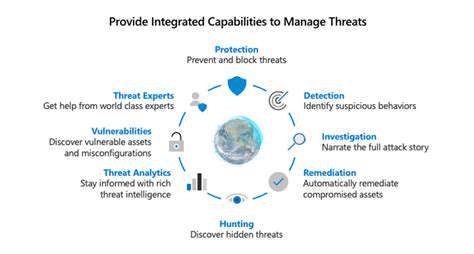
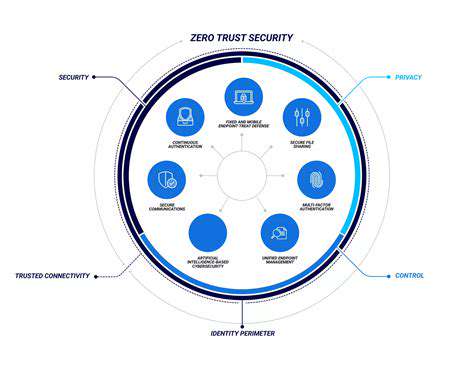
Zero Trust Architecture: A Shift in Security Paradigm
Zero Trust security is a fundamental shift from the traditional network security model. Instead of assuming trust within a perimeter, Zero Trust operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. This means every user, device, and application, regardless of location, must be authenticated and authorized before accessing any resource within the network. This approach significantly increases security posture by reducing the attack surface and limiting the impact of a breach.
This paradigm shift requires a complete re-evaluation of security policies and procedures. It necessitates a move away from relying on perimeter defenses and towards a more granular, dynamic approach that continuously assesses and validates access requests. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and protect sensitive data more effectively.
Verifying Identities and Access Requests
A critical component of Zero Trust is the rigorous verification of identities and access requests. This involves implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identities beyond simple passwords. Beyond user authentication, it also scrutinizes the device's identity and authorization status. This granular approach ensures that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Implementing robust identity and access management (IAM) systems is essential for ensuring that access privileges are properly managed and monitored. This includes creating and enforcing access policies that control what users can access and when. Regular audits and reviews of access permissions are crucial to detecting and responding to any unauthorized access attempts.
Microsegmentation for Enhanced Security
Microsegmentation is a key technique in Zero Trust architectures. It involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a security breach. If a malicious actor gains access to one segment, their ability to move laterally and compromise other parts of the network is significantly restricted. This segmented approach ensures that the impact of a security incident is contained to a specific area, safeguarding sensitive data from widespread compromise.
Implementing microsegmentation requires careful planning and consideration of network topology and resource dependencies. It is a critical step for reducing the attack surface and enhancing the overall security posture of the organization.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust security demands continuous monitoring of network activity and user behavior. Implementing comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) solutions is crucial for detecting anomalies and potential threats in real time. These systems can identify suspicious activity, such as unusual login attempts or unusual data access patterns, allowing security teams to respond swiftly to potential breaches.
Advanced threat detection technologies, incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence, can help organizations identify and respond to increasingly sophisticated attacks. This proactive approach to monitoring and detection is essential for maintaining a strong security posture in a dynamic threat landscape.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Data Security
Zero Trust principles heavily emphasize Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies. Implementations must include robust DLP measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization's controlled environment. Data encryption, access controls, and data masking are crucial components of this strategy. This ensures that even if an unauthorized user gains access, the data remains protected. This also extends to protecting data in transit and at rest.
Regular security assessments and penetration testing are essential to identify vulnerabilities in the data security architecture. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and protect sensitive data effectively.
Policy Enforcement and Compliance
Zero Trust mandates a strong emphasis on policy enforcement. Organizations need to develop and enforce clear policies regarding user access, data handling, and security procedures. This ensures consistent security practices across the organization and helps to maintain a unified security posture. This includes establishing clear guidelines for password management, device security, and data handling procedures.
Compliance with relevant industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is critical. Zero Trust frameworks must align with these regulations to ensure data protection and compliance. This approach ensures that organizations are meeting their legal obligations and protecting sensitive data while adhering to industry best practices.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Zero Trust Applications
Implementing Zero Trust at Scale
Scaling zero trust implementations requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. A crucial aspect is the development of a robust identity and access management (IAM) system that can accurately and dynamically assess the trustworthiness of users and devices. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users and devices, regardless of location or network connection. Furthermore, continuously monitoring and analyzing user behavior patterns is essential to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. This proactive approach allows for the swift identification and mitigation of suspicious activities, ensuring the security of sensitive data across the organization's entire infrastructure.
Effective communication and collaboration between security teams and other departments are paramount. Clear communication protocols should be established to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a secure environment. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of security awareness, enabling employees to recognize and report potential threats effectively. Furthermore, regular training and awareness programs should be implemented to educate employees about the importance of zero trust principles and how to apply them in their daily work routines.
Zero Trust and Cloud Security
The cloud environment presents unique challenges and opportunities in the implementation of zero trust. A critical component of cloud zero trust involves securing access to cloud resources by leveraging advanced access controls. This includes implementing microsegmentation to isolate cloud workloads and enforcing strict access policies to limit the potential impact of a breach. Effective security controls must be in place to verify the identity and trustworthiness of cloud users and devices, regardless of their location.
