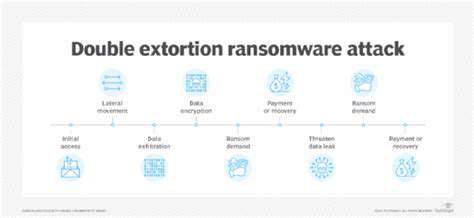
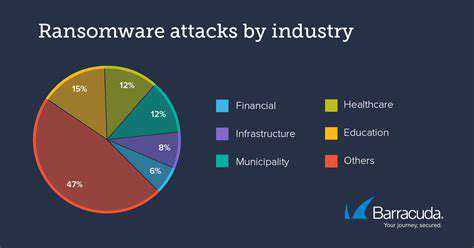
Modern applications face relentless threats from security vulnerabilities that permeate systems across all sectors. When exploited, these weaknesses trigger devastating outcomes including compromised data, financial hemorrhaging, brand erosion, and regulatory penalties. Development teams must grasp both the technical nuances and business implications of these exposures to mount effective defenses. Neutralizing vulnerabilities during early development phases remains the most cost-effective strategy for creating resilient systems.
Today's intricate software architectures, with their complex interdependencies, create fertile ground for security flaws to proliferate. Poor coding standards, architectural oversights, and rushed implementations all contribute to this growing problem. Effective mitigation demands security integration that transcends basic compliance checkboxes, embedding protective measures into every development workflow.
Protecting Against Cyberattacks: A Multi-Layered Approach
Comprehensive security frameworks must defend against vulnerability exploitation throughout the entire software lifecycle - from initial design through ongoing maintenance. Implementing rigorous security validation at each development phase forms the backbone of this protective strategy. This preventive methodology focuses on discovering and eliminating weaknesses before attackers can weaponize them.
Effective defense requires multiple security layers working in concert to counter diverse threat scenarios. Organizations typically combine specialized security solutions with operational protocols, including anomaly detection systems, granular permission structures, and systematic patch management. Equally critical is continuous security education for staff to minimize human-factor vulnerabilities.
Ensuring Software Reliability and Trust
Establishing digital trust requires demonstrating consistent protection of user data and system integrity. Meticulous attention to data encryption, access governance, and secure processing forms the foundation of user confidence. In our hyperconnected reality, security has transitioned from optional to fundamental - a core requirement rather than afterthought. The staggering costs of security failures demand that organizations institutionalize protective practices throughout their development methodologies.

Emerging quantum techniques are revolutionizing feature engineering in machine learning pipelines. Traditional methods often demand excessive computational resources for statistical processing and dimensionality reduction on large datasets. Quantum feature transformation methods can produce superior data representations that enhance model accuracy while dramatically reducing training cycles. These advantages prove particularly transformative for computer vision and natural language processing applications handling complex, high-dimensional data.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous Monitoring for Early Detection
Proactive monitoring systems serve as critical early warning mechanisms for supply chain vulnerabilities. These solutions continuously audit dependencies, code modifications, and third-party components for known security issues. Automated monitoring of code repositories, package ecosystems, and threat intelligence streams enables rapid identification of potential compromises. Early detection facilitates immediate containment measures, drastically reducing incident impact.
Ongoing vulnerability evaluation of all system components must integrate seamlessly into development workflows. This real-time scrutiny allows immediate remediation of emerging threats rather than reactive firefighting after breaches occur.
Incident Response Plan Development
Effective security incident management requires meticulously documented response protocols. These plans must detail comprehensive procedures for threat detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery. Clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and communication pathways enable response teams to act decisively during critical events.
Vulnerability Management Strategies
A systematic vulnerability management framework must address risks across all supply chain components. This includes continuous scanning of open-source libraries, third-party integrations, and proprietary codebases. The process must feature robust tracking mechanisms, risk-based prioritization, and standardized remediation workflows. Regular end-to-end security assessments help identify systemic weaknesses before exploitation.
Collaboration and Communication
Security effectiveness hinges on seamless cross-functional collaboration. Organizations must establish clear communication channels connecting development, security, and vendor teams. Standardized reporting procedures and accessible documentation foster collective security ownership and rapid incident response.
Automated Security Tools Integration
Embedding security automation throughout the SDLC creates continuous protective coverage. Automated code scanners, dependency analyzers, and behavioral monitoring tools provide real-time threat detection when integrated into CI/CD pipelines. This automation ensures security becomes an inherent quality attribute rather than periodic checkpoint.
Training and Awareness Programs
Regular security education cultivates organizational resilience. Tailored training programs should equip all stakeholders - from developers to executives - with current threat knowledge and mitigation techniques. Ongoing awareness initiatives help maintain security vigilance across all business functions.
Supply Chain Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Comprehensive vendor risk evaluation identifies exposure points across the software supply chain. Assessment criteria should examine vendor security postures and potential breach impacts. Mitigation tactics may include vendor diversification, security requirement enforcement, and secure integration protocols.