The Rise of Wearable Health Tech and the Security Imperative

The Growing Demand for Convenience
Wearable health technology has seen unprecedented growth as consumers increasingly prioritize convenient health monitoring solutions. Rather than scheduling clinical visits, individuals now prefer tracking vitals, activity, and sleep patterns through discreet devices. This shift toward proactive health management continues to drive innovation in wearable tech.
The portability and user-friendly nature of these devices make them indispensable for health-conscious individuals. Their widespread adoption reflects a cultural transformation toward self-monitoring and preventive care, empowering people to take charge of their wellness journeys.
Breakthroughs in Sensor and Processing Technology
Modern wearable devices benefit from remarkable advancements in miniaturized, high-precision sensors. These innovations enable accurate measurement of various physiological parameters, delivering comprehensive health insights previously only available in clinical settings.
Enhanced processing capabilities now allow for immediate data analysis and customized feedback. This real-time functionality helps users make timely adjustments to their daily routines, significantly increasing the practical value of these devices.
Transforming Lifestyles Through Data Insights
Wearable technology profoundly influences user behavior by making health metrics visible and actionable. Tracking daily activity, sleep quality, and stress levels motivates meaningful lifestyle changes.
The feedback loops created by these devices serve as powerful motivators, encouraging regular exercise, better sleep hygiene, and effective stress management. This data-driven approach leads to sustainable improvements in overall health and wellness.
Connecting With Healthcare Providers
The healthcare industry increasingly incorporates wearable data into patient care. Seamless data sharing enables more informed consultations and collaborative treatment planning between patients and providers.
This integration facilitates early detection of health concerns and tailored treatment strategies. Remote monitoring capabilities represent a significant advancement in preventive medicine and chronic condition management.
Balancing Innovation With Privacy
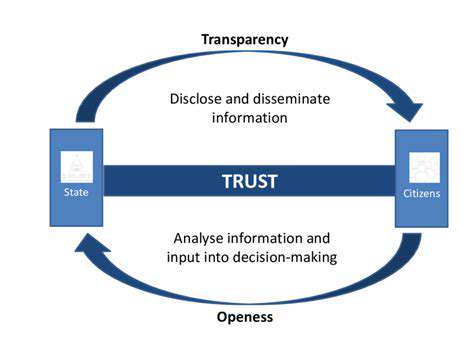
As wearable tech becomes more prevalent, protecting sensitive health data remains paramount. Implementing stringent security protocols and transparent data policies builds essential trust in these technologies.
Ongoing development of comprehensive data protection standards will be crucial for sustaining growth in this sector while safeguarding user privacy.
Personalized Medicine's Digital Frontier
Continuous health monitoring through wearables enables truly personalized healthcare. The constant stream of physiological data allows for early interventions and customized wellness plans.
This real-time approach promises a future where healthcare becomes increasingly predictive and preventive, potentially improving outcomes while reducing system costs.
Expanding Access to Health Technology
While benefits are clear, ensuring equitable access to wearable health tech remains challenging. Developing affordable options will be crucial for reaching diverse populations.
Innovations in cost-efficient design and manufacturing can help democratize access, particularly for underserved communities that stand to benefit most from these technologies.

Protecting Data Through Secure Communication Protocols
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
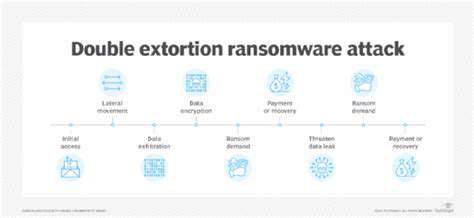
TLS protocols form the backbone of secure data transmission for wearable devices. By establishing encrypted connections, they prevent unauthorized access to health data in transit. Proper implementation requires careful selection of cipher suites and diligent certificate management to maintain robust protection against interception attempts.
Authentication and Authorization
Effective security requires verifying both device and user identities. Multi-factor authentication significantly reduces unauthorized access risks by combining multiple verification methods. Role-based access control ensures sensitive data remains accessible only to authorized individuals with legitimate needs.
Data Encryption at Rest
Encrypting stored health data protects against breaches from lost or stolen devices. Strong encryption algorithms and proper key management are essential for maintaining data confidentiality when devices aren't actively transmitting information.
Secure Hardware Modules
Dedicated security chips in wearable devices provide hardware-level protection for cryptographic operations. These components safeguard encryption keys and resist physical tampering attempts that might compromise device security.
Ongoing Security Maintenance
Regular system audits and timely software updates address emerging vulnerabilities before exploitation. This proactive approach is critical for maintaining long-term security as threats evolve.
Educating Users
Informed users form the first line of defense against security threats. Clear guidance on password security, device handling, and data sharing helps prevent many common security incidents.
Vulnerability Management
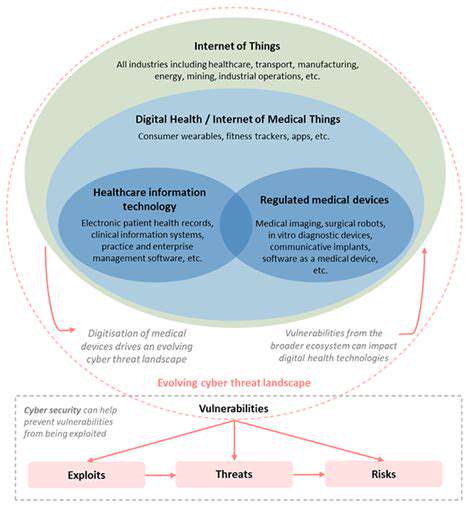
A systematic approach to identifying and addressing security weaknesses helps maintain system integrity. Quick response to newly discovered vulnerabilities is essential for protecting sensitive health information.
Addressing the Role of Device Manufacturers and Users
Manufacturer Responsibilities
Device makers must prioritize security throughout the product lifecycle. This includes implementing robust encryption, secure authentication methods, and comprehensive security policies. Regular security testing and compliance with industry standards help ensure devices maintain strong protections against evolving threats.
User Awareness and Best Practices
While manufacturers provide security features, users must understand their role in protecting their data. This includes creating strong passwords, keeping devices updated, and being cautious with data sharing. Physical security measures and prompt reporting of suspicious activity further enhance protection.
Users should remember that wearables complement rather than replace professional medical advice. Understanding what data gets collected and how it's used helps maintain appropriate expectations about device capabilities and limitations.