Data Protection Strategies for Modern Manufacturing

Ensuring Precision in Industrial Data
Modern manufacturing systems generate vast amounts of operational data that drive critical decisions. Inaccurate measurements or corrupted datasets can lead to quality issues, wasted materials, and production delays. Automated validation systems that cross-reference multiple data sources are proving invaluable for detecting anomalies before they impact operations.
Emerging technologies like blockchain are being adapted for industrial use, creating immutable audit trails for critical process parameters. These solutions complement traditional quality control methods while providing new levels of transparency and traceability throughout manufacturing workflows.
Standardizing Data Across Manufacturing Systems
The proliferation of smart devices in factories has created challenges in data harmonization. Different equipment often generates information in proprietary formats, making system-wide analysis difficult. Industry consortia are developing common data models specifically for manufacturing applications to address this challenge.
Middleware solutions that normalize data streams in real-time are gaining adoption, enabling comprehensive analytics across heterogeneous equipment fleets. These systems preserve the richness of source data while ensuring compatibility with enterprise systems and third-party applications.
Layered Security for Industrial Data
Protecting manufacturing data requires specialized approaches that account for unique operational requirements. Traditional IT security solutions often prove inadequate for industrial environments where availability frequently takes precedence over confidentiality.
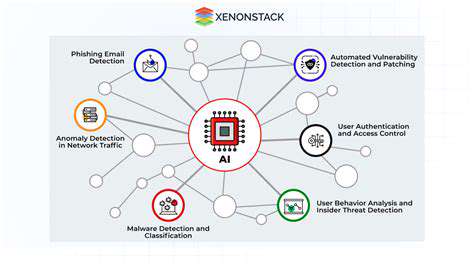
Modern industrial cybersecurity frameworks emphasize adaptive protection that responds to changing threat conditions without disrupting operations. Techniques like behavioral anomaly detection can identify potential threats while minimizing false positives that might unnecessarily interrupt production processes.
Disaster Recovery for Manufacturing Systems
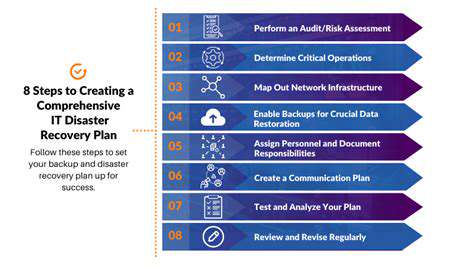
The consequences of data loss in manufacturing extend beyond information technology to physical operations. Contemporary backup solutions now incorporate machine state preservation, enabling not just data recovery but complete system restoration to known good configurations.
Hybrid cloud architectures are being employed to maintain secure, geographically distributed copies of critical manufacturing data and configurations. These systems often feature automated integrity verification to ensure backup reliability when needed most.
Holistic Security Approaches for Industrial Facilities
Addressing the Convergence of Physical and Digital Risks
Modern industrial security strategies must account for the growing interconnection between physical and cyber threats. Unauthorized physical access to equipment can lead to digital compromises, while cyber incidents can have direct physical consequences in industrial settings.
Integrated security operations centers that monitor both physical and digital indicators are becoming essential for comprehensive threat detection. These centralized units correlate data from surveillance systems, access logs, and network monitoring tools to identify potential security events.
Granular Access Management in Industrial Settings
The principle of least privilege takes on added significance in manufacturing environments where equipment operation can have safety implications. Modern identity and access management systems now incorporate context-aware authentication that considers location, time, and operational status when granting system access.
Biometric authentication is seeing increased adoption for critical systems, supplemented by behavioral analytics that can detect unusual access patterns. These technologies help prevent both external breaches and insider threats while maintaining operational fluidity.
Protecting Critical Control Systems
Industrial control systems require specialized security measures that account for their unique architectures and operational requirements. Passive monitoring solutions that don't interfere with real-time control functions are particularly valuable in these environments.
Network segmentation strategies have evolved beyond simple zoning to incorporate microsegmentation that isolates individual machines or processes without compromising necessary communications. This approach limits the potential spread of malware or unauthorized access while maintaining operational flexibility.
Preparing for Security Incidents
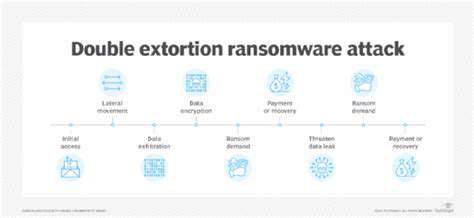
Effective incident response in industrial settings requires specialized playbooks that account for operational constraints. Traditional IT response procedures often prove inadequate when dealing with physical processes that can't be simply powered down.
Tabletop exercises that simulate operational impacts are becoming standard practice for preparing response teams. These drills help identify potential conflicts between security protocols and operational requirements before actual incidents occur.
Continuous Security Enhancement
The dynamic nature of industrial cybersecurity demands ongoing adaptation. Leading organizations now employ security metrics specifically tailored to manufacturing environments that track both technical indicators and operational impacts.
Machine learning algorithms are being applied to security data from industrial systems, identifying subtle patterns that might indicate emerging threats. These advanced analytics complement traditional security monitoring while adapting to the unique characteristics of industrial networks.