Protecting sensitive data residing in cloud environments requires a comprehensive approach to data encryption and access control. Implementing encryption at rest and in transit is crucial to safeguard data from unauthorized access. Furthermore, implementing robust access controls that limit access to only the necessary data and resources is essential.
Data Security and Privacy in Zero Trust
Data security and privacy are paramount in a zero trust architecture. Implementing granular access controls based on the principle of least privilege is essential to limit the potential impact of a security breach. This requires a meticulous assessment of the data's sensitivity and the users who need access to it. A strong data loss prevention (DLP) system is necessary to detect and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization's control. This includes monitoring data access patterns and implementing alerts for suspicious activities.
Zero trust principles demand a commitment to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA. Compliance with these regulations requires the implementation of data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques, as well as ensuring that data is collected, used, and stored in accordance with applicable regulations. Implementing robust data governance policies is necessary to ensure that data is handled responsibly and ethically.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response
Advanced threat detection and response capabilities are crucial components of a robust zero trust implementation. Implementing advanced security information and event management (SIEM) systems is essential to detect and analyze suspicious activities in real-time. This allows security teams to quickly identify and respond to potential threats, minimizing the impact of security incidents. Integrating threat intelligence feeds into the SIEM system provides valuable context and insights for threat detection and response.
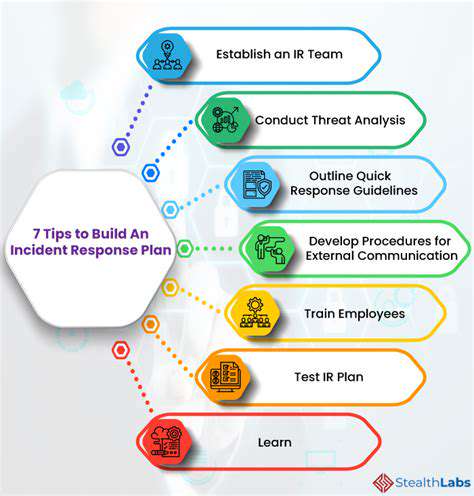
Developing and implementing automated response mechanisms is critical to reduce response time in the event of a security incident. This includes automating the blocking of malicious actors, isolating compromised systems, and initiating incident containment procedures. Furthermore, having well-defined incident response plans is crucial for handling and recovering from security incidents effectively.
The Future of Data Protection with Zero Trust

The Evolving Landscape of Data Breaches
Data breaches are no longer a rare occurrence; they are a growing concern for organizations of all sizes, from small startups to multinational corporations. The methods employed by cybercriminals are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and targeted. This necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach to data protection, moving beyond reactive measures to embrace predictive and preventative strategies. Understanding the latest attack vectors is crucial to safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating potential financial and reputational damage.
The rise of cloud computing and interconnected systems has expanded the attack surface, making data more vulnerable than ever before. This requires organizations to adopt robust security protocols that extend beyond traditional firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Addressing the vulnerabilities of these new environments is paramount to ensure data integrity.
The Role of AI in Data Protection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and data protection is no exception. AI-powered tools can analyze vast datasets to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities in real-time, enabling organizations to proactively address risks before they materialize. This proactive approach to threat detection is significantly more effective than traditional methods.
Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize patterns indicative of malicious activity, flagging suspicious behavior and enabling faster response times. This automated approach saves valuable time and resources in the face of increasingly complex cyber threats. It is also critical to understanding the ethical implications of using AI in data protection to ensure fairness and accountability.
Strengthening Data Encryption Practices
Robust encryption is a cornerstone of modern data protection. Implementing strong encryption protocols across all data storage and transmission methods is essential to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. This includes utilizing the latest encryption standards and regularly updating security protocols to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Data encryption should not be treated as a one-time implementation, but rather as an ongoing process that adapts to the ever-changing technological landscape. Regular audits and assessments are vital to ensure the continued effectiveness of these crucial security measures. Properly managing and securing encryption keys is also crucial to maintaining data confidentiality.
The Importance of Data Minimization
Data minimization is a fundamental principle in data protection. Collecting and storing only the data necessary for legitimate business purposes is crucial. Organizations must thoroughly assess the data they collect and identify what data is truly essential to their operations. This approach minimizes the amount of data that needs to be protected and reduces the potential impact of a data breach.
The Impact of Regulations on Data Protection
Data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, are becoming increasingly stringent. Organizations must comply with these regulations to avoid significant penalties and maintain consumer trust. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is not just a legal requirement; it's a critical aspect of maintaining a positive brand reputation and fostering customer loyalty. Organizations need to ensure that their data protection policies align with these evolving legal frameworks.
Staying informed about emerging data protection laws and adapting policies accordingly is essential. Ignoring or misinterpreting these standards can lead to severe repercussions for both organizations and individuals. Implementing a data governance framework that supports regulatory compliance is key.
The Future of User Education and Awareness
Educating users about data protection best practices is critical for overall security. Raising awareness about phishing scams, password security, and social engineering tactics can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks. Empowering users with knowledge is a powerful defense mechanism against malicious actors. Regular training programs and readily available resources can equip individuals with the tools to protect their data and contribute to a stronger overall security posture.
Organizations must prioritize user education and training as an integral part of their data protection strategy. This proactive approach empowers individuals to become active participants in maintaining a secure digital environment. This includes providing clear and concise information on data protection policies and best practices.