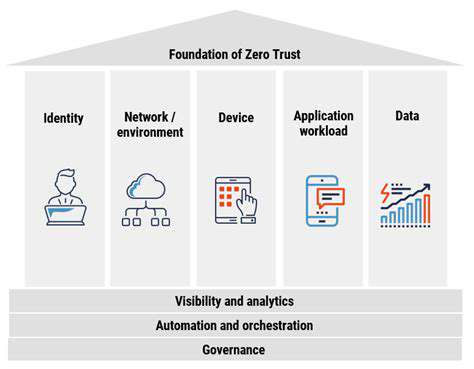
Zero Trust Principles
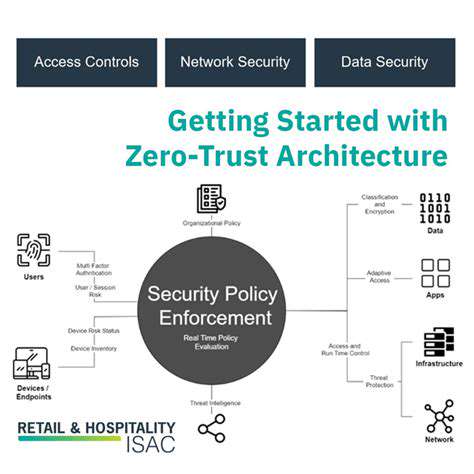
At the heart of Zero Trust lies the fundamental principle of never trusting, always verifying. This means that every user, device, and application, regardless of its location or perceived trustworthiness, must be authenticated and authorized before granting access to resources. This stringent approach contrasts sharply with traditional network security models that often rely on implicit trust within a perimeter. This shift in mindset is crucial for mitigating the risks associated with insider threats, malicious actors, and compromised devices.
Implementing Zero Trust requires a thorough understanding of the network's components and their interactions. Every connection must be scrutinized and validated, minimizing the impact of a breach should one occur. The focus is on granular control and continuous monitoring, ensuring that only authorized entities have access to sensitive data.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
A robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) system is critical to Zero Trust security. This involves meticulously verifying the identity of every user and device attempting to access resources. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a key component, significantly enhancing security by requiring multiple forms of verification beyond simple usernames and passwords.
Strong IAM practices are the bedrock of Zero Trust security, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive data. Careful consideration must be given to the level of access granted to each user and device based on their specific needs and roles within the organization.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is a cornerstone of Zero Trust. Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments limits the potential impact of a security breach. This compartmentalization restricts the movement of malicious actors within the network, hindering their ability to access sensitive data and critical systems.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust security relies heavily on continuous monitoring and real-time threat detection. Implementing advanced security tools and techniques is essential to identify suspicious activity and respond swiftly to potential threats. Proactive security measures are paramount in mitigating risks and maintaining the integrity of the network.
Constant vigilance and the ability to adapt to evolving threats are essential aspects of effective Zero Trust implementation. Regularly analyzing security logs and network traffic patterns, in tandem with employing intrusion detection systems, helps in quickly identifying anomalies and vulnerabilities.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are integral to Zero Trust. These measures protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or exfiltration, whether accidental or intentional. Employing DLP tools and policies is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and complying with relevant regulations.
Implementing robust DLP protocols ensures that only authorized users have access to classified data, mitigating the risk of data breaches and maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.
Policy Enforcement and Governance
Zero Trust requires a well-defined set of policies and a strong governance framework. These policies dictate access permissions, security protocols, and response procedures in the event of a security incident. Clearly outlining these policies and procedures is essential for effective security management and incident response.
Maintaining a consistent and up-to-date policy framework is essential. Regular reviews and updates are vital to ensure that security policies remain aligned with the evolving threat landscape and organizational needs. This ongoing process ensures that the Zero Trust framework remains effective and responsive to emerging vulnerabilities.
Implementing Encryption with Zero Trust Principles
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust security operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. This fundamentally shifts the traditional security model, which often relies on perimeter defenses. Instead, Zero Trust assumes that no user, device, or application, regardless of location or previous access history, should be implicitly trusted. Every access attempt is scrutinized and validated, requiring continuous authentication and authorization to ensure only legitimate entities gain access to sensitive data and resources.
This approach recognizes that networks are no longer contained within a single perimeter. With remote workforces, cloud-based applications, and the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, relying solely on network segmentation is insufficient. Zero Trust mandates that access be granted on a granular, need-to-know basis, significantly reducing the attack surface and mitigating the impact of a breach.
Implementing Encryption for Enhanced Security
Encryption plays a crucial role in the Zero Trust framework, providing a critical layer of protection for sensitive data transmitted across networks. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, organizations can ensure that even if an attacker gains unauthorized access to the network, they will be unable to decipher or exploit the confidential information. This enhanced security posture is essential in today's environment where data breaches are becoming increasingly common.
Implementing robust encryption protocols, such as AES-256, across various communication channels, including email, file sharing, and databases, is a cornerstone of Zero Trust security. Proper key management and secure storage are also vital components to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of encrypted data. This diligent approach helps bolster the overall security posture and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Integrating Encryption into the Zero Trust Access Model
Zero Trust access models leverage encryption to control access to data and applications based on granular user permissions. By encrypting data both at rest and in transit, sensitive information is protected even if an attacker compromises a system. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, which are a constant threat in today's connected world.
Integrating encryption into the Zero Trust access model requires careful consideration of the specific needs of the organization. This includes selecting appropriate encryption algorithms, implementing strong key management procedures, and ensuring seamless integration with existing security infrastructure. Effective implementation is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture and safeguarding sensitive data in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.